
Potato cancer is considered a dangerous disease, occurring in many regions. It is especially dangerous for tubers. Failure to detect infestations promptly can result in significant crop losses.
When growing potatoes, many gardeners encounter a disease called canker. The fungus attacks the tubers, rendering them unfit for consumption. The disease is considered a quarantine disease and can completely destroy the crop.
Symptoms
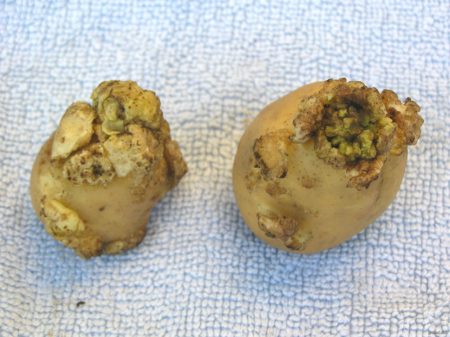
Infected tubers develop light-colored bumps. Over time, these turn brown and form growths. These growths resemble cauliflower florets. These bumps also appear in the leaf axils and on the florets.
In hot weather, cancer can also appear in other forms: leaf-shaped, corrugated, scab-like:
- Leaf-shaped - growths appear on the skin, taking the shape of leaves.
- Corrugated – the surface becomes uneven, the skin becomes wrinkled.
- Scabby - small scabs appear on the skin.

Biology
The disease begins to develop when the soil becomes overly moist. Tubers are primarily affected. Growths appear when adjacent cells come into contact with infected ones. After a certain period of time, zoosporangia form. In the fall, they enter the soil and overwinter, becoming active again in the summer.
The danger of potato cancer
The disease is also dangerous for humans. Infected vegetables lose their marketable appearance and are unfit for consumption.

Paths of cancer spread
Potato cancer is shown in the photo. There are many causes for the spread of the disease, the main ones being:
- cysts in the soil;
- moist soil;
- failure to observe crop rotation;
- infected root crops;
- cultivation of unstable varieties.
Methods of control and protection against potato cancer
There are several ways to protect crops from disease. Each option will help preserve the harvest.
Agrotechnical methods
Agronomic methods involve opening as many cysts as possible. After the winter period, only 30% of zoosporangia awaken.
To protect plants, the following measures must be taken:
- Corn, rye, and legumes should be planted in the beds where potatoes were grown. These crops can clear the area of spores;
- In the spring, add manure to the soil. If necessary, you can disinfect the soil with granulated urea;
- Preference should be given to varieties that are resistant to cancer.
Chemical methods
To preserve the harvest, the tubers must be treated with chemicals before planting. To do this, soak the planting material in a solution of Benomyl or Fundazol for half an hour.
To eliminate the source of the infestation, the soil must be treated with pesticides. Nitrofen solution has proven effective. The procedure is dangerous and should be left to professionals.

Preventive measures
Cancer prevention also yields good results. As we know, prevention is better than cure.
To avoid infection, you should take the following steps:
- Potatoes can be returned to their original location only after 3 years;
- You cannot plant nightshade crops near potatoes;
- carry out weeding in a timely manner;
- Select seeds and manure carefully, avoiding quarantine zones.

Which potato varieties are resistant to cancer?
You can recognize potato cancer from a photo. Protecting your crops from the disease and getting a good harvest is easy. Experienced gardeners recommend planting only varieties that are resistant to the disease. These plants will help clear your plot of the fungus within a few years.
As for mid-early varieties, you can choose from the following: Ogonyok, Stolovy 19, Zorka, Smachny, Lvovskiy white.

Among the mid-late varieties, the following can be distinguished: Vilia, Sulev, Pavlinka, Candidate.
If we consider imported varieties, Arosa, Bellarosa, and Rosara have proven themselves well.
Reviews
Many gardeners face the problem of potato wart. Careful care of crops is essential, as the disease can destroy an entire harvest. Gardeners are happy to share their tips, and some of them may be helpful.
Yuri, 46 years old:
Potato cancer is a dangerous disease. It appeared on my garden plot relatively recently. The tubers, leaves, and flowers became infected. We had to get rid of some of the crop.
The following year, I planted potatoes in a new plot. No outbreaks were observed. Furthermore, I used resistant varieties and regularly inspected the crops. I can say with confidence that if the potatoes are properly cared for, there shouldn't be any problems."
Even a novice gardener should be familiar with the signs of potato wart. This will help protect crops and preserve the harvest. It's important to remember that an infected area becomes a quarantine zone and is unsuitable for growing crops. A number of measures will need to be taken to eliminate the spores.
 Potato planting dates according to the moon for 2021 in the Moscow region
Potato planting dates according to the moon for 2021 in the Moscow region Potato varieties: names with photos, descriptions, and characteristics
Potato varieties: names with photos, descriptions, and characteristics When to dig up potatoes in 2020 according to the moon and how to best store them
When to dig up potatoes in 2020 according to the moon and how to best store them List of potato varieties with names, descriptions, and photos
List of potato varieties with names, descriptions, and photos