Many people associate cacti with deserts, hot sun, rocky terrain, and constant drought, which leads to numerous mistakes in caring for these plants. Furthermore, each individual species has its own characteristics and requires specific growing conditions. In reality, it's not that complicated, and any cactus can become a true home decoration if you research the different types of these houseplants and determine the climate and conditions typical of their native habitat before purchasing.
The homeland of cacti and the history of growing indoor flowers
The existence of cacti has been mentioned as far back as Aztec times: scientists have discovered images of cacti-like plants on rocks. Such rock art, according to experts, dates back 50 million years.
Scientists have discovered that the Aztecs used the plant for medicinal purposes, ate it, and used it in rituals to connect with the afterlife. Experts claim that this species has not undergone significant structural changes since ancient times. Ancient varieties are known as Melocactus, Opuntia, and Cereus.
Furthermore, in ancient Greece, there were small, spiny plants called "cacti." The plants received their modern name thanks to Carl Linnaeus, who brought a new species from America to Europe in the 16th century. At the same time, the first collection of cacti was assembled and exhibited in London by the apothecary Morgan. And in 1958, Theodorus Tabernaemontanus published a book with a detailed description of cacti varieties.
The first mention of the cacti's origins dates back to the 16th century. It was during this time that reports of unusual plants appeared in South America. South and North America are considered the birthplace of this now-houseplant.
Since their first mention, these plants have adapted to habitats on different continents. The main characteristic of this species is its ability to survive without water for several years thanks to its ability to store moisture. The water reserve inside the flower's body is created by synthesizing the sap of a mucilaginous structure.
Furthermore, the plants have a special leathery shell that minimizes moisture evaporation in hot conditions. There are also subspecies—epiphytes—that inhabit forests with constant rainfall. In the wild, cacti reach large sizes and can form entire forests.
Popular types of cacti
Since their discovery, cacti have gained widespread popularity and spread across all continents, resulting in the formation of four large families:
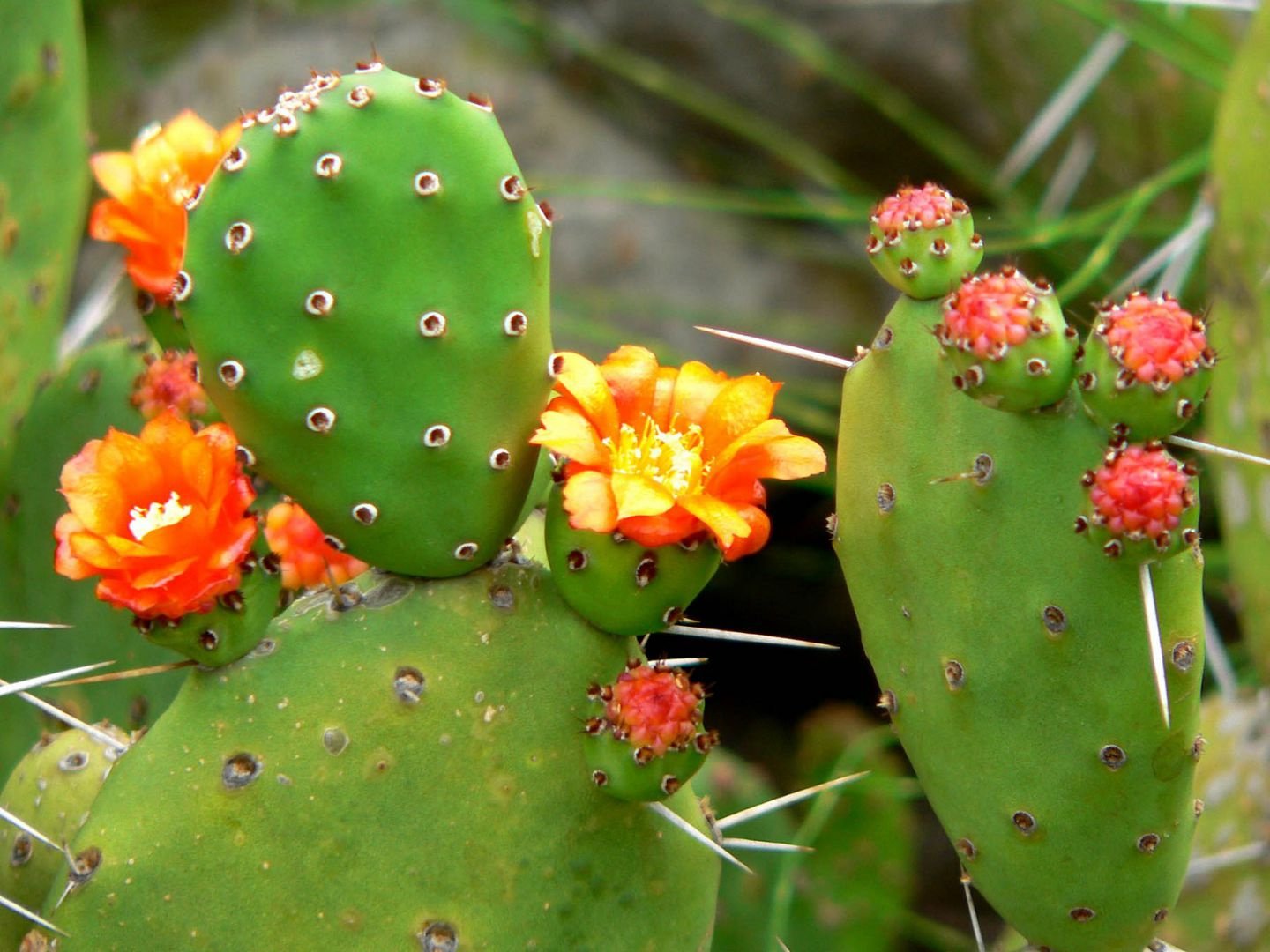
- Opuntia cacti are considered one of the most numerous families, comprising approximately 16 genera and 500 species. Their distinctive feature is the presence of a glochidia—a small spine with a hook-like tip that easily clings to an object when in contact with it.
This mechanism ensures the species' spread and reproduction. Succulent stems and reduced leaves at the top of the plant are also distinctive features of this family. Opuntia flowers have vibrant, rich, and varied hues. Each species blooms individually; some may flower year-round, while others bloom only in summer or not at all.

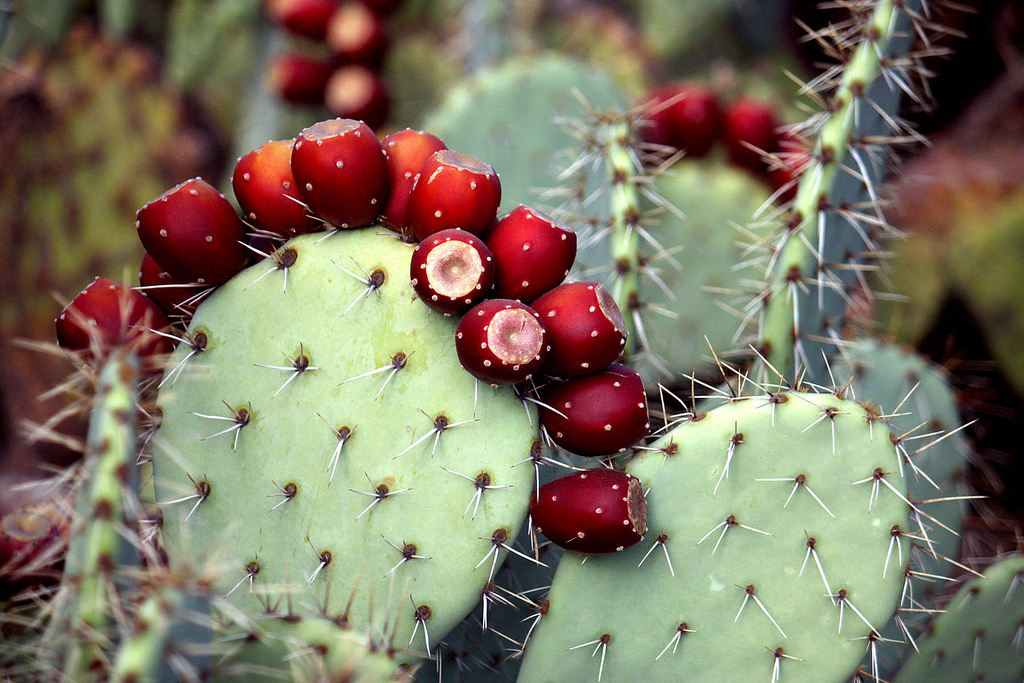
Prickly pear In place of the flowers, large, round fruits, completely covered in spines, form. Inside, the fruits are soft and juicy, containing seeds. If harvested correctly, they can be eaten. The fruits of the Opuntia family are often called prickly pears. Opuntias are widespread in Canada, the United States, Western India, and Patagonia.
- Mauhyeniaceae is a subfamily native to Pantagonia. This family was previously classified within the Opuntiaceae, but after extensive research, it was decided to place them in a separate genus due to significant differences. Mauhyeniaceae comprises only two species.
Cacti have cylindrical stems with small leaves. Cacti in this family grow rapidly, forming dense thickets. Mauchienaceae tolerate low temperatures well and can be grown outdoors in pots year-round. A distinctive feature of this family is the absence of flowering plants.
- The Pereskiaceae family comprises 8 species and 4 subspecies. The family is characterized by individuals growing from 1 to 8 meters in height, with some species reaching up to 10 meters. The stem of this cactus is woody at the base and densely covered with spines. The leaves are round, elongated, fleshy, arranged alternately on the stem, and attached by a small petiole. During periods of drought, the leaves fall off.

Pereskia At the top of each shoot are peduncles. These can be spike-shaped or single flowers. Coloration varies. Edible, berry-like fruits form in the place of the flowers. Pereskiaceae grow in South America, West India, and Mexico, where tropical climates prevail.
- The Cactaceae family includes all remaining species. A distinctive feature of this family is the complete absence of leaves or the presence of rudimentary leaves. Unlike Opuntiaceae, cacti lack glochidia. The vegetative part is spherical or cylindrical.
The family includes several epiphyte species with vine-like stems, as well as xerophytes whose shape varies widely. They are native to South America and western India and are widely grown as ornamental houseplants.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Rare and exotic species
In addition to the widespread representatives, there are also those that are rare and have an unusual appearance.
Navajoa is a flower native to the United States, divided into three species. Its main characteristics include a wide, green stem with a bluish tint, adorned with cylindrical papillae. The flowers are small and tubeless.
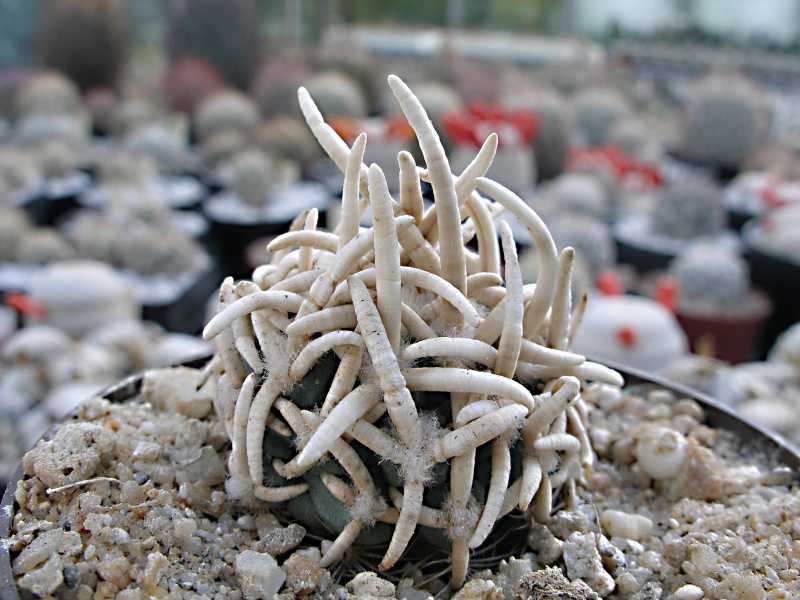

The Encephalocarpus is a flower native to Mexico that resembles a conifer cone. The stem is rounded, about 10 cm tall, and has a pubescence of white hairs at the top. The stem has papillae arranged in a spiral pattern. There are about 10 spines, and the flowers are small and appear at the crown.

Creating natural conditions for indoor cacti
Although the flowers are native to America and are adapted to drought, it is necessary to know some nuances in caring for the plant to bloom regularly and not get sick.
Lighting and temperature
During warm periods, it is advisable to place plants on a loggia or veranda.
These plants thrive on plenty of light, so it's recommended to place them on sunny windowsills, and use lamps if the light is insufficient. Experts recommend south- and east-facing windows.
 You may be interested in:
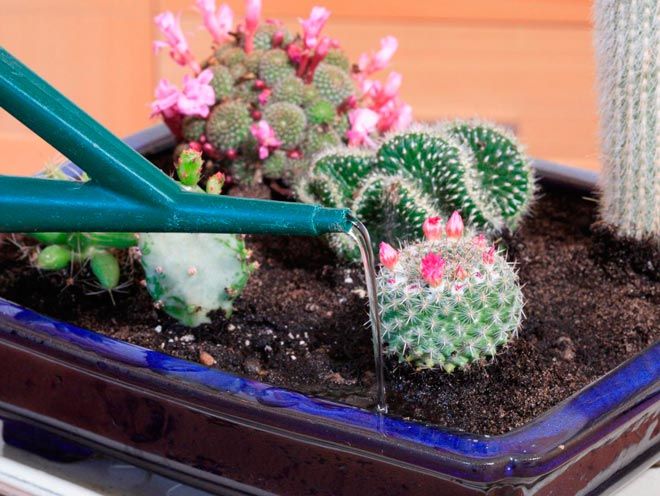
You may be interested in:Watering and fertilizing
It is recommended to water the flowers with melted snow or rainwater. If this is not possible, filtered water is preferred. In spring and summer, water daily or every other day. In autumn, watering is reduced to once every seven days, and in winter, once every two weeks is sufficient.

For top dressing, choose fertilizers with increased levels of nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, and calcium. Top dressing is applied during the growing season, that is, in spring and fall. Experts do not recommend fertilizing plants with damaged roots.
Transplantation and propagation
When repotting, it's crucial to choose the right pot size. To do this, remove the plant from its container and examine the root system. This will determine the size and shape of the pot. It's not recommended to buy metal containers, as corrosion can damage the plant.
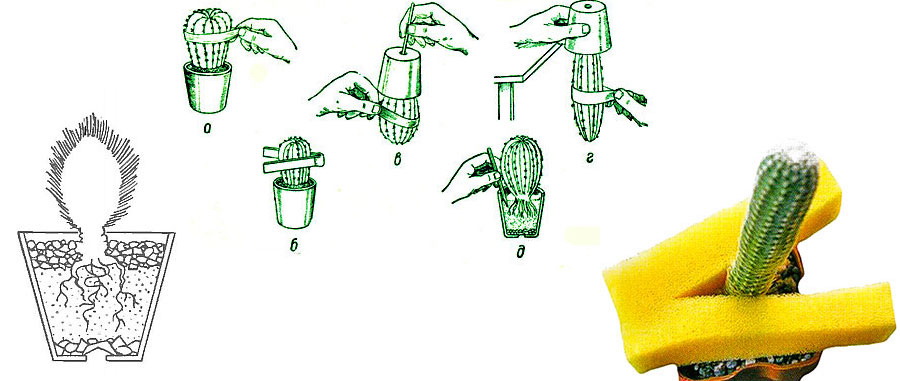
The soil should contain leaf mold, old greenhouse soil, sod, clay soil, humus, sand, and crushed charcoal. Furthermore, the soil's pH should not exceed 6.0. The pot should have drainage holes to prevent excess water from stagnating during watering.
The most common method of propagation is by cuttings and offsets. To do this, the offset or cutting is separated from the mother plant and disinfected. The offset is placed in a container of water. Once roots appear, it is allowed to dry for several days and rooting begins. To do this, prepare a substrate rich in sand and plant the offset without covering the root collar. The pot is placed in a cool, dark place for several days. After rooting, the young plant is acclimated to normal conditions.
Diseases and pests
The most common fungal diseases are wet and dry rot. Initially, the disease causes few symptoms, developing internally and gradually spreading to the outside. It is caused by overwatering. Treatment involves pruning away the damaged areas and treating the plant with fungicides.
Common parasites include spider mites, nematodes, and scale insects. Their presence can be identified by the presence of larvae and beetles on the vegetative parts. Broad-spectrum insecticides are used for treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
The most common questions are about the growing conditions, such as in the plant's native habitat:
Cacti are widespread plants popular for their unique appearance and low maintenance. This genus is diverse and widely used as an ornamental houseplant.


















 The most fashionable flowers of 2025
The most fashionable flowers of 2025 Large ceramic pots and planters: what's the difference and how to choose the right one for your plants?
Large ceramic pots and planters: what's the difference and how to choose the right one for your plants? Beauty and Ease of Care: Top 10 Most Beautiful and Easy-to-Care Indoor Flowers
Beauty and Ease of Care: Top 10 Most Beautiful and Easy-to-Care Indoor Flowers Top 15 Flowers That Last Long in a Vase
Top 15 Flowers That Last Long in a Vase