Muscovy ducks are the most popular poultry species, requiring minimal care and generating maximum profits. They are large ducks with a wide, long body and short neck, with fleshy structures near the beak and a crest on their head.

Breeding Muscovy ducks are bred as pets in almost every country. This domestic, calm, and beautiful bird doesn't quack or create unnecessary noise, doesn't require special care, and doesn't require a pond. They have high growth rates and are very viable. This article will provide a detailed explanation for beginners about breeding Muscovy ducks at home.
Origin of Muscovy ducks and specifics of their maintenance
The main habitat of wood ducks (muscovy ducks) is South America and Mexico. Locals domesticated them and began exporting them to other countries. They were brought to Russia from Turkey in the late 18th century.
The name "muscovy duck" derives from the musky scent emitted by wild ducks from their head growths. In Russia, the more common name is "indoutka," referring to a hybridization of a duck and a turkey. The latter name presumably refers to its origins, namely, the Indian duck.
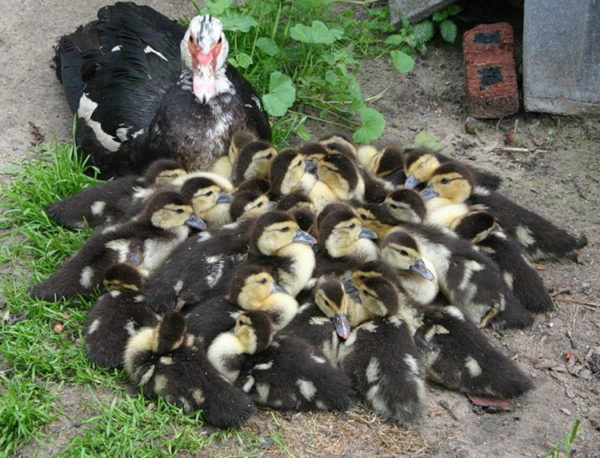

Important! Temperatures below -5°C are dangerous for birds. They can get frostbite on their feet or catch a cold, which can lead to death. Muscovy ducks prefer warmth, so cold water bodies are not suitable for them. They spend more time on the shore than in the water. They can practically do without a reservoir.
The main requirement for their maintenance is:
- Muscovy ducks need to be housed in a flock of 1 family or 8 ducklings per 1 m2.
- A warm, dry room without drafts and with ventilation, with access to the grass.
- The room temperature should be approximately 180°C. An incandescent lamp can be hung from the ceiling; if it's cold, the Muscovy ducks will warm themselves under it.
- The poultry house must be equipped with lighting of approximately 5 W.
- The floor is covered with straw or wood shavings.
- It's necessary to build a flat perch (due to the webbed feet) 20 cm above the floor. This can be boards or sloping beams.
- Feeding them is quite simple; they eat everything. Just remember to remove spoiled food from their feeders and wash them.
- The feeder should be long, approximately 5 cm per bird, 10 cm high, and 20 cm wide.
- Pour water into a baby bucket and cover it with a shallow bowl larger in diameter than the bucket. Turn it over, and the waterer is ready. The bird won't be able to bathe in it during the cold season.
- There should be no broken glass, nails or metal fragments in the walking area.
- In the summertime walking area, dig a hole and place a water container there. They'll use it for bathing and drinking.
- Ducks should be let out of the poultry house no earlier than 10 o'clock, so that there is no dew, and by this time the ducks will have left the nests.
- They need to be kept separately. They don't get along well with other birds, and as a result, they don't eat well.
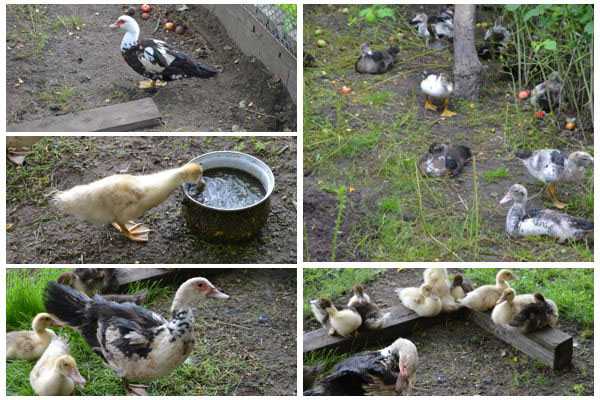

Obtaining offspring in the household
To raise offspring, you need to purchase or retain a family from a previous brood: three ducks and one drake. Create favorable living conditions and balance their diet.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Ducks incubating a brood
They begin laying eggs in March, depending on your region. Every morning, the duck greases and turns the eggs, preparing the clutch. When the nest has 15-20 eggs, the hen sits down to incubate the ducklings.

To encourage the duck to lay eggs sooner, you can add eggs from other ducks or other birds to the nest. Muscovy ducks are very responsible brood hens. They emerge for literally 5 minutes once a day to eat, drink, and bathe. During the brooding period, the mother hen loses a lot of weight and becomes weak. Ducklings begin to hatch at 32-35 days.
Hatching ducklings in an incubator
We select Muscovy duck eggs for hatching. We store them for about 17 days; these eggs have an excellent hatchability rate. They are kept at 150°C in a room where humidity is maintained.

The incubator is pre-checked, adjusted, and warmed up for about 4 hours. Then the eggs are laid, preferably in the morning.
Incubation mode
|
Indicators
Periods |
Humidity, % | Dry bulb thermometer, 0WITH | Wet bulb thermometer, 0WITH | Number of rotations per day |
| 1 week | 55-60 | 38 | 30 | 24 |
| 2-4 weeks | 40-45 | 37 | 27 | 24 |
| Week 5 | 70-75 | 37 | 32 | — |

The intricacies of breeding Muscovy ducks
Breeding Muscovy ducks is easy. However, there are some subtleties:
- During the period of incubation and raising of the chicks, the drake is isolated from the duck so that he does not crush the clutch, and subsequently the ducklings.
- The drake should be kept separate from other birds when all his ducks are occupied. When isolated from the ducks, he will fight, resulting in the death of the birds.
- If two ducks sit on the same clutch, one of them should be removed, otherwise they will steal eggs from each other.
- The first hatched chicks are taken away for a while so that the duck can sit on all the eggs, otherwise she may leave with the ducklings, leaving the clutch.
- It's important to ensure that other ducklings don't approach the mother hen. She may also follow the ducklings away from her nest.
- The duck will not sit on a new clutch until the fledged young are removed from her.
- Ducklings from the incubator are released to the adult ducks once they have fledged. During bad weather, they may be caught in the rain.

Feeding
Muscovy ducks are the most unpretentious birds. They don't need antibiotics, and their food is very inexpensive because they eat everything.
If there's a pond nearby, Muscovy ducks don't need to be fed; they feed on whatever grows. Since they're good hunters, they catch and eat frogs, small birds, snails, beetles, and they're especially fond of earthworms. During the first few days, ducklings eat only moving food. Therefore, finely chop hard-boiled eggs and sprinkle them on top of the ducklings, except for the head. The chicks collect the crumbs from their neighbor's back. The next day, they should be given a mixture of mashed hard-boiled eggs mixed with milk. While the chicks can't eat on their own, they should be fed. After two days, they begin to feed themselves.

At home, it's convenient to feed Muscovy ducks vegetables. The cheapest food is grated zucchini and ground grain in a 2:1 ratio. The ideal food for a balanced diet is wheat-corn porridge. You can also add vegetables, greens, bran, and oilcake. If you're raising Muscovy ducks for meat, you should supplement their diet with 15% ground peas, soy, or sunflower seeds. Muscovy ducks produce delicious, lean, tender meat.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Clipping the wing
Muscovy ducks are freedom-loving birds. They learn to fly very quickly. Therefore, fledged young should have their wings shortened, or more precisely, their flight feathers trimmed with large scissors. To do this, unfold the wing and trim the longest feathers in half. Adult Muscovy ducks undergo this procedure once per season.

Nesting
The nest is built in a dark corner of the coop, or several nests can be built near a wall. It's important to separate them with a partition. A box or sturdy cardboard with an open entrance for the duck can be used. The nest should be no smaller than 30 cm and no smaller than 50 cm.
Line the bottom with straw, burlap, or cotton fabric, leaving a small depression in the center to prevent the eggs from rolling out. Cover the top with a sheet of plywood or cardboard. Before incubation, the Muscovy duck hisses and lines the nest with her down.
Breeding
In many countries, people enjoy raising Muscovy ducks at home, and in Europe, they are even raised commercially. Muscovy ducks are much easier to breed than other birds.

Forming families
We begin forming a family when the drake is 140 days old. Three to five ducks from another family, approximately 42 days younger than the drake, are added to the family.

Natural hatching of ducklings
Muscovy ducks begin building their nest in March. A clutch typically contains up to 20 eggs. The incubation period is 32-35 days. Half an hour after hatching, the ducklings are removed and placed under a hatching lamp. Once all the chicks have hatched, they are returned to the mother. Muscovy ducks can incubate up to three clutches per season.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Incubator hatching of ducklings
The most effective way to raise chicks is with an incubator. During the incubation period, carefully monitor the temperature and humidity in the incubator at different stages, remembering to turn the eggs.

Raising chicks
From day one, hatching ducklings are kept in a box under an infrared heating lamp. The bottom of the box is lined with straw or sawdust, which should be changed daily. After 14 days, the ducklings are separated from the drakes. This is done by examining the ducklings' cloaca for sexual characteristics. After this, they can be let out into the wild, but be careful not to bathe them until they are one month old.
From the first day of chicks they feed Boiled, mashed egg, and milk is added on the second day. After this, they are already feeding independently, and bran and greens can be added to their diet. On the fourth day, meat scraps are introduced into the diet. After 10 days, they can be fed boiled potatoes. It's important to add vitamins to the water for the first 5 days.
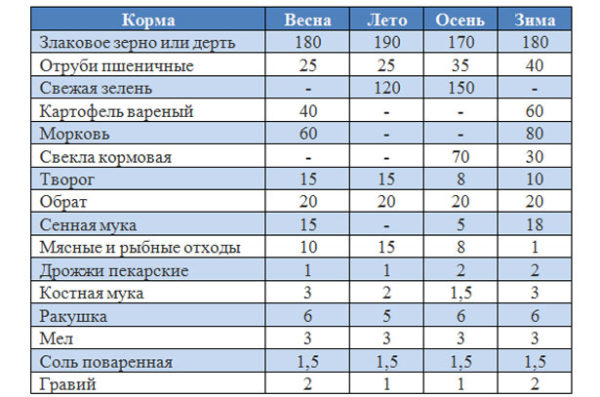
Diseases and treatment of Muscovy ducks
Muscovy ducks have strong immune systems; they generally don't get sick and don't require antibiotics. However, parasites and certain diseases do affect them. The key is to detect the development of an illness and initiate treatment promptly, separating the sick bird from the rest of the brood.
Main diseases and parasites and their control:
| View | Signs and causes | Treatment |
| feather eater | Feather loss, restless behavior | Dry bath of feed sulfur with sand |
| Goiter catarrh | Swollen crop, does not eat, open beak with fluid and sour smell | Rinse with a weak soda solution with ampicillin |
| Vitamin A deficiency | Eye disease |
In summer: carrots, pumpkin, milk. In winter: silage with beans, beans or vitamin A supplement |
Preventing diseases in Muscovy ducks is not difficult: you need to regularly change the litter on the floor and clean the feeders and waterers in a timely manner.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tlEKzh2FZ4A
Benefits of growing
For beginners, it is important to know whether breeding Muscovy ducks is profitable or not before purchasing them.
- No special conditions are required.
- Feeding is unpretentious and economical in summer.
- Survival rate is almost 100%.
- They gain weight quickly.
- Quiet, calm, not aggressive.
- Very tasty eggs and lean meat.

Sale of meat and eggs
This duck breed is often bred for sale. Duck farming as a home business only becomes profitable after three years. See the video above for more details.
The Muscovy duck's nutritious, appetizing meat and tasty, large eggs are more expensive than those of regular poultry. Sometimes demand exceeds supply. Therefore, business planning should be based on consistent poultry and egg sales.

Tatiana
The article says 180°C is the recommended temperature for storage. That's probably the baking temperature.
. ? ??????