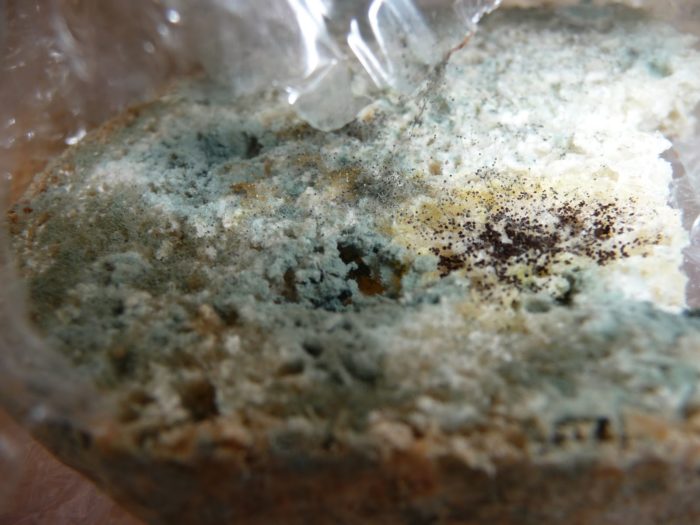
Everyone knows firsthand that leaving food at warm room temperature for an extended period of time causes it to develop a white, rough-surfaced mold that emits an unpleasant odor. This mold is called mucor. It can be found not only on food but also on soil and various organic debris.
Mucor is a fungus that can have a negative impact on humans and animals and cause disease. Despite this, it is often used to produce antibiotics, starter cultures, and fermented foods. Another name for this microorganism is white mold.
Characteristic features of mold fungi
Mucor belongs to a group of lower mold fungi from the class Zygomycetes. This class consists of 60 species. A distinctive feature of mucor is the absence of partitions in the non-cellular structure of the mycelium.
Like other fungi, molds have a mycelium, which is a large, undifferentiated cell with numerous nuclei in the cytoplasm. Cell septa form during reproduction, facilitating the separation of sporangia—the reproductive organs.
Mold is unpretentious, so it can appear and grow anywhere. The main conditions for its development are nutrients and moist, warm air. Experts say that if all the necessary conditions are present, mucor can even grow in buildings between bricks or concrete.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Under unfavorable conditions, the spore becomes covered in a protective capsule, metabolic processes slow down, and the organism can survive in this form until conditions for resuming life arise. Mucor was discovered by historians during excavations of the tombs of Egyptian pharaohs, proving its widespread distribution.
Appearance and photo
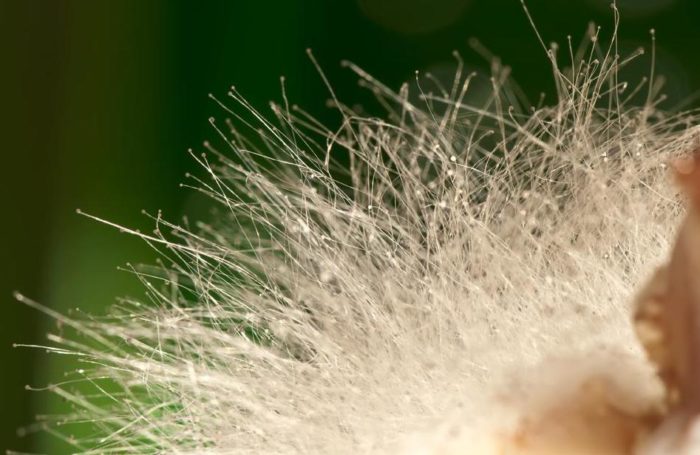
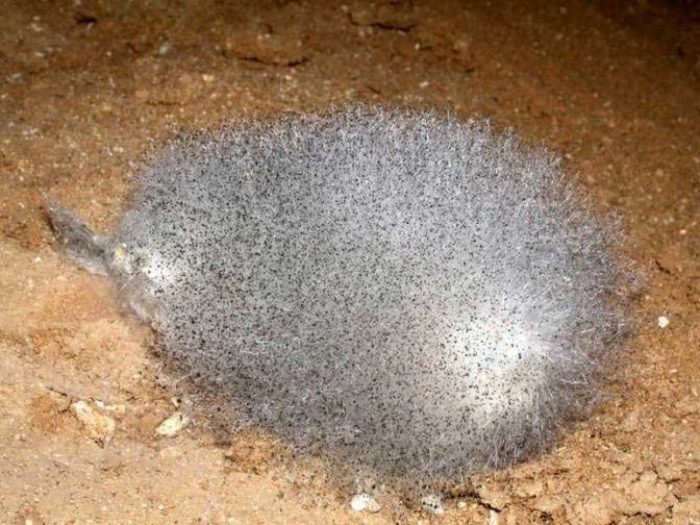
The appearance of mucor depends entirely on its developmental stage. Initially, it appears as a white fluff, hence the name "white mold." The length of the fluff depends on environmental conditions.
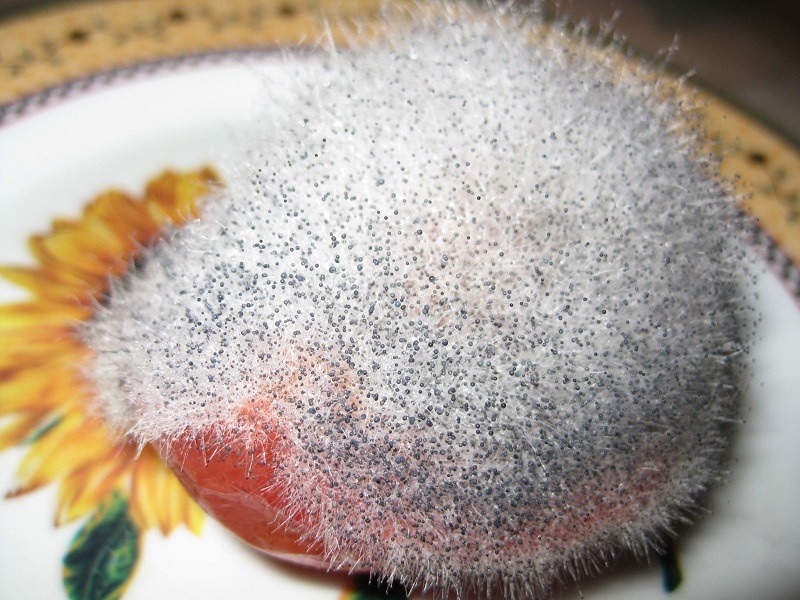

During active growth, the number of sporangia at the ends of the fungus increases, giving the organism a grayish tint. A mature organism is black. You can see what this mushroom looks like in the photo.
The structure of the Mucor mushroom
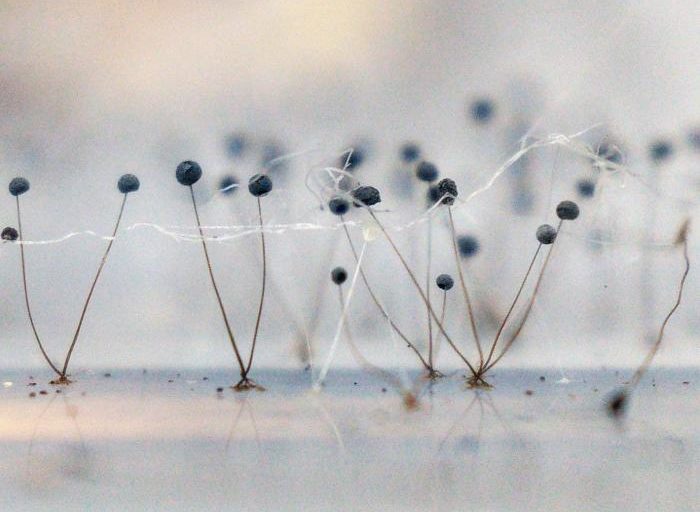
A detailed examination of the structure of white mold is only possible under a microscope. The main part of the fungus is called the mycelium, which is a cell with branches and numerous nuclei. Hyphae, which anchor the body to the substrate, are integral structural components.
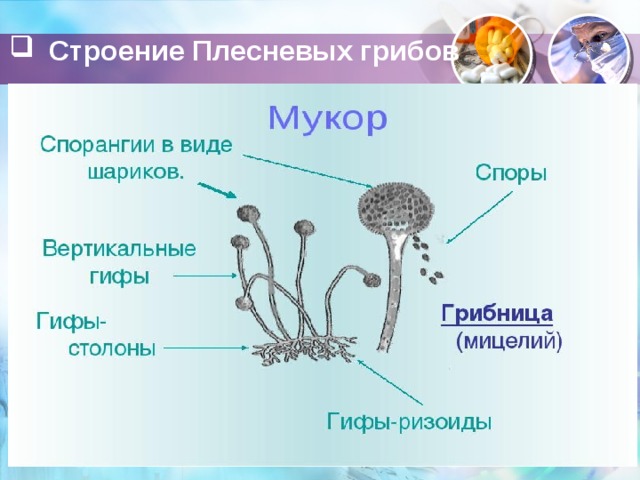
Hyphae are thin, mostly white, threads that become thinner toward the periphery. What everyone sees with the naked eye is called a colony, which consists of thin hairs called sporangiophores. These structures are responsible for the organism's reproduction and grow from the body. The size of the sporangiophores depends on conditions and can reach up to 2-3 cm in height. During reproduction, a capsule containing spores appears at the end of each hair.
Reproduction
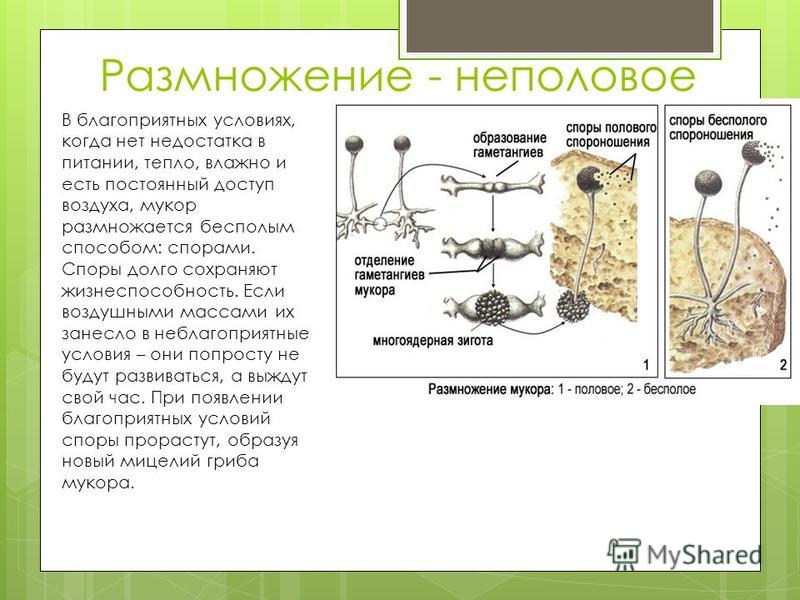
Mucor reproduction can occur in two ways – sexual and asexual:
- Asexual reproduction is possible due to the presence of spores, which form in capsules at the tips of sporangiophores. A characteristic feature of this type of reproduction is that the spores are dispersed by the wind, which explains the species' widespread distribution.

Asexual reproduction - Sexual reproduction occurs when conditions are unfavorable for the microorganism. When the substrate in which the fungus is attached lacks organic matter, the hyphae begin to converge. They fuse at the level of sexual reproduction structures called gametangia. The structure of the gametangia allows the formation of reproductive cells, or gametes, whose union results in the formation of a diploid zygote.

Sexual reproduction The zygote subsequently develops into a mature organism, which goes through all stages of development, which can only be observed under a microscope. Hyphae from different fungi can participate in the reproduction process. This type of reproduction is called heterothallic. Homothallic reproduction uses hyphae from only one mycelium.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Nutrition
Mucor is a heterotrophic nutrient, meaning it is unable to synthesize organic matter from inorganic substances. For adequate nutrition, the organism requires high humidity, warmth, oxygen, and readily available organic matter.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uya_RWai94M
Therefore, mold appears in areas with large amounts of undecomposed plant matter, such as food and manure. This species can also be classified as saprotrophic organisms, as they typically extract organic matter from dead material. High-calorie foods such as potatoes, flour products, and fruit attract white mold.
Useful properties and scope of application
There are approximately 60 species of mold, which are widely used in various human activities. In the food industry, mucor is used to make well-known cheeses such as tofu and tempeh. These cheeses are made using a fungal starter culture.
In Italy and Spain, renowned for their abundant meat products, white mold is used in the production of sausages. The sausages are stored in a cool, dark place under a layer of mold for a month, after which they are processed, and after a few months, they hit store shelves.
The fungus is often used to produce potato alcohol. This use is based on the activity of the fungus's enzymes. It is also used in the production of fermented milk products. Mucor is considered a valuable material in medicine, where it is used to produce the antibiotic ramycin.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Due to its wide range of uses, mucor is grown in specialized laboratories. To do this, a favorable environment is created in a separate container, for example, by moistening a piece of bread. The container is then insulated and tightly covered. The container with the substrate is placed in a warm place with a temperature of at least 20 degrees Celsius, where, after a couple of days, colonies of the fungus begin to grow.
The danger of mucor for living organisms
Despite the mushroom's beneficial properties, it remains dangerous not only to human health but also to animals. Mucor is the causative agent of mucormycosis, a disease that simultaneously affects multiple body systems and is toxic.
Symptoms of mucormycosis include:
- fever;
- malaise, headache;
- swelling and hyperemia of the skin;
- discomfort and pain in the facial muscles;
- disturbances in the functioning of the visual analyzer;
- sputum with streaks of blood, which indicates lung damage;
- acute pain in the lower back, which is a symptom of kidney damage.
A doctor can make a definitive diagnosis after conducting a series of biochemical tests. The most common type is the rhinocerebral type. The pathogen enters the body through inhalation of its spores from contaminated air, and infection is also possible through contact of damaged skin with mold. People with diabetes, neutropenia, and weakened immune systems are at risk.
In animals, infection is possible when animals consume contaminated food. The disease has three forms: cerebral, intestinal, and pulmonary.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Let's look at the most frequently asked questions about mucor:
Mucor, or mold, is a microorganism that forms on food when it's improperly stored, as well as in areas with high humidity and temperature. This species is often used in the food industry and medicine, but it also causes a dangerous disease called mucormycosis.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y3w2bDtariU











 What are the benefits and harms of oyster mushrooms for humans (+27 photos)?
What are the benefits and harms of oyster mushrooms for humans (+27 photos)? What to do if salted mushrooms become moldy (+11 photos)?
What to do if salted mushrooms become moldy (+11 photos)? What mushrooms are considered tubular and their description (+39 photos)
What mushrooms are considered tubular and their description (+39 photos) When and where can you start picking honey mushrooms in the Moscow region in 2021?
When and where can you start picking honey mushrooms in the Moscow region in 2021?
Edward
Thank you! Great article. I recently wanted to start studying mycology, and this article was the first step in that process. Thank you.