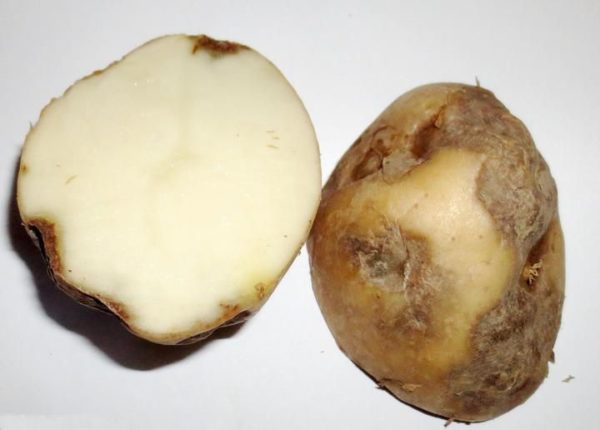

Many gardeners grow potatoes, but not everyone knows that Alternaria wilt can lead to crop losses. Although growing potatoes is a simple process, it's important to approach the task carefully. This will help protect your crops and increase your yield several times over.
Description of the causes and symptoms of potato Alternaria blight
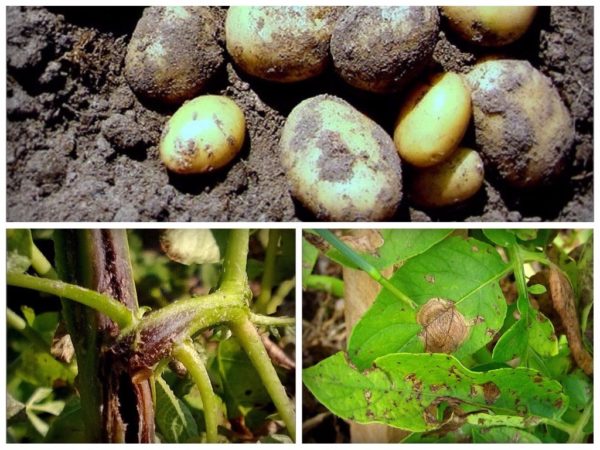
The disease is quite common. In most cases, it affects tubers, leaves, and stems. If Alternaria appears on leaves, dark brown spots may appear on the blades three weeks before flowering. If the disease is not detected promptly, the spots will coalesce into one large spot, covering the entire surface. As a result, the leaves will turn yellow and fall off.
Elongated spots may also form on the stems.

When tubers are infected, the fruit becomes covered with dark spots. If cut, rotten areas can be found inside.
The causes of diseases are the following factors:
- dry or hot weather;
- insufficient soil moisture;
- adverse weather conditions;
- barren lands;
- insufficient application of mineral fertilizers;
- improper preparation of seed material for planting.

Biology of Alternaria
The photo shows potato Alternaria wilt. Diseases can be spread by insects, wind, and rain. Alternaria wilt develops during hot weather and heavy rains. The optimal temperature for disease development is 26 degrees Celsius.
Conidia penetrate through the stomata of plants. As the plant grows, the fungus develops and secretes acid, which attacks the main parts of the plant.
Signs of the disease
Identifying the symptoms of the disease is very difficult, as there are quite a few. The most common are the following:
- The appearance of brown spots on the leaves. They appear 3 days after infection. The diameter of the spots increases over time;
- After infection, the leaf blades become brittle, causing them to die;
- gradually signs of infection appear on the stems;
- Brown spots may also appear on the tubers. Over time, wrinkles may also appear on them.

Source of infection
The main sources of infection are conidia and mycelium. They are found in the soil and survive on plant debris and tubers. To protect crops, it is necessary to carefully remove weeds from the area and implement preventative measures.
Methods of control and treatment of alternaria
To get rid of potato Alternaria blight, it's important to learn about disease control measures in advance. Experts distinguish between biological and chemical treatments. Each group deserves attention.
- Biological products. The following products fall into this group: Baktofit, Integral, Agat-25, and Planriz. These products are intended for treating seeds before planting. This procedure helps reduce weed infestation during the growing season.
- Chemicals. The list of products is extensive, but the most common are Profit, Thanos, Acrobat, Pilon, Novozri, Tsikhom, and Folman. These products are used for spraying crops during the growing season.
In addition, before storing tubers, they must be treated with the Maxim preparation.
Prevention
Preventative measures can also help protect crops from Alternaria blight. The following are the most effective:
- Diseased plants must be removed from the area. Deep plowing will help eliminate the source of the infection.
- Proper crop rotation will protect your crops. Potatoes can be returned to their original location only after three years. Experts recommend avoiding growing potatoes near tomatoes.
- Fertilizers should be used alternately. The soil should not be oversaturated with any one component. Everything should be used in moderation.
- Preference should be given to varieties that are resistant to the disease.
- Tubers should not be left in the plot; harvesting must be done carefully. Furthermore, crops should be monitored regularly. At the first sign of infestation, the bushes should be destroyed.
- Processing of seed material before planting.

Reviews
Elena, 47 years old:
"I recently encountered Alternaria wilt on my potatoes. I studied the disease description from a photo and began treatment. Dark spots appeared on the potato leaves, and they only grew larger. I removed the affected plants from the area and burned the tops.
"I also treated the crops with chemicals. This helped protect the plants and ensure a good harvest."
Tatyana, 64 years old:
"I'm no stranger to Alternaria wilt. It often affected my crops. A friend recommended planting potato varieties resistant to the disease. Now the crops are safe, and I have peace of mind about my harvest.
Moreover, the tubers are always large, neat, and have a marketable appearance.”
Andrey, 57 years old:
"We've been growing potatoes for many years. I believe it's best to take preventative measures early. Simple measures will help protect your crops and ensure a bountiful harvest."
Alternaria wilt of potatoes is a dangerous disease. Although the cultivation technology is simple, basic rules must be followed. This will help preserve the harvest and allow you to enjoy delicious fruits throughout the winter.
 Potato planting dates according to the moon for 2021 in the Moscow region
Potato planting dates according to the moon for 2021 in the Moscow region Potato varieties: names with photos, descriptions, and characteristics
Potato varieties: names with photos, descriptions, and characteristics When to dig up potatoes in 2020 according to the moon and how to best store them
When to dig up potatoes in 2020 according to the moon and how to best store them List of potato varieties with names, descriptions, and photos
List of potato varieties with names, descriptions, and photos