Mushrooms are a very healthy food, containing numerous beneficial vitamins and minerals. However, they are also a highly allergenic food. In addition to causing allergic reactions, the fruits can impede digestion, causing bowel upset, and abdominal discomfort.
There are contraindications to using forest mushrooms in the diet, such as childhood. Also, consuming certain types of mushrooms while breastfeeding can be harmful to the baby.
Potential harm of mushrooms for mother and baby
The greatest risk of consuming mushrooms while breastfeeding is their ability to accumulate radionuclides, heavy metal salts, and other toxic substances, which can be absorbed through milk into the developing infant's body and cause severe intoxication. Some species can form spores that are inhaled into the lungs, causing allergic reactions and bronchial smooth muscle spasms.

Mushrooms contain chitin, a large amount of fiber, and carbohydrates, making them considered a heavy food that can negatively impact intestinal motility and cause increased gas production. In infants, this can lead to increased intestinal fermentation, leading to flatulence and colic.
The infant may experience bowel upset or vomiting. Cases of poisoning are common. The fruits are also very hard on the liver, gallbladder, and kidneys, and can trigger an exacerbation of inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, colitis) in both mother and child.
Whether or not to eat mushrooms during pregnancy and breastfeeding is determined by each woman individually, taking into account the characteristics of her body and her baby's feeding schedule.
Mushrooms that can be eaten while breastfeeding and their benefits
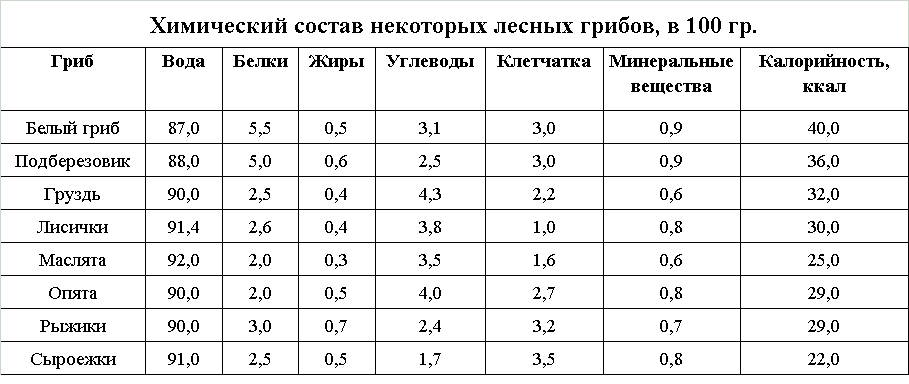
Mushrooms contain several times more protein than meat and vegetables, but their digestibility is slightly lower. They also contain amino acids, vitamins, fiber, and minerals not found in other foods. Mushrooms are rich in I, Ca, P, and Zn. This composition makes them considered a good antiviral agent. Their antioxidant properties can be used to prevent cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women are allowed to eat small amounts of mushrooms after proper cooking. Breastfeeding mothers can eat mushrooms grown on organic farms and in greenhouses that have not been chemically treated. The safest varieties are button mushrooms and gray oyster mushrooms.
Mushrooms are grown in special industrial facilities, so they have low toxin levels. Their high water content improves digestion, helps remove excess minerals and toxins from the body, and increases breast milk production.
Mushrooms are easily digestible and can help regulate bowel movements and relieve constipation. Dishes containing them are low in fat and simple carbohydrates. Cooked mushrooms have a low energy value (25-40 kcal/100 g), which depends on the cooking method.
Oyster mushrooms are also safe. They are often included in diets due to their high protein content and easy digestibility, as well as their high amounts of dietary fiber. These fibers stimulate digestion, have a positive effect on intestinal microflora, and help remove toxins from the body.
Wild mushrooms such as porcini and chanterelles can add variety to a woman's diet during lactation. Porcini mushrooms have high absorption properties and can accumulate radionuclides and nitrates. They are best introduced into the diet after the transition to mixed feeding or after introducing solid foods to the baby. They slow down digestion in the stomach, but also provide energy and strength, and strengthen the immune system.
When prepared correctly, chanterelles can not only add variety to your diet but also provide health benefits: they possess adaptogenic properties, which is essential for a woman's rapid recovery after childbirth and lifestyle changes.
Safe consumption of mushrooms during breastfeeding
Breastfeeding mothers should not introduce this product until they are 4-6 months into lactation. It is recommended to consume it no more than a few times a month.
Processing
During pregnancy and lactation, only freshly prepared mushrooms should be consumed. Dried or frozen mushrooms, as well as spoiled, rotten, wormy, or those with significant mechanical damage, should never be consumed. Stewed or baked dishes are permitted.
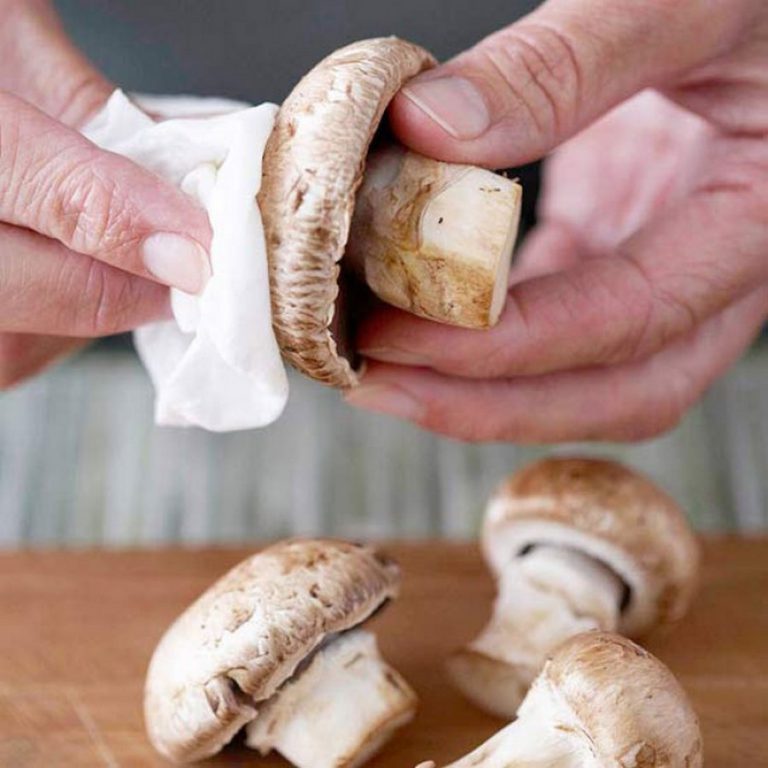

Before cooking, carefully sort through all the mushrooms. Then wash them thoroughly, removing any roots or moss. Rinse again. To ensure that this product is thoroughly cooked or fried, cut the caps into small, uniform pieces.
When preparing the dressing, use only high-quality vegetable oil or low-fat sour cream. Add salt, ground black pepper, or other spices to taste to add flavor and aroma. Under no circumstances should you add mayonnaise, ketchup or hot spices (chili, paprika) to the dish.
Healthy mushroom recipes
A nursing woman can eat the following healthy mushroom dishes:
- Porridge with mushrooms:
- champignons – 150 g;
- cereals (rice, buckwheat) – 1 cup (100 grams);
- half a carrot.
- half an onion;
- sunflower or olive oil – 15 ml.

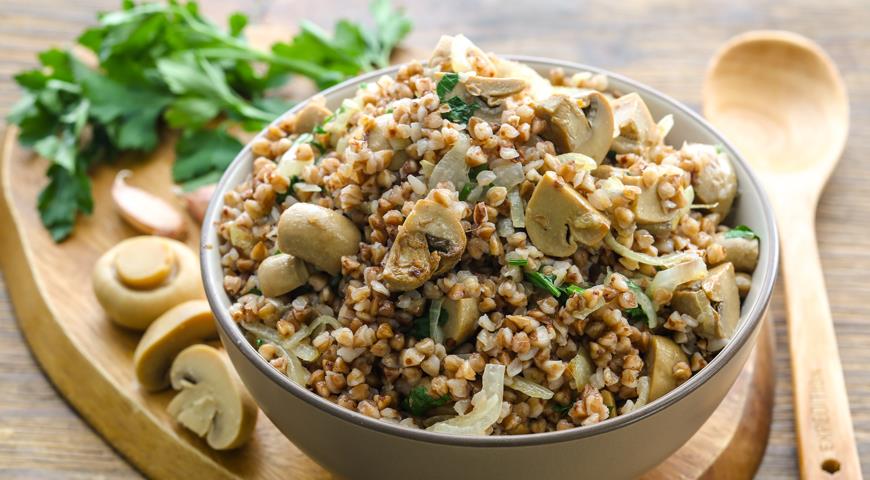
Porridge with champignons
Chop the vegetables and lightly fry in vegetable oil. Add the finely chopped mushrooms to the pan and simmer for 10-15 minutes. Add the cereal, season with salt, and pour boiling water over the mixture. Cover and simmer over low heat until tender.
- Casserole:
- oyster mushrooms (can be replaced with champignons) – 400 gr.;
- turkey – 600 gr.;
- cream – 250 gr.;
- 2 medium onions;
- cottage cheese – 250 gr.;
- sunflower (olive or flaxseed) oil – 2 tbsp.

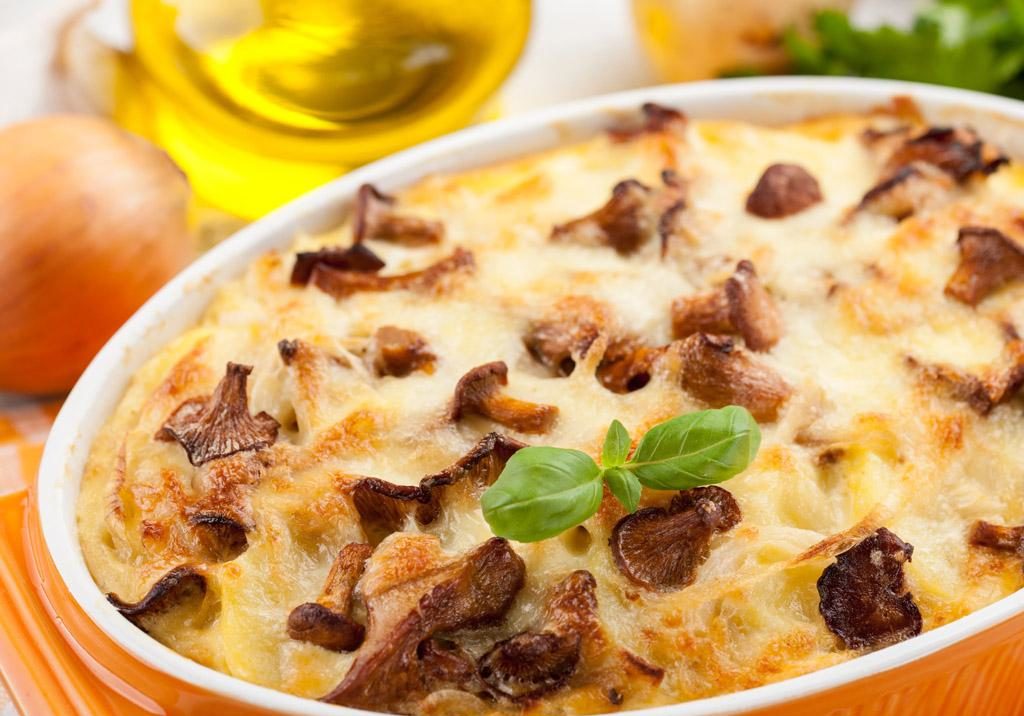
Mushroom casserole
Finely chop the oyster mushrooms and turkey. Grease a baking dish with vegetable oil. Mix all ingredients except the cottage cheese. Add sour cream, salt, and pepper, and pour everything into the dish. Mix the cottage cheese with the remaining sour cream and spread on top. Bake for 45 minutes at 200 degrees Celsius.
- Champignon salad:
- champignons – 250g;
- chicken breast – 300 gr.;
- chicken liver – 100 gr.;
- cheese;
- cucumber – 1 pc.;
- sour cream – 100 gr.;
- salt and pepper to taste.

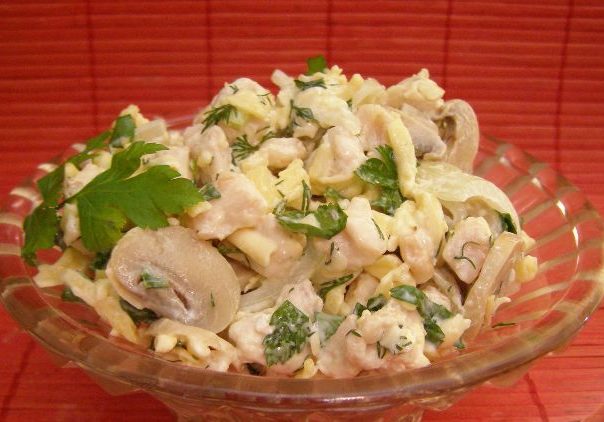
Chicken salad with mushrooms and cheese
Separately boil the mushrooms, chicken breast, and liver. Cut everything into strips. Mix and season with sour cream. Add salt and pepper to taste. Sprinkle with grated cheese.
Restrictions and contraindications
If a woman is unsure of the quality and safety of mushrooms, it's best to avoid them. During breastfeeding, avoid half-raw, raw, and pickled mushrooms entirely, and only eat properly prepared dishes. Pickled mushrooms can cause poisoning, heartburn, stomach upset, and even colic in infants.
Answers to frequently asked questions
There are many questions about taking mushrooms while breastfeeding. Here are some of them and their answers:
A cleansing enema can remove any remaining product from the intestines. Afterward, sorbents should be taken, such as activated charcoal, white carbon, or Polysorb. If the fever rises or symptoms persist, hospitalization is required. Breastfeeding should be discontinued at the first sign of symptoms.
Whether or not a nursing mother can eat mushrooms remains controversial, as they can be both beneficial and harmful due to their toxicity. If a woman decides to include them in her diet, it's important to choose only safe varieties and the most appropriate cooking methods when planning her menu.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1bE-3sNCVyk



















 What are the benefits and harms of oyster mushrooms for humans (+27 photos)?
What are the benefits and harms of oyster mushrooms for humans (+27 photos)? What to do if salted mushrooms become moldy (+11 photos)?
What to do if salted mushrooms become moldy (+11 photos)? What mushrooms are considered tubular and their description (+39 photos)
What mushrooms are considered tubular and their description (+39 photos) When and where can you start picking honey mushrooms in the Moscow region in 2021?
When and where can you start picking honey mushrooms in the Moscow region in 2021?