
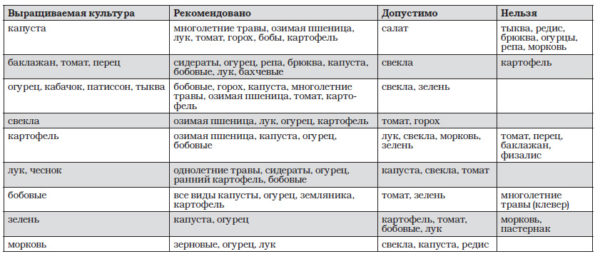
Crop rotation requires the mandatory rotation of vegetables, fruits, and berries. These requirements are driven by the need to maintain good soil condition and produce a high-quality, abundant harvest. Knowing what to plant after potatoes guarantees a rich, high-quality harvest.
Crop rotation rules require the mandatory rotation of various vegetable and fruit crops. Many beginning gardeners are interested in what can be planted after potatoes to maintain good soil condition and ensure a bountiful harvest. Proper rotation of vegetables and fruits ensures plant protection from pests and diseases, improves taste and nutritional quality, and promotes a bountiful harvest.
What can be planted after potatoes next year?
During the growing season, potatoes draw large amounts of phosphorus and potassium from the soil. Therefore, it's advisable to replenish these nutrients, and special fertilizers are permitted for this purpose. Potato tops must be removed, as they increase the risk of soil contamination.
Strawberries and strawberries should also not be planted after potatoes. Both berries can be planted after at least three years.
Otherwise, it's recommended to select crops based on their nutrient requirements. This is the core principle of proper crop rotation.
When wondering what to plant after potatoes, green crops are one option. However, it's still recommended to plant them elsewhere to ensure a large, high-quality harvest.

Gardeners often choose rye, lupine, and oats. These herbs help improve soil fertility by restoring the balance of nutrients.
Crop Rotation Rules
What is this?
Crop rotation is the foundation for successfully growing a variety of vegetables, fruits, and berries. This is because some crops degrade the soil. Meanwhile, other vegetables enrich the soil, allowing for a bountiful harvest with minimal effort.
Gardeners, according to the rules of crop rotation, conventionally divide crops into 4 large groups:
- leafy and green plants are particularly sensitive to the nitrogen content in the soil;
- Legumes have special requirements for phosphorus;
- Root vegetables require increased potassium content;
- Legumes help replenish nitrogen, so it is advisable to use them in crop rotation.
Knowing what to plant after potatoes next year can guarantee a high-quality and bountiful harvest.

Why alternate?
Large plots are usually allocated for potatoes, so several crops can be combined later. In any case, the same plot should not be used for potatoes again. Furthermore, vegetables from the same family (for example, tomatoes, peppers, or eggplants) should not be grown together. If crop rotation is incorrect, numerous unwanted problems can arise.
The main goals of alternating vegetable and fruit crops:
- Despite serious preventative measures, pathogens may remain in the soil, as a result of which the future harvest is at risk;
- pest larvae can overwinter in the soil;
- Crops from the same family require similar nutrients, so the soil quality rapidly deteriorates.
For the above reasons, it is extremely important to adhere to proper crop rotation.
What to plant after potatoes
Potatoes can only be planted in the same location after 2-3 years. When considering what to plant after potatoes, it's recommended to pay particular attention to the following options:
- carrot;
- cucumbers;
- onion;
- turnip;
- beet;
- radish or horseradish;
- daikon;
- green crops (celery, lettuce, spinach).

After the soil has rested, you can plant pumpkins, squash, zucchini, or cucumbers before the potato season. In the spring, you can plant cabbage and legumes.
The above vegetables will grow well as they require different nutrients.
What shouldn't be planted after potatoes?
Nightshade vegetables such as tomatoes, eggplants, and peppers should not be planted after potatoes. These crops are susceptible to virtually all the same diseases that attack potatoes. This increases the risk of pest infestations and other diseases. Furthermore, if you plan to grow unsuitable crops, you'll need to provide intensive soil nutrition, which will require a significant amount of effort to achieve a successful harvest.
What a useful neighborhood
To ensure a bountiful harvest, it's recommended to plant adjacent plants correctly. This approach ensures easier seedling development, enhanced growth, and fruiting.
Many gardeners plant beans between rows of different vegetable crops. Beans provide nitrogen to the soil, while potatoes can protect legumes from bruchus.

Potatoes also pair well with onions, garlic, cabbage, corn, horseradish, spinach, eggplant, and mint. Growing these crops nearby improves soil quality, helps control pests, and prevents many diseases.
Tomatoes, sunflowers, and fruit trees (cherries, raspberries, cherries, and rowan) should not be planted near potatoes, as this will increase the risk of late blight.
Reviews
Elena:
"Planting potatoes in the same spot for many years is prohibited. Otherwise, the soil quality will deteriorate significantly, causing serious problems with growing vegetables. I was advised to plant corn. I heeded the advice. As it turns out, the corn root system loosens the soil and enriches it with minerals within a couple of years. I was satisfied!"
Sergey:
"I grow potatoes consistently in the same spot. I believe crop rotation isn't necessary. I add plenty of organic matter and sow green manure a couple of times a season. I usually use phacelia, mustard, and barley. By focusing on more active gardening, I can maintain good soil condition and eliminate the risk of unwanted infection in the potatoes I've planted. Plus, a high-quality, abundant harvest remains affordable."

Sofia:
"I never plant potatoes twice in a row in the same soil. Potatoes greatly deplete the soil, as this vegetable crop requires phosphorus and potassium. Before planting a new crop, I always apply fertilizer, urea, and manure. I believe that applying such fertilizers guarantees the restoration of the soil's nutrient composition. After harvesting potatoes, you can plant green manure (rapeseed, clover, phacelia, oats, lupines). If desired, you can plant peas, mustard, and oats after potatoes. Green manure improves the soil composition in the shortest possible time. Subsequently, I also plant pumpkins, beets, and green crops. I am confident that this approach improves the yield of each vegetable."
Irina:
"Proper crop rotation is essential. We typically use white mustard and winter rye. It's worth noting that rye is cheaper, but mustard grows faster. We sow mustard and rye immediately after harvesting, mixing the soil thoroughly when planting. If we plan to garden during a dry period, it's best to wait until the rains arrive. If the soil is very dry, rye and even mustard may fail to germinate. Following these simple rules guarantees a good potato harvest in the future, but it will still take a couple of years."
Knowing what to plant after potatoes helps ensure proper crop rotation and maintain good soil condition. As a result, a bountiful potato harvest becomes possible.
 Potato planting dates according to the moon for 2021 in the Moscow region
Potato planting dates according to the moon for 2021 in the Moscow region Potato varieties: names with photos, descriptions, and characteristics
Potato varieties: names with photos, descriptions, and characteristics When to dig up potatoes in 2020 according to the moon and how to best store them
When to dig up potatoes in 2020 according to the moon and how to best store them List of potato varieties with names, descriptions, and photos
List of potato varieties with names, descriptions, and photos