Healthy seedlings should have a developed root system, a strong trunk, and green leaves. Mistakes in growing seedlings can lead to stem elongation. seedlings may outgrow, become diseased, or die. Even after planting young plants in the garden, you don't always get a good harvest. Contaminated soil, cramped containers, dense planting, poor-quality seed, and improper care are the main mistakes that lead to problems during seedling germination.
Seed material
 After collecting the seeds, they must be dried and aired. Store them in moisture-proof jars with the lids tightly closed until sowing. If storage conditions are not met, the seeds may become moldy, turn black, or rot. Such material is unsuitable for planting.
After collecting the seeds, they must be dried and aired. Store them in moisture-proof jars with the lids tightly closed until sowing. If storage conditions are not met, the seeds may become moldy, turn black, or rot. Such material is unsuitable for planting.
Planting seeds too deeply can affect seedling germination. The recommended planting depth is 1-2 cm. If planted deeper, the seeds may fail to germinate, as they won't be able to penetrate the thick soil layer. Some plant varieties aren't planted deep, but rather left on the soil surface and watered periodically.
When purchasing seeds at the store, check the expiration date on the packaging. Expired seeds will not germinate, or only some will. When unpacking, carefully sort and inspect all seeds.
Planting soil
 Infected soil can slow plant growth or kill seedlings. You can't simply scoop up soil from your garden and plant seeds. To grow strong seedlings, you'll have to put in the effort—either making your own nutritious soil or buying it at the store. Typically, this includes turf, peat, sand, and humus. Each crop requires its own soil mixture and proportions.
Infected soil can slow plant growth or kill seedlings. You can't simply scoop up soil from your garden and plant seeds. To grow strong seedlings, you'll have to put in the effort—either making your own nutritious soil or buying it at the store. Typically, this includes turf, peat, sand, and humus. Each crop requires its own soil mixture and proportions.
To disinfect, freeze the substrate, pour boiling water over it, or bake it in the oven (for 20 minutes at 80-90 degrees Celsius). This will kill pests, viruses, and fungi. Another method of disinfection is to water the soil with a potassium permanganate solution.
Containers for seedlings
Cramped containers and pots without drainage can hinder plant growth. Seedlings begin to get sick, and the cause is unclear. Many seeds rot in such pots and die. The root system needs to develop freely; seedling growth depends on it.
It's best to use special seedling containers. If these aren't available, use cups measuring 10 cm by 10 cm. Peat pellets and pots, plastic containers, and cassettes are often used.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Pre-sowing preparation
 Like soil, seeds need to be disinfected. Untreated material can become infected, spreading the disease to neighboring plants.
Like soil, seeds need to be disinfected. Untreated material can become infected, spreading the disease to neighboring plants.
Soak the seeds in a potassium permanganate solution for half an hour. Rinse and place them in damp cheesecloth for two days to germinate. This procedure reduces the germination time for the seeds. Store-bought seeds are usually pre-treated, so no further steps are required.
Timing of sowing for seedlings
When the soil warms up to 10-13 degrees Celsius, the seedlings are planted in the beds. Timely sowing will ensure timely germination, and the seedlings will be fully grown by the time the soil warms up. It's not advisable to miss this period. The timing of planting depends on the regional climate, the plant variety, and the growing method (under or without plastic).
Calculate the seedling growth period, from sowing to planting. Immature seedlings will bloom later, while overgrown ones will take a long time to establish.
Temperature and lighting
 Each plant species has its own germination temperature. Some require temperatures as low as 5-7°C, while others will only germinate at temperatures of 18-22°C. Heat-loving seedlings should not be planted in cold soil or a greenhouse. At low temperatures, moisture evaporates less, and plants absorb fewer nutrients from the soil. Cold soil promotes the growth of fungi. Plant growth slows, and they become susceptible to disease.
Each plant species has its own germination temperature. Some require temperatures as low as 5-7°C, while others will only germinate at temperatures of 18-22°C. Heat-loving seedlings should not be planted in cold soil or a greenhouse. At low temperatures, moisture evaporates less, and plants absorb fewer nutrients from the soil. Cold soil promotes the growth of fungi. Plant growth slows, and they become susceptible to disease.
To avoid this, harden off the seedlings before planting, taking them outside for 2-3 hours each day. Leave them in a warm room overnight.
Each vegetable crop requires its own daylight hours, ranging from approximately 12 to 16 hours. Without light, seedlings begin to stretch, grow vigorously, and their stems become thin. These plants become susceptible to disease and do not tolerate transplanting or transplanting well.
To solve the problem during short winter days, additional lighting is needed. A south-facing windowsill or a glazed balcony facing south is suitable for containers with seedlings.
Dense planting
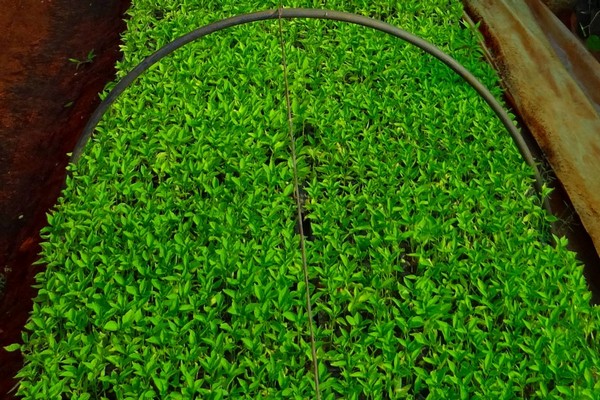 If seedlings are planted too close together, the plants will stretch and lack light. If planted too closely, the crops will not be aerated and will lack nutrients. There is a risk of fungal diseases.
If seedlings are planted too close together, the plants will stretch and lack light. If planted too closely, the crops will not be aerated and will lack nutrients. There is a risk of fungal diseases.
Densely planted plants should be thinned out, leaving 2-3 cm between seedlings. Individual containers are the best option for sowing, eliminating the need for thinning and pricking out.
Dive
 Picking This is a mandatory procedure for many plant species. After 2-3 leaves appear, the seedlings are transferred to individual containers. If not pricked out in time, the seedlings will become stretched and weakened when planted too close together.
Picking This is a mandatory procedure for many plant species. After 2-3 leaves appear, the seedlings are transferred to individual containers. If not pricked out in time, the seedlings will become stretched and weakened when planted too close together.
Replanting young plants must be done correctly. Damage to the root system will result in the death of the plants. Often, transplanting to another container occurs along with the root ball containing the plant. If the seedlings were grown in peat pellets, there is no need to replant them. Planting in holes should be done with peat.
The seedlings are planted deep to the cotyledons or the roots are shortened by 1/3. The main root and thick roots should not be disturbed. For the first three days after transplanting, the seedlings are left in a shaded area. The first watering occurs 4-5 days after transplanting. Some crops should not be transplanted, as their growth and development will be slowed.
Irrigation irregularities
After sowing the seeds, the soil should be kept moist, but not wet. It's best to mist the soil a couple of times a week instead of watering. Dry soil will prevent germination, and excessive moisture will encourage fungal growth.
The frequency of watering depends on the plant species—moisture-loving plants require more moisture than drought-tolerant ones. Seedlings should be watered with settled, melted, or rainwater, but not cold (18-20°C).
Seedling diseases
If you ignore the first symptoms of plant disease, you can lose a large portion of your crop. Fungi are spread quickly, and neighboring plants can also become infected.
When leaves turn yellow or fall off, when the trunk turns black, when plants dry up, weaken, or stop growing, immediate action is needed. First, identify the cause of the disease, then take action. Diseased seedlings are removed, and the remaining ones are treated with fungicides. For prevention, apply Gliocladin and Trichodermin to the soil. Pre-planting preparation, including disinfection of the soil and seeds, is essential.
Hardening off young plants is crucial when growing seedlings. If they aren't hardened off, the young seedlings will freeze during cold weather. When plants begin to stretch, hardening off the seedlings slows their rapid growth. Overgrown seedlings don't take root well. You can slow down growth by reducing watering. While you can learn from mistakes, it's better to use tips and tricks to avoid making mistakes when growing seedlings.

 How to successfully grow seedlings at home
How to successfully grow seedlings at home Seedling calendar 2024: planning planting in April
Seedling calendar 2024: planning planting in April All About Seedlings: An Easy Path to a Bountiful Harvest
All About Seedlings: An Easy Path to a Bountiful Harvest From seed to vigorous sprout: why seedlings are the key to a bountiful harvest
From seed to vigorous sprout: why seedlings are the key to a bountiful harvest