Mealybugs are one of the most dangerous pests of ornamental plants. These homoptera-like coccids attack shoots, buds, leaf blades, and flowers. If mealybugs appear on houseplants, they must be dealt with immediately. Otherwise, this pest will not stop until the flower is completely destroyed. Houseplants are often attacked by a similarly named disease, powdery mildew, which, however, is a different, fungal disease but has similar symptoms.
What is the danger of mealybugs developing on plants?
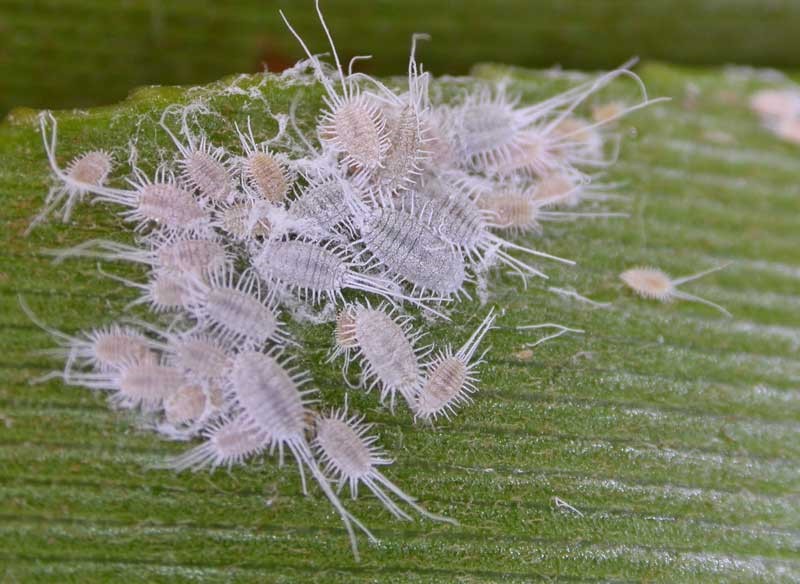
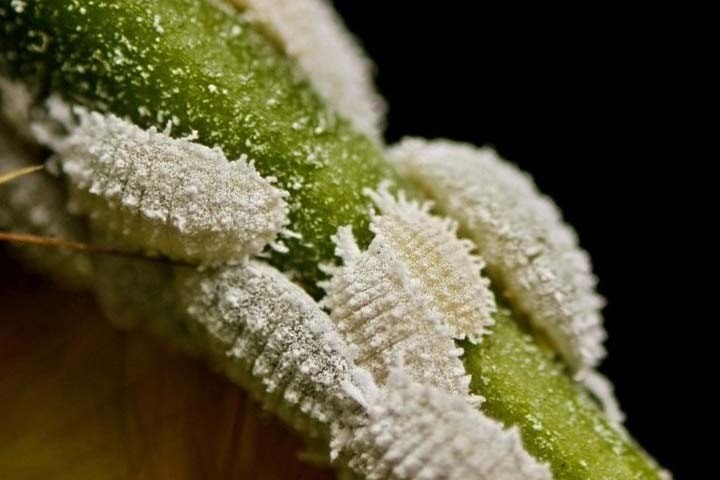
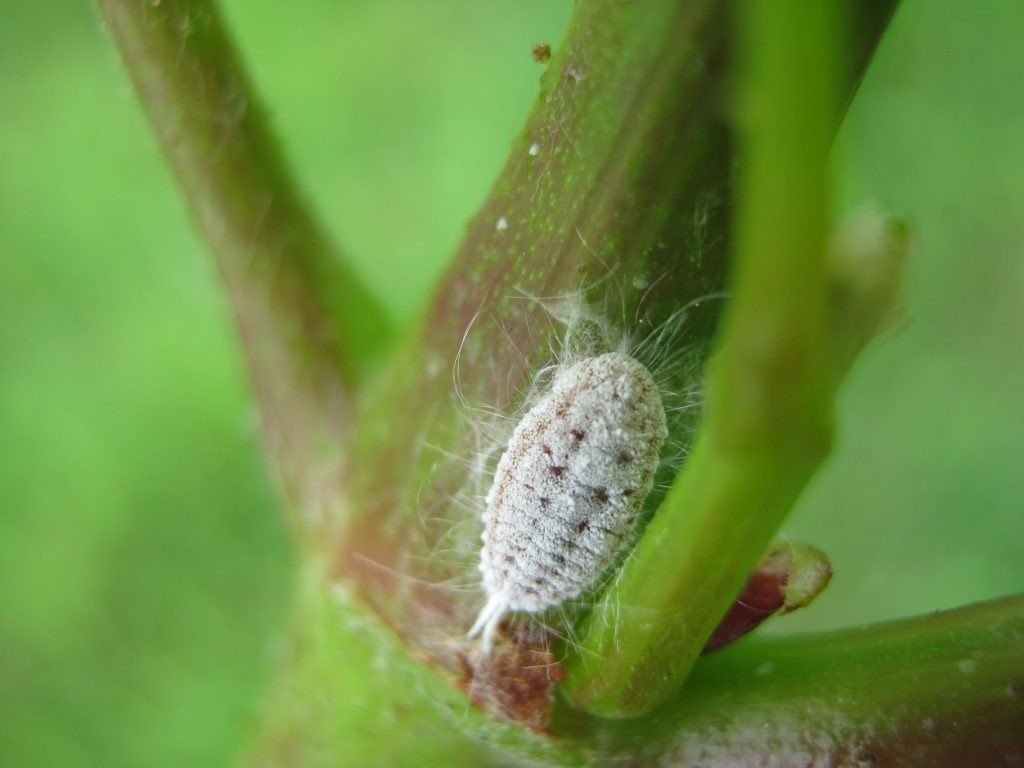
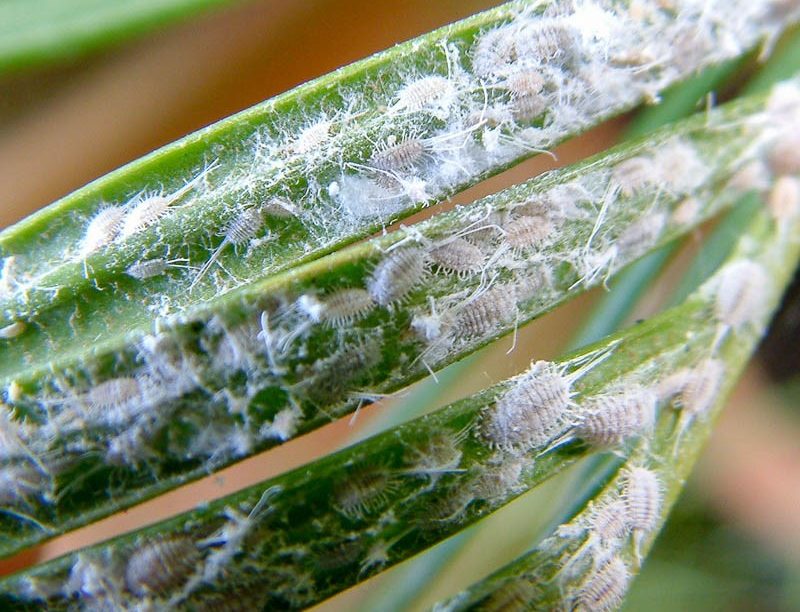
Mealybugs live solely on plant sap, damaging virtually every part of the plant. These parasites aren't always detected promptly, so if a flower begins to wilt, it's essential to inspect it carefully. Feeding on the sap, the parasites secrete a sweet, powdery substance reminiscent of cotton wool. Plants infested with scale insects for long periods become covered in sooty mold. If left untreated, the flower will eventually die, and the insects will seek out new "victims."
The following types of scale insects most frequently attack ornamental crops:
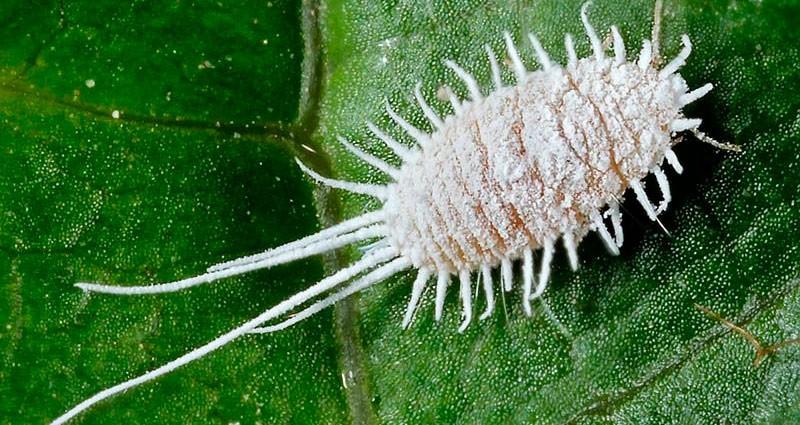
- Setoid scale insects are a fairly large group of members of the family. Their elongated bodies reach 3.5 mm in length. The scale insect itself is light pink or yellow, but its surface is covered with a smoky white bloom. Setoid scale insects form colonies that are located on the underside of leaves. They often attack axillary buds and young stems of the plant.

Bristly scale insects Affected leaf blades gradually turn yellow and die, and stems stop growing. The bristle bug most commonly infests plants of the Orchidaceae, Palm, Cactaceae, Tea, Onagraceae, Apocynaceae, and Araceae families. These pests can also be seen on Kalanchoe, bulbous plants, rhododendrons, asparagus, Saintpaulias, vines, and China roses.
- Grape mealybugs are similar in appearance to the previous species. They are characterized by a pinkish or lemon-colored appearance. These mealybugs spread throughout the flower, forming a large colony. These parasites infect various outdoor and indoor grape varieties.

Grape mealybugs - The sea mealybug is the most common species of hairy lice. Its members have relatively small, elongated bodies with a grayish-pink hue. This species is found on houseplants of the Rutaceae, Rhododendrons, Cacti, Palms, Onagraceae, Tea, Asteraceae, and Araceae families. It also occasionally attacks China roses and succulents.

Primorsky mealybug - Citrus mealybugs reach 4 mm in length. Their light pink bodies are covered with a dull coating. This species of parasite attacks plants of the Rutaceae family, including trifoliate, pomelo, kumquat, calamondin, and others.

Primorsky mealybug - Palm mealybugs have a broad, creamy body. These parasites reach 2.5 mm in length. Like other species, their bodies are covered with an ashy coating. This species feeds on the sap of many greenhouse crops, including chamaedorea, anthurium, phalaenopsis, and laurel.

Palm scale insects
Signs of pests in indoor plants
A thorough inspection will help determine if your houseplant is infested with mealybugs. A diseased plant has several characteristic signs:
- a smoky white coating resembling flour;
- sticky mucus has appeared on the buds or leaf blades, and elongated white insects are sitting all over the plant;
- The leaves droop and wither, becoming soft to the touch.
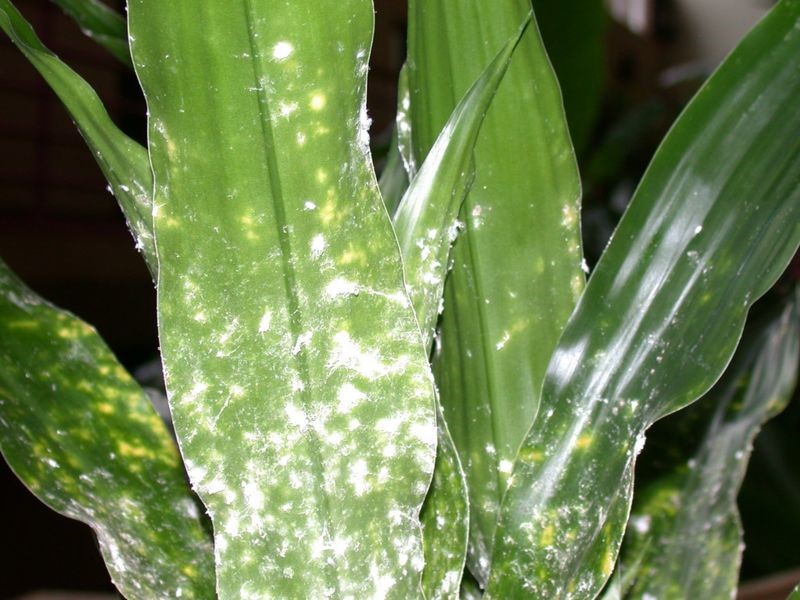

It's worth noting that all these signs don't appear simultaneously, so it's not always possible to detect the pests in time. However, as soon as the plaque appears on the plant, immediate action is necessary.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Methods of combating mealybugs
Mealybugs can be controlled using a variety of means. In the early stages of infestation, simple home remedies can be used. Severely infested plants should be treated with chemicals.
Chemicals
To kill scale insects, you can use specialized chemicals called insecticides. These can be roughly divided into three groups:
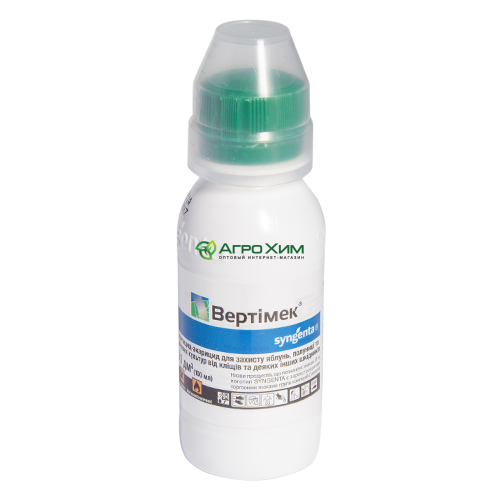
- Intestinal and contact pesticides are agents that enter the pest's body through the mouth or outer covering. Among these, the natural product Vertimek stands out. It's ideal for treating ornamental grapes and other potted plants. Citrus plants can be treated with a vaseline-based product called Preparat 30 Plus. Other popular similar products include Actellic, Admiral, Bankol, Inta-Vir, and Fitoverm.

Vertimek - Contact insecticides enter the insect's body through its outer covering. It's worth noting that contact insecticides can have a negative impact on the health of the plant. For example, Malathion is not suitable for treating crassulas, ferns, gerberas, orchids, petunias, or pili.
- Systemic pesticides are absorbed into plant sap. Among these, Aktara stands out as being extremely safe for animals and humans. This product is ideal for treating grapes, violets, and orchids.

Aktara
Pests at various stages of development can be present on a flower at the same time. Therefore, to completely eliminate scale insects, several treatments at intervals of 1-2 weeks may be necessary. Insecticides are toxic, so it is important to carefully follow the instructions for use.
Home remedies
At the early stages of infestation, you can resort to simple home remedies. First, remove the plaque from the surface of the flower. To do this, soak a cotton ball in a soapy solution and gently wipe the stems and leaves of the plant. Afterwards, you can spray the plant with a homemade solution. For example, you can use:
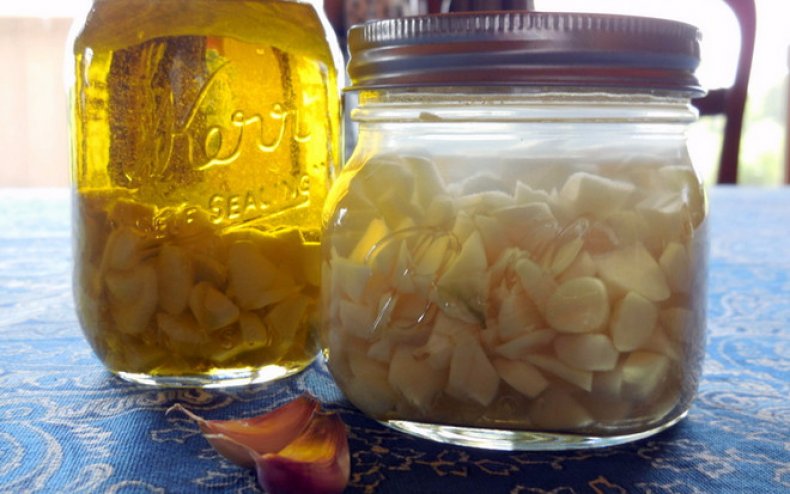
- Garlic infusion. To prepare the remedy, steep 5 cloves of garlic in 2 cups of water and let steep for 4 hours.

Garlic infusion - Soap solution with alcohol. Dilute 10 ml of alcohol and liquid soap in 1 liter.
- Calendula tincture. Soak a cotton swab in the prepared tincture and wipe the affected areas.
Folk remedies can help combat a small number of young parasites. Older individuals become less vulnerable and are extremely difficult to remove. Therefore, treatment should be carried out immediately after detection of scale insects.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:What is powdery mildew?
Powdery mildew is a disease caused by ectoparasitic powdery mildew fungi and requires treatment. The mycelium of these microorganisms attacks the leaf blades, covering them with a pale coating. After the spores mature, dark brown droplets, similar to dew, form on the surface of the coating. The leaves become sticky and soft to the touch. The fungi typically appear on the lower leaves and gradually affect the entire surface of the flower.
This disease is unrelated to mealybugs. It's worth noting that the symptoms of mealybug infestation are similar to those of mealybugs. In both cases, a light-colored coating appears on the plant.
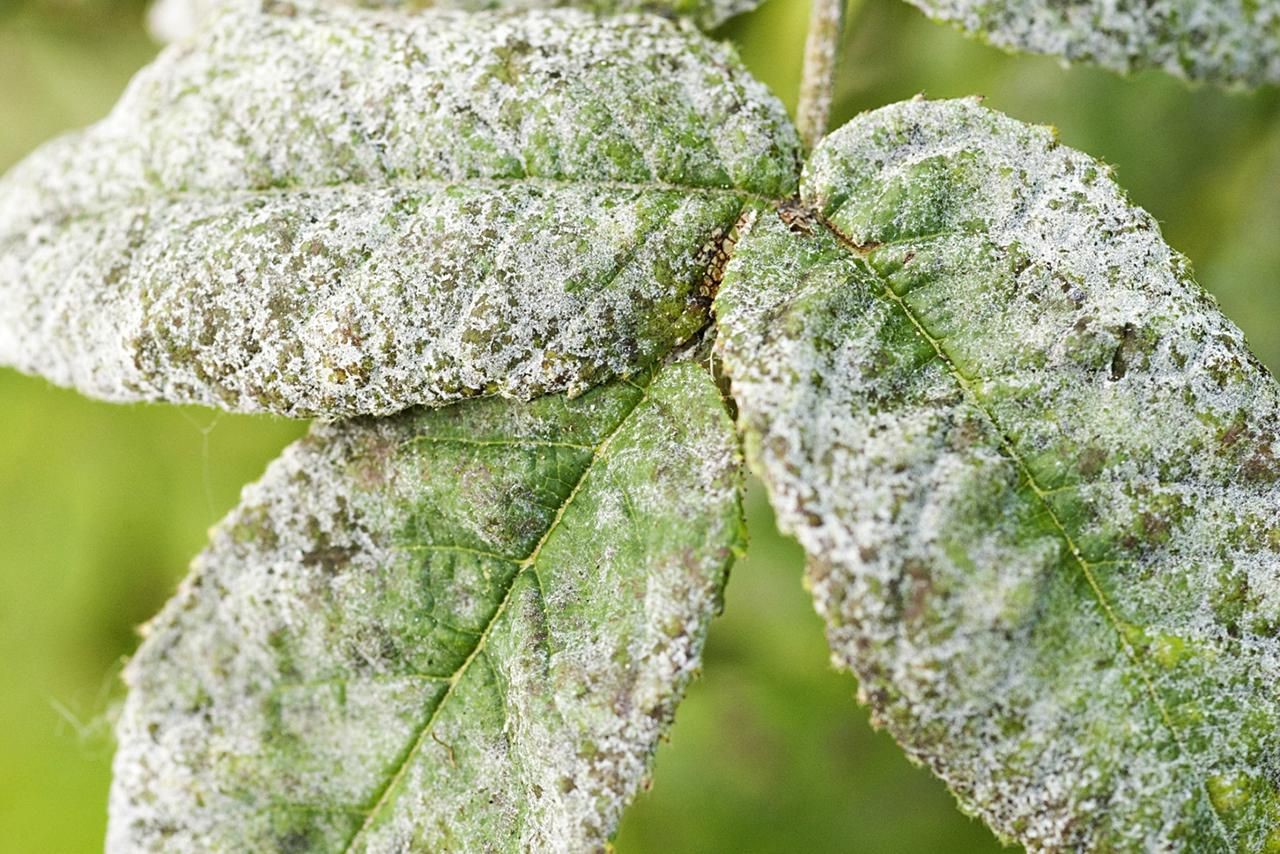

Flowers affected by the ash borer lose their attractive appearance: they become wilted, leaves fall off, and new ones grow twisted and wrinkled. Affected fruits crack and rot.
The white coating interferes with the flower's respiration, photosynthesis, and evaporation processes. Fungi feed on the plant, which leads to nutrient deficiencies and stunted flower growth. Over time, the coating becomes increasingly dense, and the flower's vital processes cease completely.
Treating plants against powdery mildew
Plants infected with ash fungus often die. However, this doesn't mean you shouldn't try to combat the disease. It's important to remove all diseased parts of the plant. Ash fungus mycelium can be present in the top layer of the substrate, so it's advisable to replace it. However, these measures won't be enough; to get rid of the fungus, you need to spray the plant with a special solution. This can be either a chemical solution or a solution prepared according to a folk remedy.
Chemicals
Antifungal pesticides, such as fungicides, can be used against ash:
- Benomyl;
- Jackpot;
- Acrobat MC;
- Agate;
- Discor;
- pureflower;
- Coronet.
These chemicals inhibit fungal growth and eventually destroy them completely. Indoor plants need to be treated several times.
Traditional methods
The most common folk methods of combating ash beetle include the following recipes.
Sodium carbonate and soap solution. Ingredients:
- 3 teaspoons sodium carbonate;
- 5 liters of hot water;
- a teaspoon of liquid soap.

Mix all ingredients and refrigerate. Spray the surface of the flower and substrate every seven days.
Serum solution. Ingredients:
- half a glass of whey;
- 5 glasses of water.
Mix the ingredients and spray the plant with the resulting solution in dry weather. Repeat this procedure twice a week.
Iodine solution. Ingredients:
- iodine – 1 ml;
- skim milk – 1 l;
- water – 9 l.
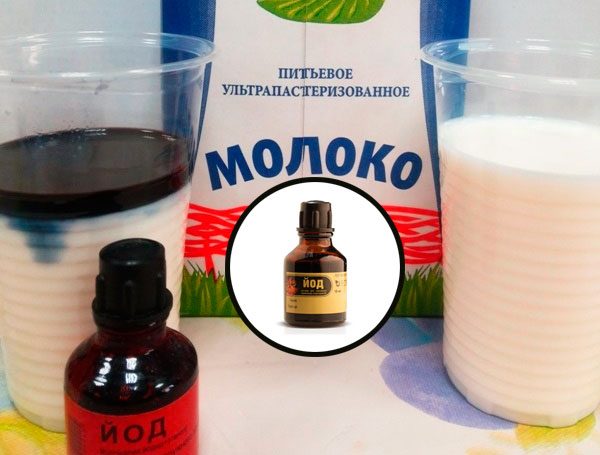

Preparation: mix all ingredients.
Application: spray the flower every 14 days until complete recovery.
Horsetail decoction. Ingredients:
- 100 grams of fresh horsetail;
- 1 and 5 liters of water.
Preparation: steep the horsetail in a liter of water for 24 hours. Then simmer over low heat for 1-2 hours. Strain the resulting infusion, cool, and dilute with 5 liters of water.
Application: Treat the plant every 5 days. At least 3 sprays are required to treat the disease.
Disease prevention
To avoid severe pest or fungal infestations, it's important to regularly and thoroughly inspect your flower. This will help identify problems early and prevent their spread. It's also important to always remember the proper flower care guidelines.
Mealybugs don't tolerate high humidity, preferring dry, warm places. Fungal diseases, on the other hand, thrive in moist soil. Therefore, it's important to properly care for the plant, maintain a regular watering schedule, and avoid overwatering or excessively dry soil. It's a good idea to regularly wipe the leaves with a damp cloth and remove any diseased or wilted areas immediately.
To prevent saffron flakes from infecting ornamental plants, regularly spray them with a potassium permanganate solution. Nitrogen fertilizers should be used sparingly, but phosphorus or potassium supplements are helpful. The room where the plant is kept should be well-ventilated, but avoid drafts. It's best to buy the plant's substrate from a store, as this will reduce the risk of pests or fungi spreading through the soil.
When purchasing a flower, inspect it carefully. The leaves shouldn't be wilted or covered in unnatural spots. After purchasing, isolate the flower from other plants for a while. Remember that mealybugs can infest the plant's roots, so consider repotting it in a transparent pot. This will make it much easier to spot the pests early.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Frequently Asked Questions
Houseplants are susceptible to pests and various diseases. Mealybugs and powdery mildew are particularly prominent. Plants infected with mealybugs become covered with a white coating. The insects themselves can also be seen on the plants. Ash fly also causes a coating, but it is caused by a specific fungus. Although these diseases have different causes, they are both very dangerous, so proper care is essential to prevent them.







 How and what to use to combat pear psyllid
How and what to use to combat pear psyllid Oidium of grapes (photo) and how to treat it
Oidium of grapes (photo) and how to treat it The most effective aphid control methods without chemicals
The most effective aphid control methods without chemicals How to treat fruit trees in the fall against diseases and pests
How to treat fruit trees in the fall against diseases and pests