Bell peppers are a relatively easy-to-grow crop that thrives in southern climates. Growing them in temperate climates can present some challenges due to the long growing season, so the seeds need to be germinated before planting. Experienced gardeners prefer to grow their own pepper seedlings, not only for the economic benefit but also for the quality of the seedlings.

Pre-planting bell pepper seeds to produce seedlings allows for a bountiful harvest not only in a greenhouse but also in the open field. Particular attention should be paid to sowing timing and seed preparation, as this affects not only germination but also the subsequent development of the plants.
Timing for sowing bell pepper seeds for seedlings in different regions
Seeds are sown in late winter, but the exact date should be chosen based on the climate and growing conditions (greenhouse or open ground). The sowing time also depends on the variety, as late-ripening and early-ripening peppers are sown at different times.
For the Southern Urals
Until recently, growing peppers in the Urals presented significant challenges due to the harsh climate. However, specially hardy varieties have now been developed for cultivation in this region. However, heat-loving bell peppers only mature in the open ground during the short summer in the Southern Urals; in other areas of the Northern region, they are grown only in greenhouses with supplemental lighting. In any case, pre-cultivation of seedlings is necessary—both before planting in the ground and in a greenhouse.
When sowing seeds, most gardeners rely not only on planting dates but also on favorable days according to the lunar calendar. This is why beginners are advised to pay attention to the moon's phases. Favorable days for residents of the Urals include February 9, 19, and 23, and March 7, 20, and 22. It's best to sow quickly, otherwise the peppers simply won't have time to ripen (in open soil).
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:For the Moscow region
In the Moscow region, bell peppers can be grown both in greenhouses and in garden beds, but either method requires pre-germination of the seeds indoors. Each vegetable grower chooses the most suitable growing conditions for themselves. To determine the approximate time for sowing seeds for seedlings in this region, it's best to consider the ripening period of the peppers; early varieties are sown after March 15th.

For central Russia
Pepper varieties come in early, mid-season, and late varieties. On average, it takes 100-135 days from germination to harvest. Add another 14-20 days (germination period) to calculate the fruiting period that suits the gardener. If you have a heated greenhouse, you can harvest several weeks earlier.

Selecting the right variety and preparing sweet pepper seeds for planting seedlings
Today, there are approximately two thousand known varieties of sweet peppers, each differing in taste and appearance. To select the right variety, a novice gardener should carefully read the plant's description on the packaging and determine the appropriate growing conditions.
For small greenhouses, it's best to choose low-growing varieties. For outdoor use, early peppers, which ripen more quickly in the open ground, are often chosen. If you plan to harvest seeds from the resulting crop, it's best to avoid heterozygous hybrid varieties, although they are more disease-resistant.
The best pepper varieties, according to vegetable growers, for growing in open ground:
- F1 Buratino is an early pepper with oblong-shaped red fruits. Each fruit weighs up to 100 g, and the walls are 5-6 mm thick. The bush grows to a height of no more than 70 cm.

F1 Buratino - Atlantic F1 – an early maturing plant, the height of which reaches 110 cm. Barrel-shaped peppers are massive and can weigh up to 450 g.

Atlantic F1 - Gemini F1 is a high-yielding variety. Its fleshy, cube-shaped fruits are yellow in color.

Gemini F1
The following varieties are popular for greenhouse cultivation:
- Ivanhoe;
- Siberian format;
- Maecenas;
- Funtik;
- Eroshka;
- Country;
- Martin.
Don't sow seeds directly from the package, as this will significantly complicate the entire growing process. Seeds should be pre-treated to speed germination and ensure strong sprouts.
You can choose one of the following pre-sowing treatment methods:
- The seeds are soaked in water at a temperature of 45-50°C for approximately four hours. After this, the seeds are placed on a damp cotton cloth or gauze and left to germinate for three days at a temperature of approximately 26°C.
- You can use store-bought products specifically designed for soaking - Baikal, Ideal, Fitosporin.
- For disinfection, seeds are kept in a weak solution of potassium permanganate (1%) for 30 minutes.

Seed treatment - You can soak the planting material for 10-15 minutes in a hydrogen peroxide solution heated to 40°C (5 ml per 1 cup of water). Remove the seeds and dry them without rinsing.
- Sometimes gardeners use a method of alternating cold and heat, which promotes hardening of peppers and active seedling growth. The seeds are placed on a damp cloth, covered with two layers of film, and left for 24 hours at a temperature of 24-27°C, then taken out into a cold environment (4 to 10°C) for 4 hours. This procedure should be repeated three times.
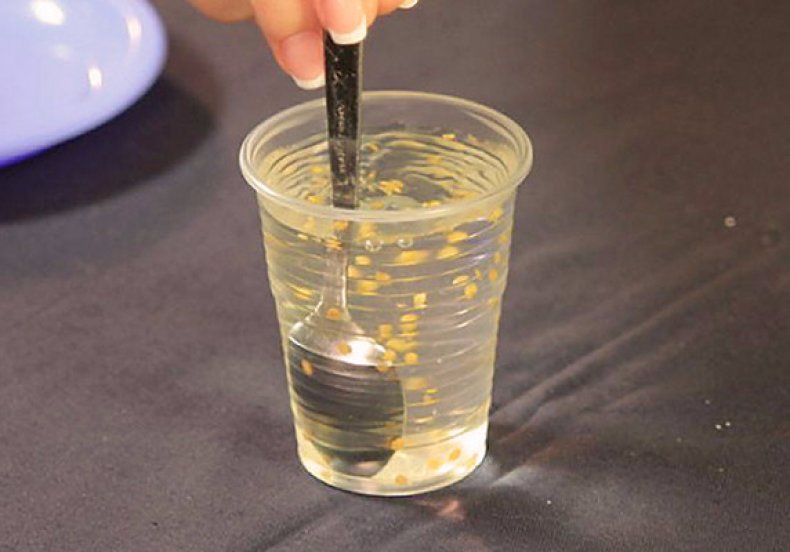

The specimens that float to the surface are discarded, and those that settle to the bottom are used for planting.
Methods for sowing bell pepper seeds for seedlings and caring for them
There are several ways to grow pepper seedlings, among which gardeners prefer to plant peppers in separate containers. Peppers have rather fragile roots, so transplanting negatively impacts their development. Seedlings that have been transplanted are more susceptible to disease and significantly stunted.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:In peat tablets
For peppers, select tablets with a diameter of 4-5 cm. Place them in a large container and cover with water. After they swell, drain off the excess water and begin sowing. Place one seed 0.5 cm deep in the center of the tablet (which has taken on a cylindrical shape). After planting, move the container to a warm room and cover with plastic wrap.
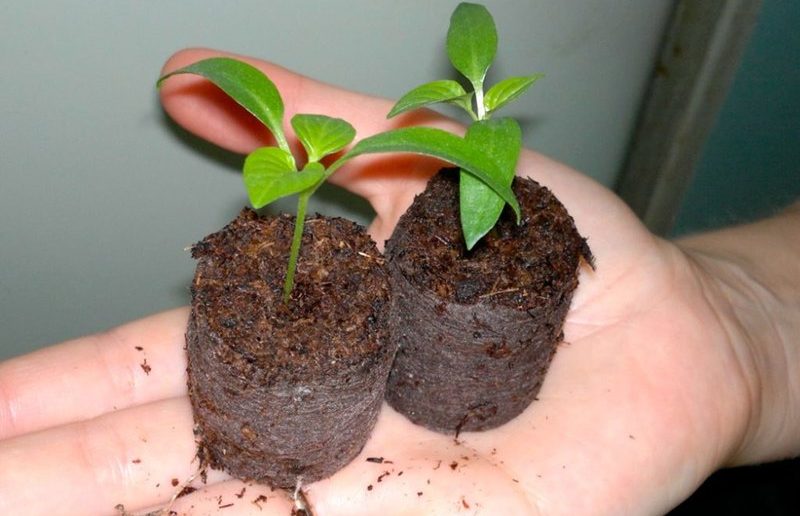

The seeds require daily ventilation for 2-3 hours. Water the seeds using the bottom watering method as the peat pellets dry out. After germination, the cylinders are placed in separate containers with prepared soil. This transplantation does not damage the roots, as they are protected by the mesh covered peat cylinder. Care for the sprouted seeds consists of watering and providing good lighting.
In cassettes
Beginners are advised to germinate peppers in individual 250-500 ml cups or trays, as this method allows for high-quality sprouts. The seed is planted 1 cm deep in the soil mixture and watered with settled water.
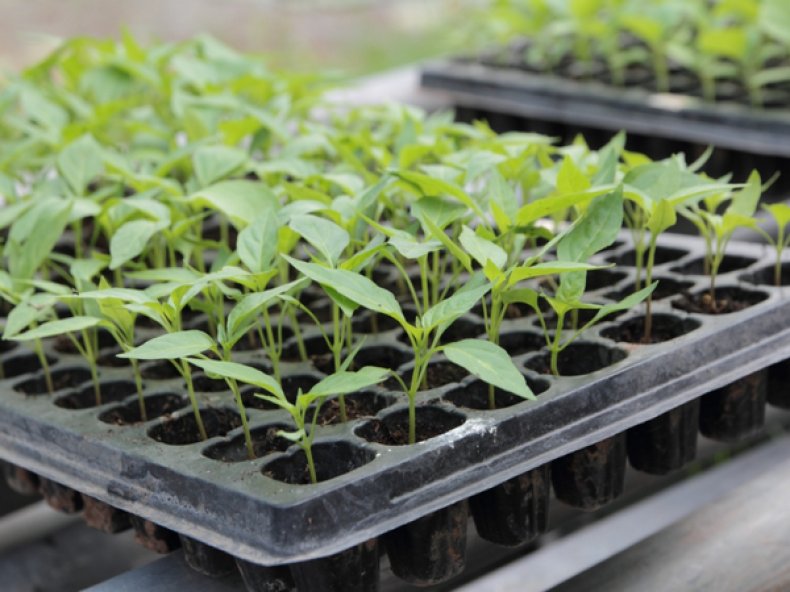

The room temperature should be no lower than 25°C. Monitor the soil level and add soil to the trays as they grow. Water the seeds bottom-up, into the tray. If growing seedlings in cups, water as usual.
In the snail
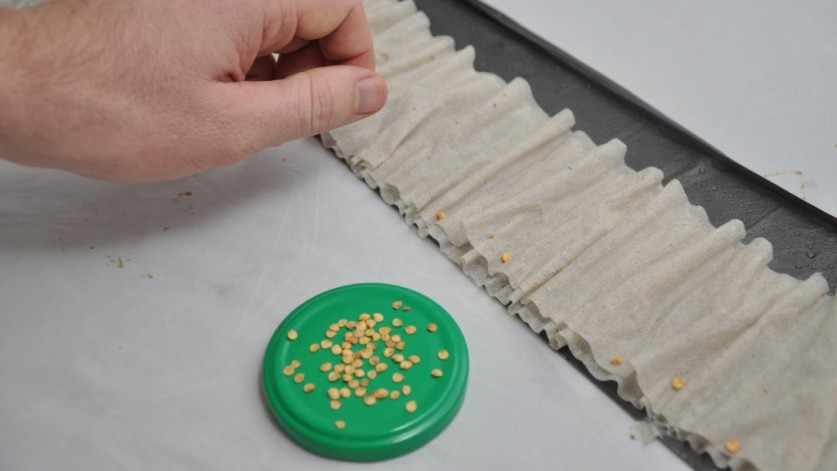
The snail roll is a relatively new method for growing seedlings, but it's already gaining popularity among vegetable growers. Its compact size makes it a great space-saver, especially if you're growing seedlings in a small apartment. You can use laminate flooring or a regular plastic bag as the material for creating the roll. The process involves the following steps:
- Place cellophane tape on a flat surface, cover it with toilet paper (it’s better to use two-layer paper) and spray it with water using a spray bottle.

It is important to remember that the edges of the bag and paper must match. - Place the planting material on the paper at a distance of about 2 cm from each other. The distance from the top edge to the seeds should be 2-3 cm;
- the seeds are covered with a layer of toilet paper and sprayed well;
- the tape is twisted into a snail, but without effort;
- The snail is secured with a rope or rubber band and placed in a container, at the bottom of which a little clean water is first poured.
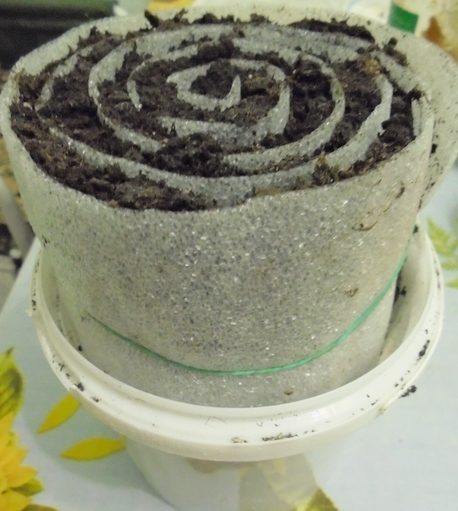

After two cotyledon leaves emerge, transplant the seedlings into the soil. Carefully unwrap the snail and cut them into individual pieces with sprouts. The seedlings are planted in a potting mix, where they will remain until they are transplanted to their permanent location.
In the boxes
To sow, take a box with fertile soil and place the seeds in it to a depth of no more than 0.5 cm. Water the soil, then cover the box with plastic wrap and place it in a warm room.
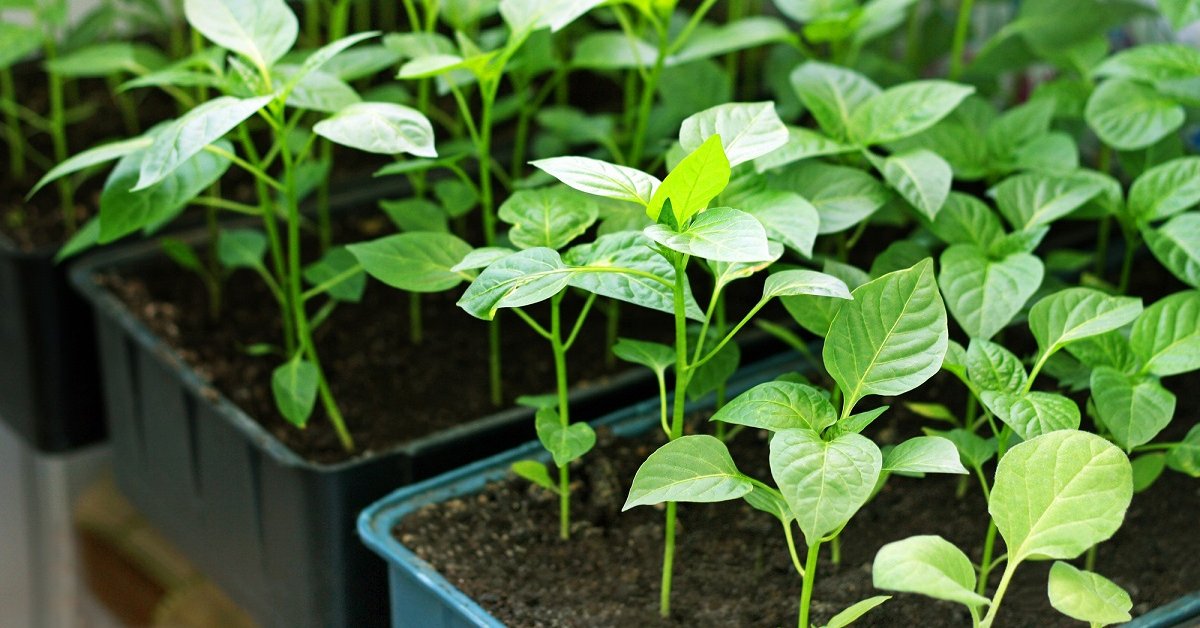

Planting seedlings and further care of plants
Pepper soil should be light, so it should be prepared a year before planting: add 5 kg of organic fertilizer per 1 m² under the previous plants, and in the fall, add 50 g of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers under deep tillage. In the first few days after transplanting, seedlings require special care, including shade and moderate watering.
In open ground
When the plant has formed 8-12 leaves, it can be transplanted into the garden. By the time of planting, the average daily temperature should be around 16°C, and the threat of night frosts should have completely passed.
Planting in open ground is done in cloudy weather or in the evening. Before planting, it's important to mark out the beds and prepare the holes.
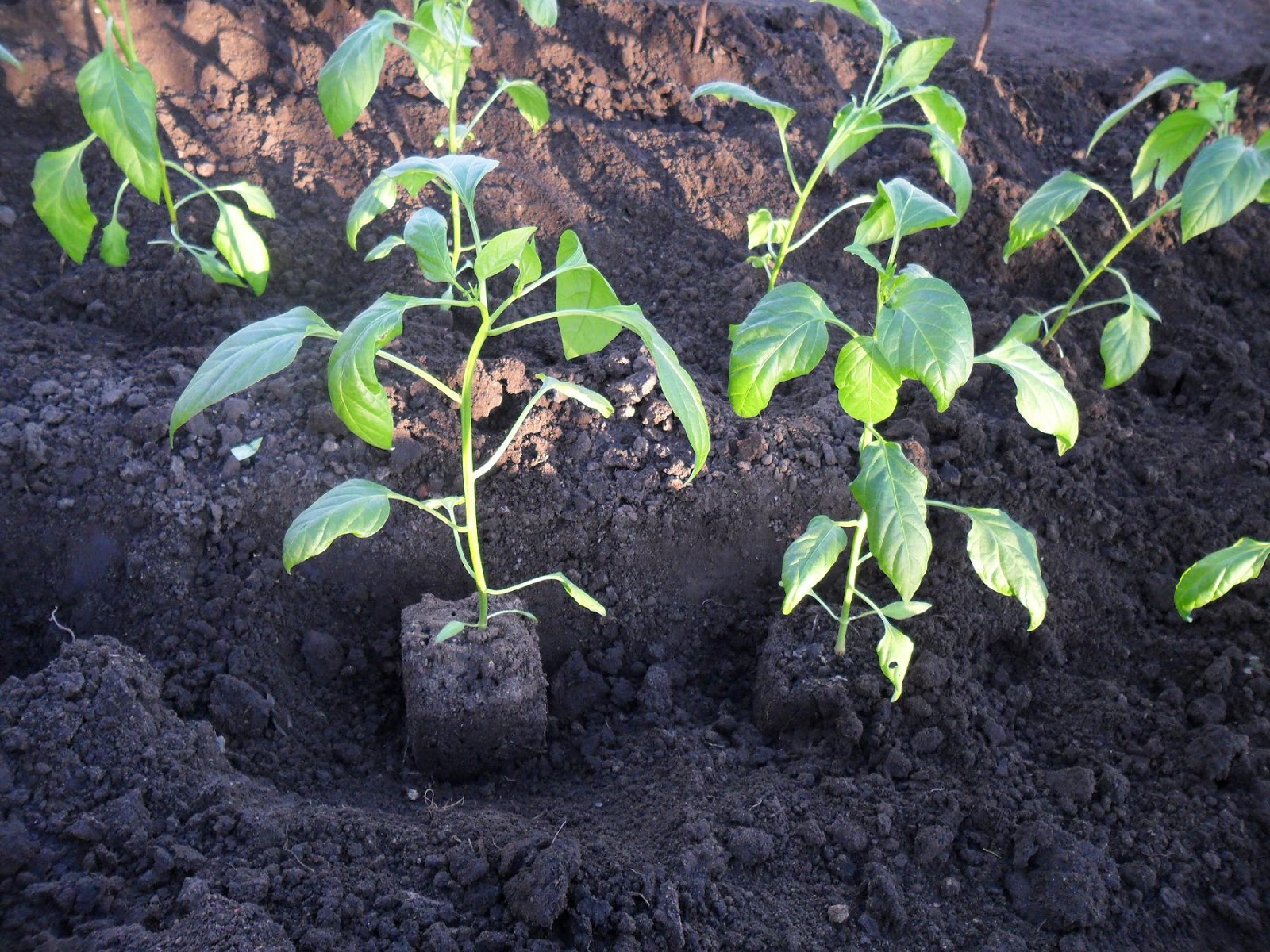

Before planting, water the plants. For prevention, it's recommended to treat the seedlings with a solution of Strela (50 g of active ingredient per 10 liters of water). The peppers are planted deep in the prepared hole so that the root collar is above ground. Water the hole, fill it with soil, and compact it slightly around the stem. After planting, cover the beds with plastic film, and remove the covering once the roots have taken root.
While the plants are adapting to their new location, it's important not to overwater, as this can cause root rot. If possible, check the soil daily and lightly moisten it near the stems (about 150 ml of water per plant). A full watering should be given 6-8 days after planting.
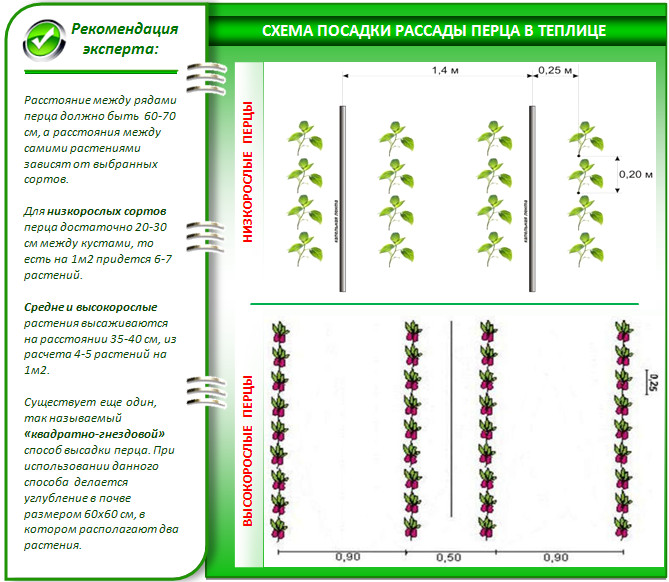
In the greenhouse
Transplanting into a greenhouse can be done after the plants are 60-80 days old (depending on the variety). If the seedlings were germinated in peat tablets, they are planted directly into the soil. If they were grown in regular pots, add a little peat to each hole before planting to help the peppers develop a strong root system. After planting, it's recommended to cover the soil with humus to help the plants adapt more quickly. Next, fertilize the soil with mineral fertilizer:
- 5 liters of water;
- 10 g calcium nitrate;
- 5 g ammonium nitrate;
- 15 g double superphosphate.
Each bush is watered generously with this solution. It is important to remember that fertilizing should be done no more than once every 10 days.
Frequently Asked Questions
Even a novice gardener can grow sweet peppers. If you follow all the recommendations, you can get not only strong seedlings but also an excellent harvest.





 Victoria Pepper: Variety Description with Photos and Reviews
Victoria Pepper: Variety Description with Photos and Reviews TOP 10 early-ripening pepper varieties
TOP 10 early-ripening pepper varieties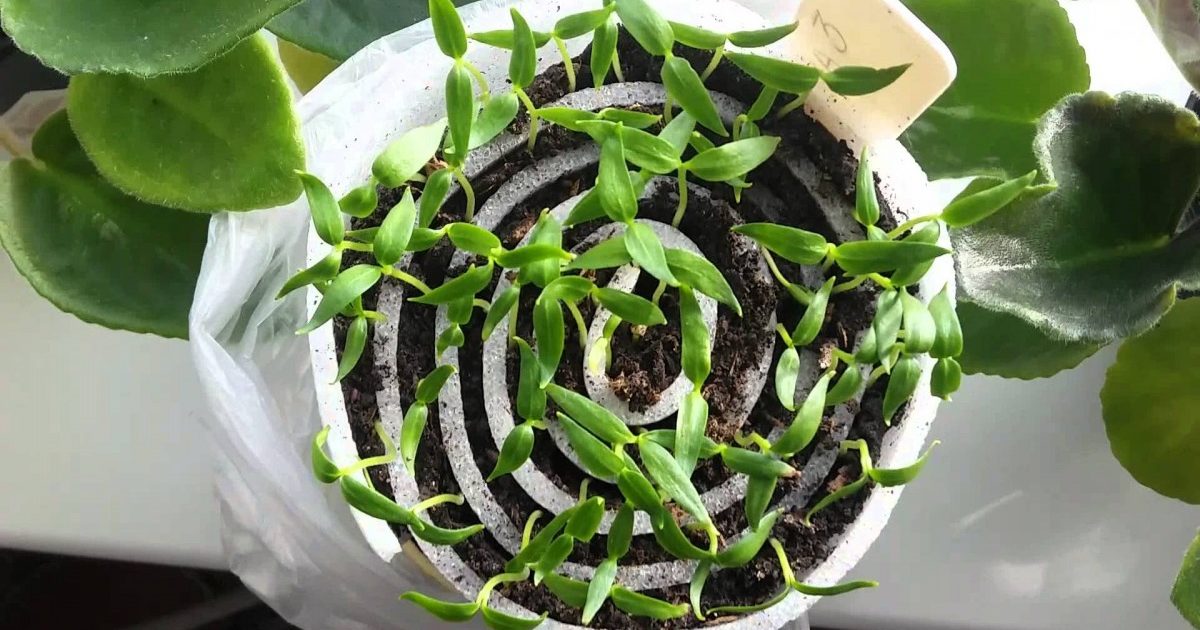 Pepper in a snail - planting seedlings without picking
Pepper in a snail - planting seedlings without picking What to do if pepper seedlings start to fall over after germination
What to do if pepper seedlings start to fall over after germination