 Without the help of a builder, you can build a heated winter greenhouse yourself, but how? There are several ways to install this type of structure yourself. They involve preparation, gathering materials, and installation, but overall, they are feasible even for those unfamiliar with construction.
Without the help of a builder, you can build a heated winter greenhouse yourself, but how? There are several ways to install this type of structure yourself. They involve preparation, gathering materials, and installation, but overall, they are feasible even for those unfamiliar with construction.
A greenhouse is an essential structure for flower and vegetable growers. Therefore, installing a winter structure will be an added benefit and give them the opportunity to tend to their plants year-round. Building a winter greenhouse that will retain heat even in cold Russian conditions is more difficult than it seems at first glance. Wall insulation and underfloor heating are essential to achieving this goal.
Selecting a building
First, you need to determine what type of building is suitable for the owner's property. Large or small? Solid or prefabricated? Depending on the available space, budget, and the owner's goals, you need to decide which characteristic is most important:
- heating type;
- functionality;
- planting paths;
- materials used;
- location of the building relative to ground level.
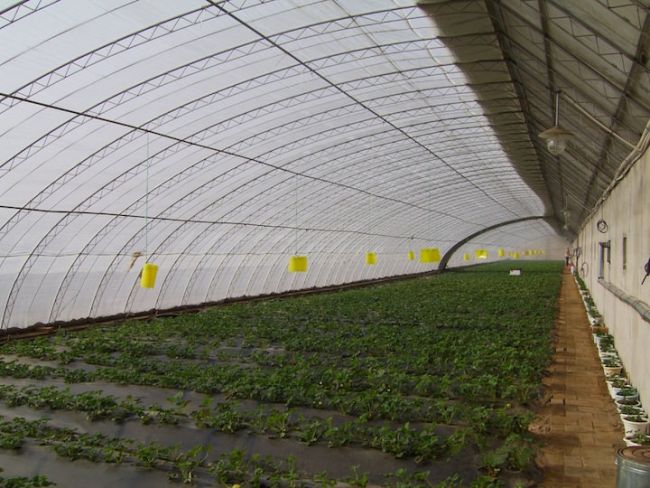
Depending on each characteristic, greenhouses are divided into several types. For example, if the owner plans to grow citrus fruits and other heat-loving crops within the structure, functionality must be high: irrigation and humidity systems must be in place. There are also greenhouses with less functionality, designed solely for northern vegetables and herbs.
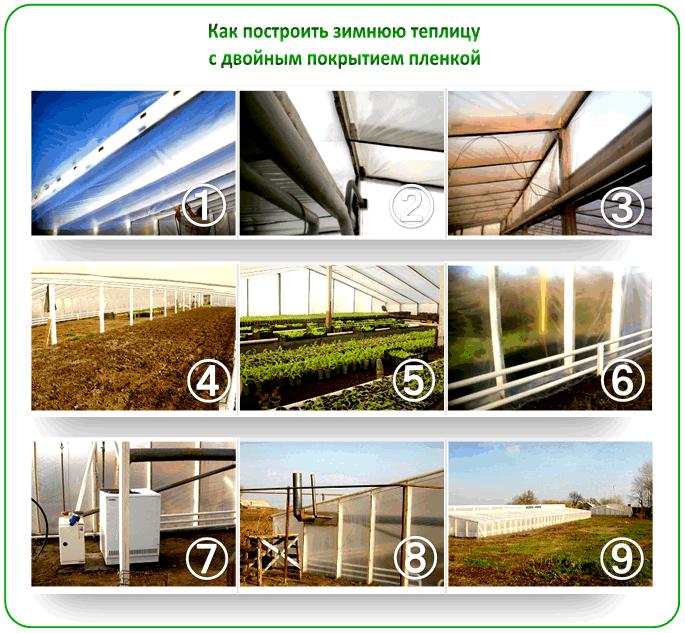

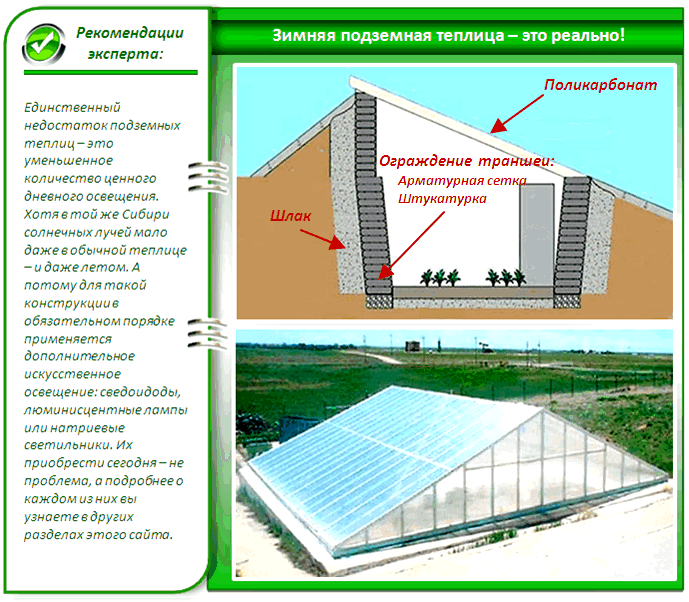
One of the most significant characteristics is the building's position relative to the ground. Structures can be partially buried in the ground to conserve heat, located above ground, or relocated to the structure of another building. The latter type is rare in Russian conditions, but when constructed correctly, it can be a functional and beautiful solution.
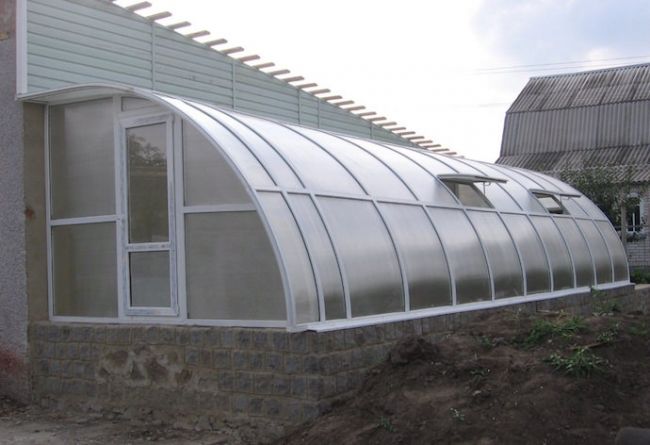
The type of heated winter greenhouse you build yourself depends heavily on the materials used. PVC is a cheap option that offers no additional benefits, while polycarbonate is considered a good thermal insulator. Glass is a traditional material that must be used with caution due to its fragility. The type of material can be chosen regardless of the shape of the future structure, which can be gable, lean-to, flat, and so on.
The choice should be based on the future builder's financial and physical capabilities. After determining the shape, materials, and layout, it's time to turn your attention to the most important part of the structure: the heating system.
Step-by-step video:
Selecting a heating system and construction site
How to build a heated winter greenhouse yourself depends heavily on the type of heating system. If brick or opaque, darkened polycarbonate sheets were used, less heat will enter from the outside, but more will remain inside.
If glass sheets are used, the greenhouse will heat up mechanically, even under the influence of the winter sun. The degree of solar influence on the greenhouse depends on its position relative to the sun.

The greenhouse must be positioned so that the sun's rays, as it travels its daily cycle, constantly hit the building's walls. Otherwise, not only will there be a lack of heat, but also a shortage of ultraviolet light, which is vital for all plant species.
The best locations for winter greenhouses are clearings, small hills, and mounds. However, elevated areas will require additional preparation to level the surface for the foundation. Lowlands are highly undesirable for greenhouses, and surrounding such structures with trees is a serious mistake.
The heating system depends directly on the location. It can be: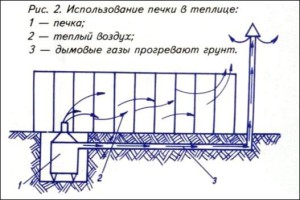
- partially dependent on the sun;
- completely independent.
Partial dependence on the daylight is expressed both in the absorption of heat from the sun through the walls, which amplify this heat, and in the collection of energy through a solar battery.
This type of construction is cheaper, as there's no need to spend extra money on high-power heating, but it's less functional. In winter, you can't rely on sunlight.
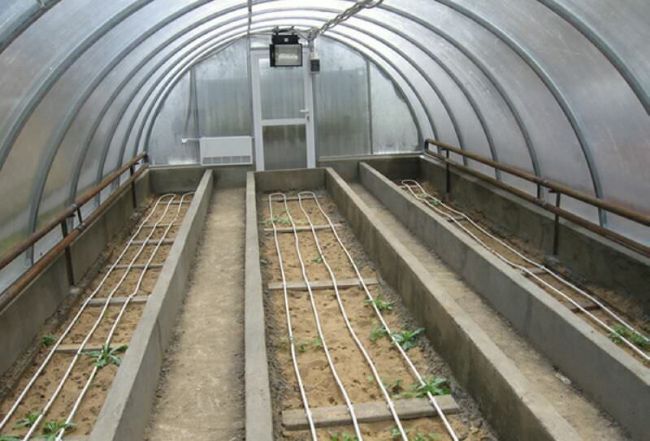
For independent construction, it's best to choose warm buildings with electric heating, which would maintain the required temperature at all times. Less popular, but equally effective, heating options include gas and hot water.
Preparation of materials
Having decided on the design, heating, and location, the owner moves on to the real work—purchasing materials and tools. For various designs, you'll need:
- frame beams (metal beams or durable plastic ones);
- transparent or translucent material for walls (polycarbonate, PVC, glass);
- finishing material for the lower part of the structure (brick, plastic, polycarbonate);
- screws, nails and other metal fasteners.
The exact type and quantity of materials is specified depending on the chosen type of construction of a winter greenhouse with heating.
[sc name=»info-attention» text=»After purchasing the materials, you need to start with the simple - let those that swell from moisture settle and take their final form, and in the meantime, start clearing the site.» ]
Preparing the area for a greenhouse
The site for the greenhouse should not be even slightly uneven, as a tilted structure will distribute moisture and heating materials unevenly. This will result in stunted growth for some plants. Therefore, before constructing the structure, level the ground using one of the following convenient methods:
- Building a wooden deck. By driving piles into the ground and installing a small wooden deck on them, you can create a stable platform for the building. Due to the high humidity around the greenhouse, this deck will need to be regularly renewed or thoroughly treated against rot in advance.
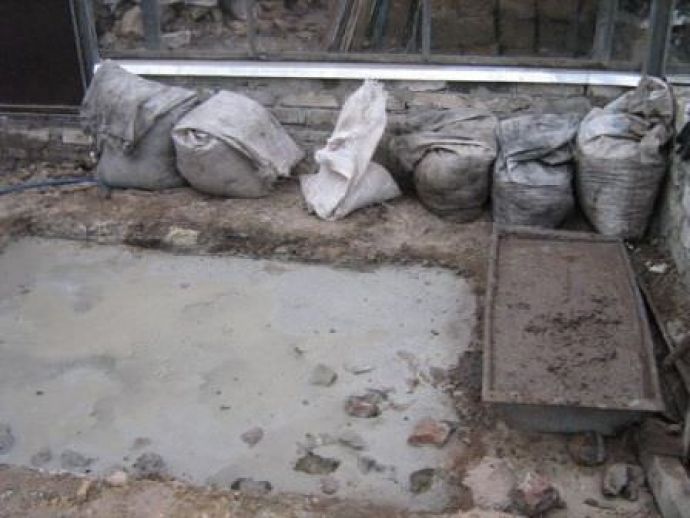
- Creating a poured concrete pad. This is the best type: durable, simple, and unaffected by temperature fluctuations and moisture. Sand and crushed stone are poured onto a leveled pad, then cement is applied on top. The concrete is left to cure for about a day, after which installation can begin.
- Simple soil leveling. This is done using a rake, shovel, and other handy tools.
The main stage: building a greenhouse
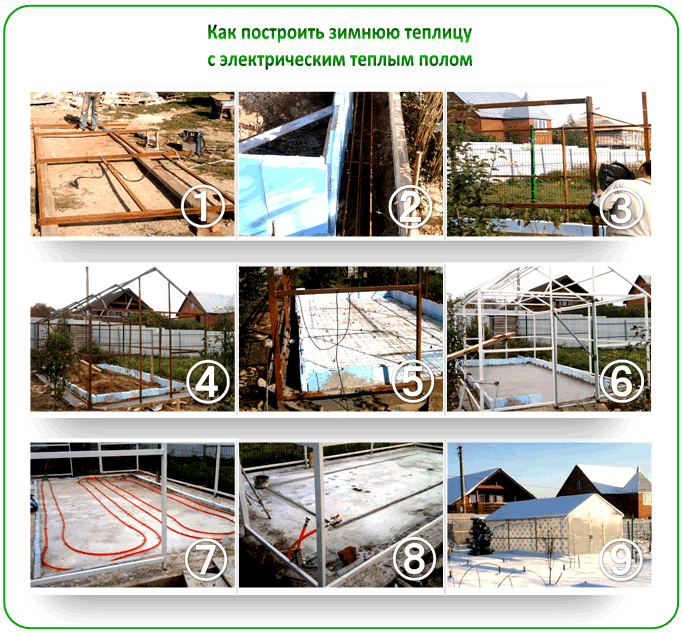
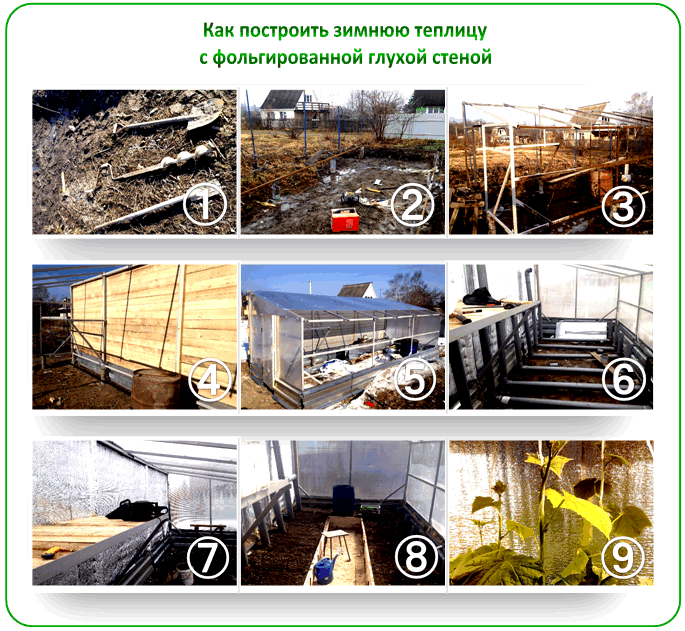
Now we can move on to how to build a heated winter greenhouse yourself. Construction begins when the space, components, and workers are fully prepared. There should be no downtime during construction, as the greenhouse must be as airtight as possible, and any long delays in installation will reduce the level of thermal insulation.
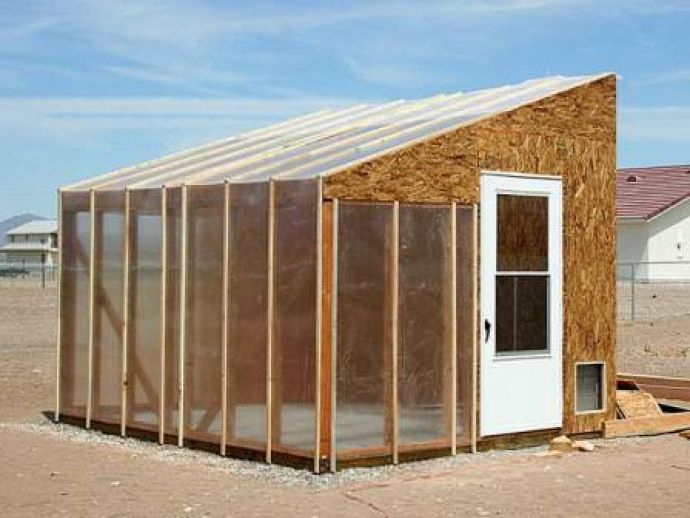
There are several types of greenhouses, but here we'll discuss the construction of the most popular—a gable-roof greenhouse sunken into the ground. The structure is finished with brick.
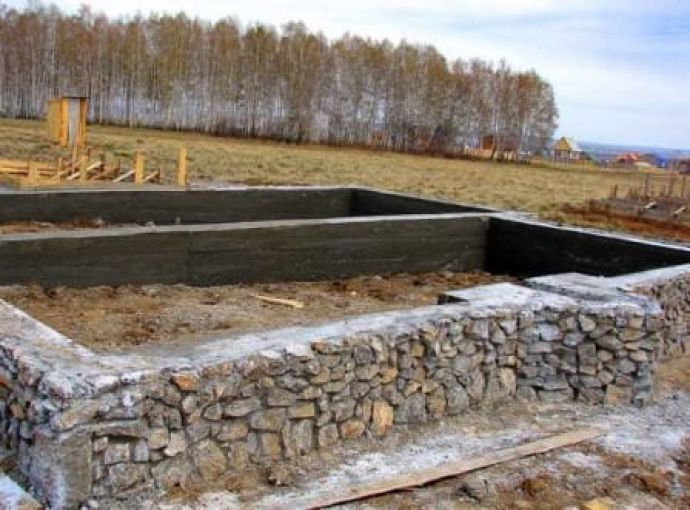
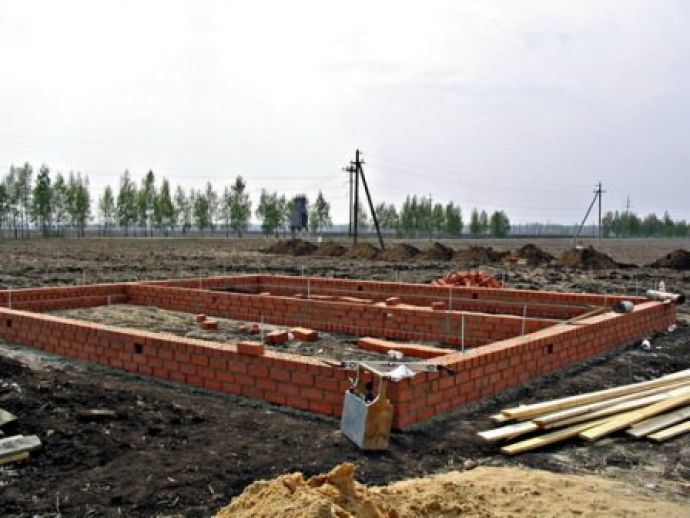
The foundation may already be prepared if the site was previously poured with concrete. If the owner hasn't done this, a strip foundation is created. It should be located deep, half a meter below ground level.
The walls of this building are also made of brick, which accounts for 60% of the structure. It is erected as a single element, approximately 20-30 cm thick.
The first layer of bricks is laid to a height of 60 cm above the ground. Windows should be installed at this point to provide natural light to the plants and create a pleasant view.
They are spaced at intervals of approximately 70 cm. Frames that will be installed inside the openings should be supplemented with vents for ventilation during warm weather.
The roof is gabled and transparent to provide additional heating. It is pitched at a 20-degree angle.
The tie beams are installed on the roofing felt, then the tie rafters are attached. The roof ridge is mounted to them. To protect the walls from water penetration through the windows, canopies are installed.
Step-by-step photos:
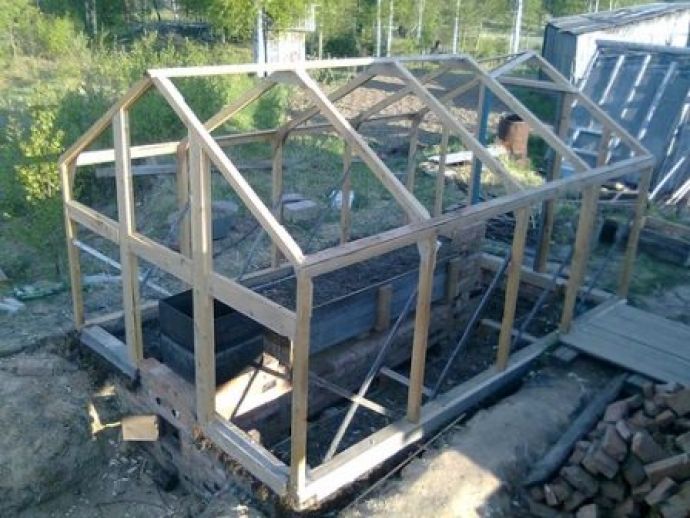
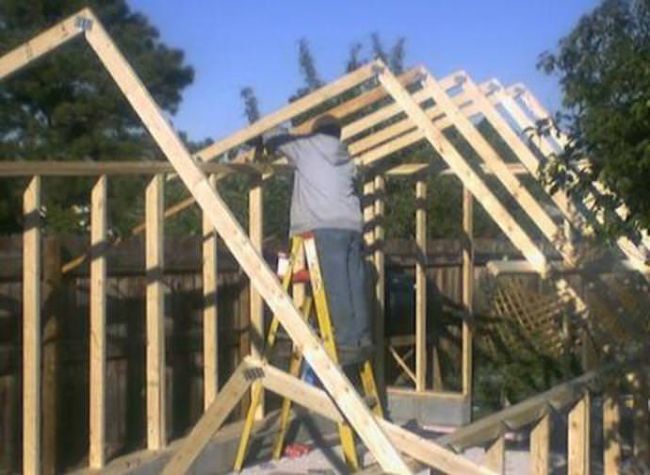





Adviсe
Building a greenhouse is no easy task. It requires special care and consistency. Professional advice will help you achieve perfection:
- To check the levelness of the greenhouse site, it is enough to use pegs and a long string if you don’t have other measuring tools at hand.
- It's best to combine heating systems: hydronic heating is as gentle as possible, while electric heating is more stable. Hydronic heating can break down during cold weather, become leaky, and fail to provide the required heat. For such cases, it's necessary to install backup heating systems.
- When constructing the structure, don't neglect helpers. They will speed up the process twice as much by holding the assembled structures and helping assemble them.
- If finances don't allow for a metal frame or expensive polymers, you can save money by switching to wood and glass. If possible, it's better to use brick for construction. It's an inexpensive insulating material that also gives your DIY heated winter greenhouse a beautiful appearance.
Greenhouse options:
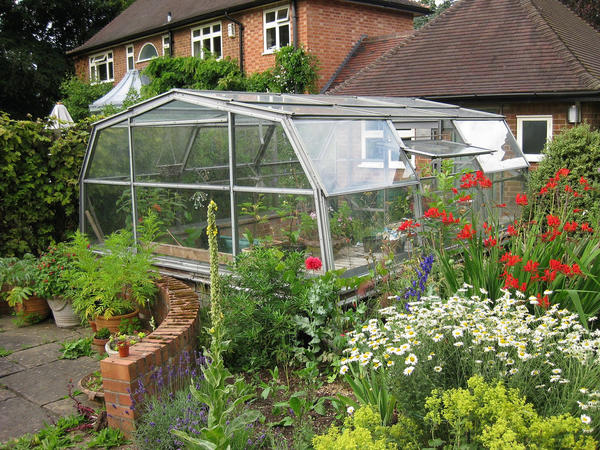
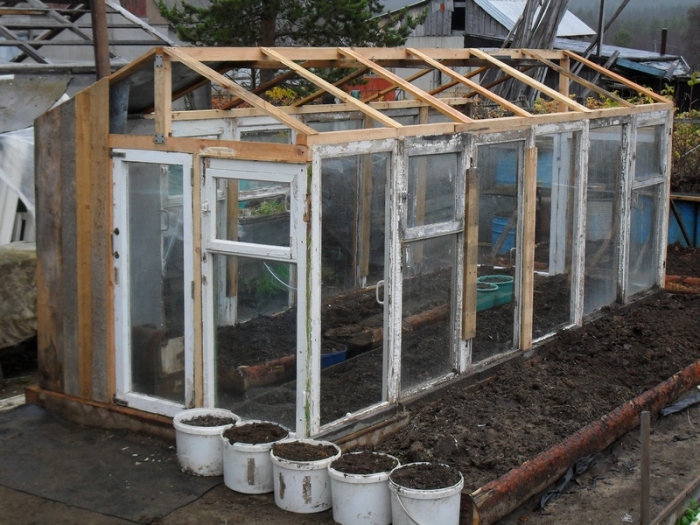







Step-by-step videos:
https://youtu.be/avZNIZ5FHGs
