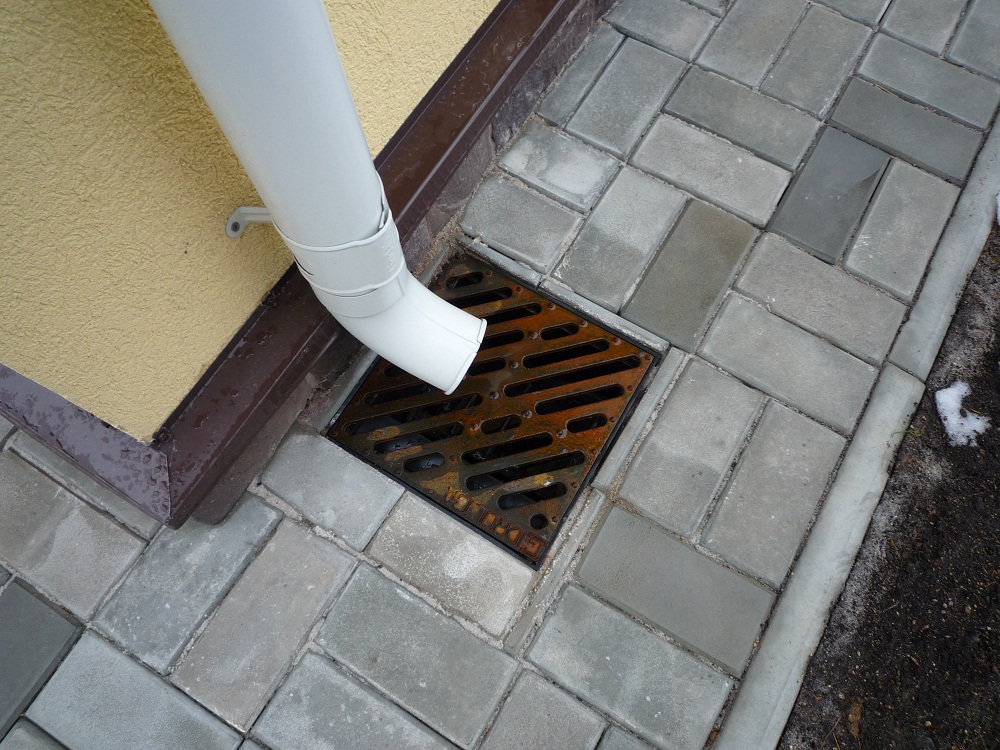
 A storm drain is a structural element of a storm drainage system, necessary to protect building foundations, road surfaces and basements from rainwater penetration.
A storm drain is a structural element of a storm drainage system, necessary to protect building foundations, road surfaces and basements from rainwater penetration.
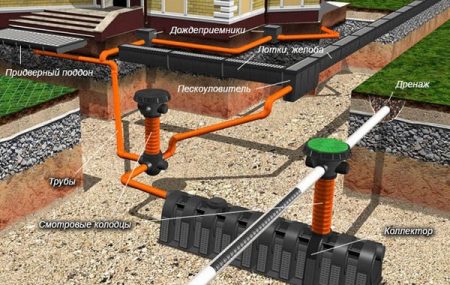
Water collected in the receiver then flows into the collector. The element is easy to install, operate, and replace. The appropriate storm drain is selected based on the type of storm drain, terrain, soil, and climate.
What is a storm drain and what is it for?

A storm drain, which directs liquid into the drainage system, can be round or square. It is installed to collect and purify accumulated liquid, sending it to the external storm sewer system. It is designed to protect building structures from the damaging effects of high humidity. In urban environments, it is used to collect water from road surfaces.
It is used not only in private housing but also in the construction of industrial facilities. In the former case, a choice is available between cubic receivers and vertical outlet options. The cubic receivers feature a localized collection of liquid, followed by discharge into the storm sewer.
The scheme of this model provides:
- lattice;
- partitions;
- basket.
Vertical drainage solutions collect liquid from pipes and gutters. The internal surface design prevents accumulated water from stagnating. These types of receivers do not include grates, allowing water to flow freely through the structure. When examining vertical drainage solutions, you may find baskets and partitions.
The option for large enterprises is a chamber with a cast iron grate. The chamber is either made of concrete rings or plastic.
What can storm drain inlets be made from?

When choosing a storm drain, the material used is paramount. Solutions are available in:
- plastic;
- cast iron;
- polymer composites;
- concrete.
Each option has its own advantages and disadvantages, dictated by its physical and mechanical properties. The final decision is made based on the type of facility for which the stormwater drainage system is being designed.
Features of stormwater inlets

The primary purpose of cast iron solutions is to remove water from road surfaces. The weight of storm drains can vary from 80 to 115 kg, depending on their shape and size. These elements are valued for their long service life and excellent flow capacity, which is crucial for industrial operations and urban infrastructure.
Suitable for residential construction projects requiring significant water drainage on a regular basis. Installation of cast iron models is impossible without specialized equipment. The manufacturing process includes a coating to protect against corrosion.
Concrete storm drains offer maximum strength. Steel fibers can be added to the elements for micro-reinforcement. Storm drains can be either cubic or cylindrical. In the former case, a plastic outlet is installed, reducing the overall weight of the structure. For particularly durable storm drains, heavy-duty concrete infused with steel fibers is used. The optimal shape in this case is cylindrical.
Concrete products are most often used in the construction of major roads and highways, at sites that have increased construction requirements for strength and reliability during operation.
This option is not suitable for private home construction due to its complex installation and inherent safety margins that will not be utilized in practice. Before installing the structure, a sand or gravel bed must be created.
Currently, the most popular solution is a plastic storm drain. Modern technology has produced an optimal plastic design that maintains its integrity even under significant external pressure thanks to its stiffening ribs. Solutions are available not only for country estates but also for large vehicle parking, withstanding loads of up to 90 tons.
A cubic plastic storm drain can drain accumulated water in any direction. Polypropylene models are popular due to their lightweight construction and easy installation, requiring no special equipment. The structure can be easily cleaned of debris. The maximum standard size is 500x500x500. Gratings are made of chemically reinforced plastic or cast iron for applications requiring heavy-duty resistance.
An optimal solution, though not yet widely available, is polymer-composite storm drains. They combine the best features of other options: simple installation and easy maintenance of plastic products, with the durability and corrosion protection of concrete solutions. High flow capacity is also a distinct advantage. Currently, polymer-composite products are more expensive than other options, so for cost-effectiveness, concrete or polypropylene are most often used in design projects.
Design features of storm drains

In practice, single-chamber storm drains with a rectangular grate installed at the top have proven to be the best choice. The grate is selected based on the need to ensure high water flow while preventing the penetration of foreign objects. Overall strength can be increased by installing stiffening ribs to resist external loads. If necessary, the structure can be reinforced with metal strips or fasteners during installation.
The use of cast iron and concrete storm drains in roadway construction does not affect the structure or integrity. To solve this problem, curb-style storm drains are installed. Some units come with a manhole, which expands their functionality.
The grate is installed to filter out debris and larger debris, protecting people from accidental injury. Some models include a filter that blocks sand and other small debris, significantly simplifying operation.
How to choose the right rain gutter

When selecting a suitable storm drain, it's important to consider more than just the storm drain design. Climate, annual and monthly precipitation, and the physical and mechanical properties of the soil are all factors to consider. All design data is provided in regulatory building documentation. To ensure the storm drain can handle the volume of water, the total area of the site for which the drainage system is being designed must be taken into account. The design process also takes into account the terrain and external factors that may impact the longevity of the system.
The most common solution for suburban areas is a small plastic storm drain equipped with a basket, partitions, and a grate with stiffening ribs.
If the property's area exceeds standard limits, a corrosion-resistant cast iron septic tank, which has a high flow capacity, can be used. Engineers do not recommend installing concrete septic tanks under standard conditions.
How to choose a storm drain according to its load class

There is a classification by load class that helps to select the appropriate storm drain for specific operating tasks:
- Class A15 (15/1.5) is considered the minimum load-bearing solution. These products are used in the design of parks and pedestrian areas. A15 is suitable for the vast majority of country houses and summer cottages.
- Class B 125 (125/12.5) is capable of supporting the load of several passenger cars. Its intended use is garages on private property.
- Class C 250 (250/25) is installed in large parking areas for vehicles and on highways. It is most often used by engineers during road construction.
- Class D 400 (400/40) is suitable for large gas stations and industrial facilities. These storm drains are suitable for draining water accumulated in factories.
- Class E 600 (600/60) for structures subject to increased loads. This design is used on piers and particularly large industrial facilities.
- Class F 900 (900/90) offers the highest possible strength. Designed for airports and military facilities.
If you take into account where the structure will be used, then the possibility of overpaying for unused safety margin is eliminated.
Installation of a storm drain
Rainwater inlets are installed in areas where water most often accumulates after precipitation. During installation, specialists select the optimal location to ensure the structure operates without any loss of water discharge.
The first step is to dig a pit taking into account the dimensions of the storm drain and provide a margin of up to 40 cm to accommodate soil deformation. Allow for a width of 3 cm to allow for concrete penetration. Next, workers create a thin sand or gravel bed. To compact it, add water, then compact the sand manually.
Before connecting the storm drain to the pipes, ensure the system is installed correctly and that all design heights for the inlet and outlet lines are maintained. The process itself takes just a few minutes. The bottom of the pit is then filled with concrete to securely anchor the element. It's important to ensure the storm drain remains stable in the designated location. Concrete is also added to the sides. For plastic products, it is recommended to install a grate to prevent possible deformation. Installation is complete after the basket and partitions are installed.
Stormwater inlets lose their performance if there are errors in concrete pouring during installation. Premature installation of the pavement on the site also impacts its effectiveness.
Expert reviews
Construction industry experts note the wide variety of wastewater receivers, their ease of installation, and ability to maintain their original reliability for several decades.
Leonid: It's best to choose storm drains with fine-mesh grates—they make them much easier to use. Almost all the models we install are made of plastic or concrete; many people consider cast iron outdated.
Dmitry: The entire storm drain system can be disrupted by incorrectly selecting the storm drain location. When installing, we consider the depth of soil freezing and the general terrain of the site. For standard applications, plastic models without stiffeners are suitable.
Ivan: Errors in installation or selection of the drain will be clearly visible in the spring and fall. If the drain is seriously impeding the operation of the storm sewer system, it's best to replace it as soon as possible to prevent the risk of undermining and damage to the foundation structure.
Rainwater inlets are effective at removing accumulated moisture. Before choosing a product, consider the terrain, the intended use of the facility, the climate, and the soil characteristics. For your first installation, it's best to hire a specialist in utility systems.
