Forests are a national treasure of Belarus, occupying a third of its territory. The forests here are mixed, rich in diverse plant species. It's no surprise that mushroom picking is a special pastime for local residents. Ecotourism, focusing on mushrooms, is quite popular in this region. Edible mushrooms in Belarus delight mushroom pickers almost all year round, and photos and descriptions are worth studying before planning a picking trip.
Spring varieties of edible mushrooms
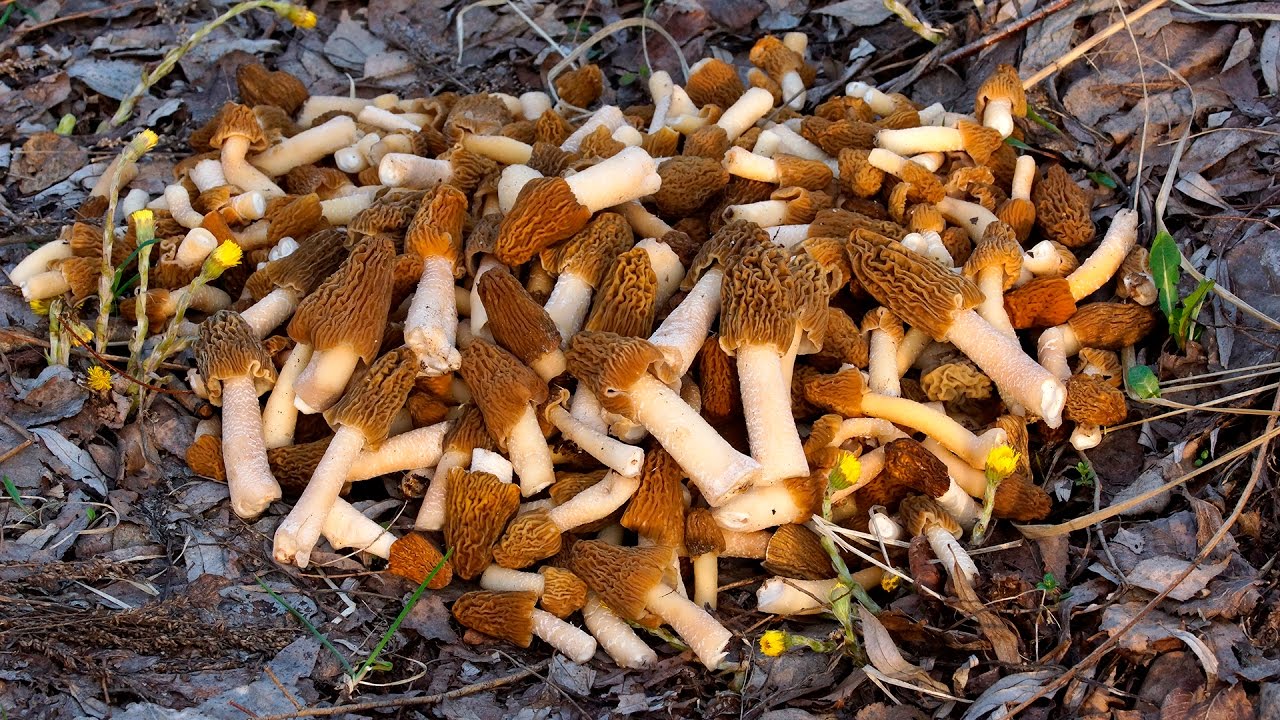
Spring mushroom picking can begin as early as April. The first specimens to be found in spring are gyromitra and morels. They have a bizarre, unusual shape. The following species are distinguished:
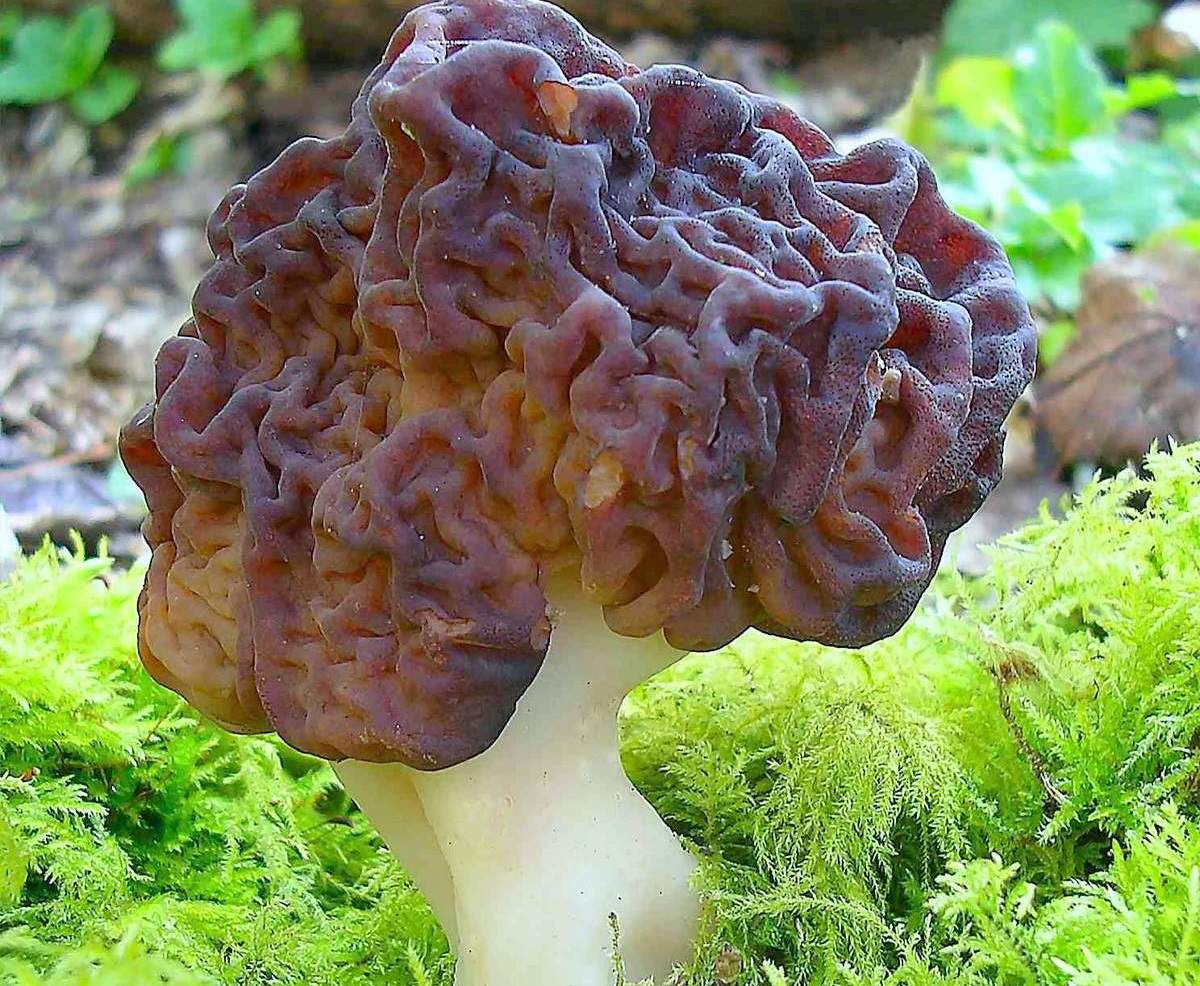
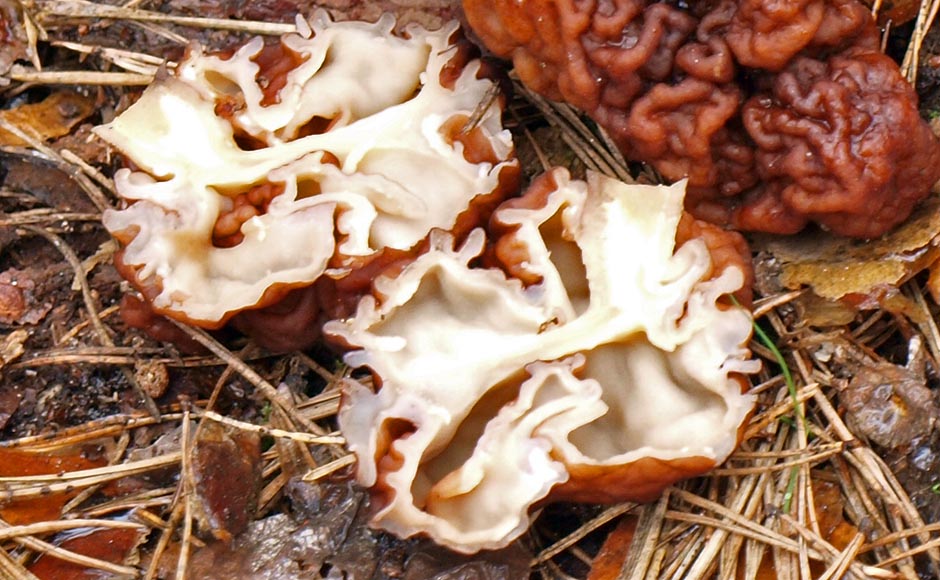
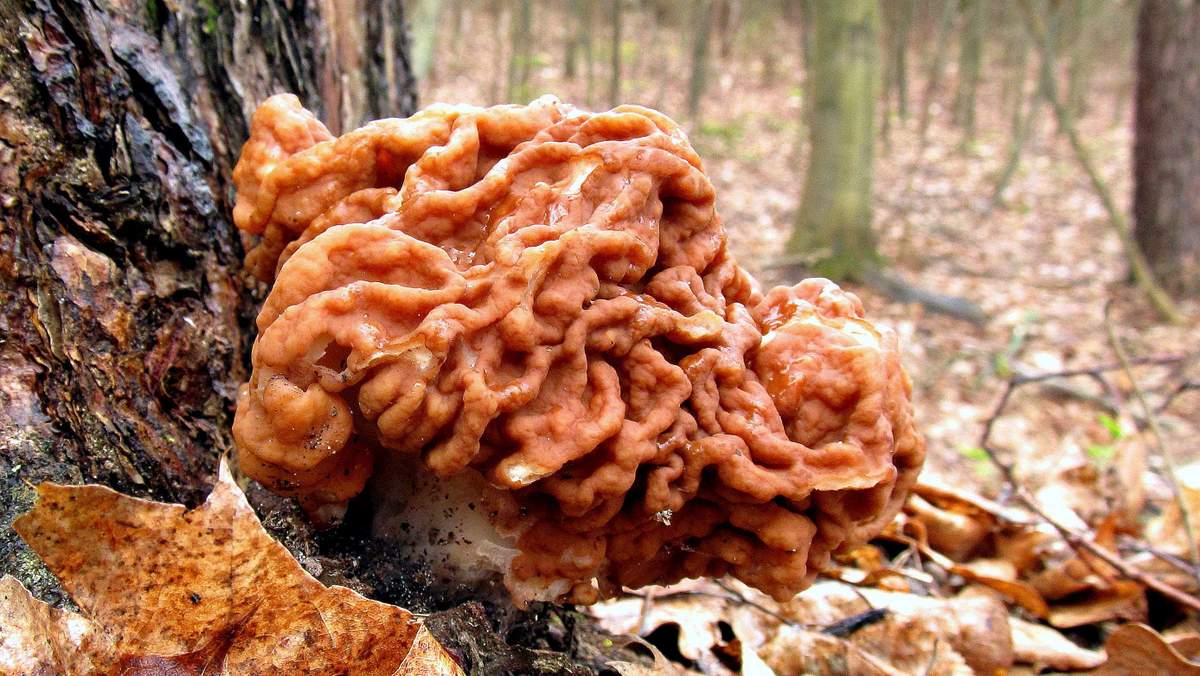
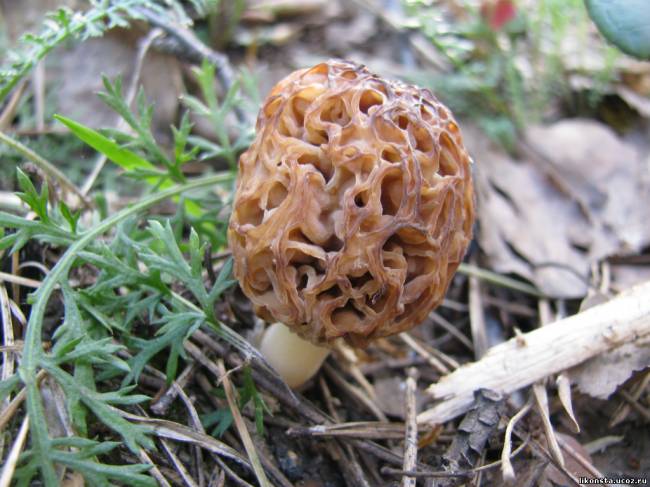
- Morel mushroom. In Western countries, eating morels is not recommended because they are toxic. In the former Soviet Union, they are considered conditionally edible. Experienced mushroom pickers collect morels in the forests of Belarus, observing all safety precautions. This species has a hollow cap, brown or russet, shaped like wavy folds, 10 centimeters in diameter.
The small stem, up to 3 centimeters tall, is also hollow, wrinkled, and white or beige. From late March to early April, the morel has a fresh, mild aroma. However, as May approaches, it develops a strong mushroomy odor. It's important to properly prepare morels for consumption, as they contain a toxic substance called gyromitrin. There are two ways to process morels.
The first is to boil them for at least 30-40 minutes in plenty of water. Afterward, drain the broth and rinse under running water. Next, pour clean water over the morels and boil for another 15-20 minutes.
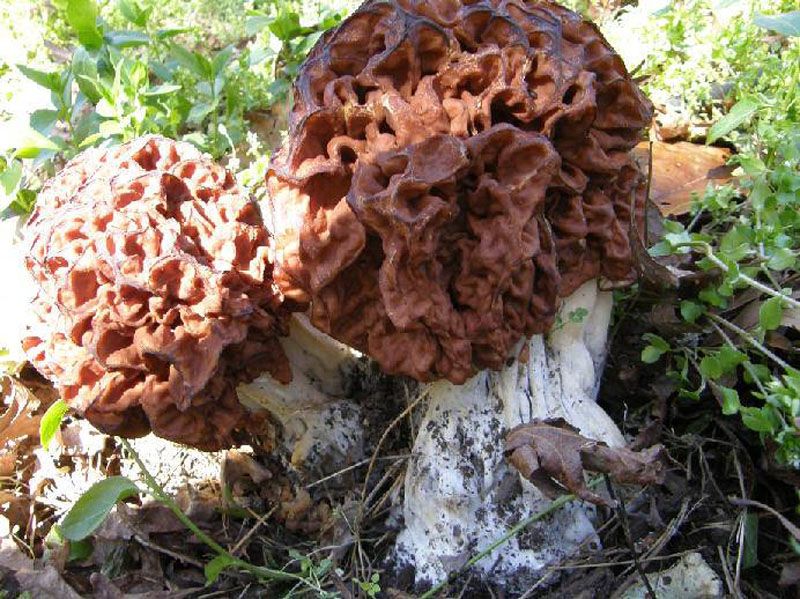
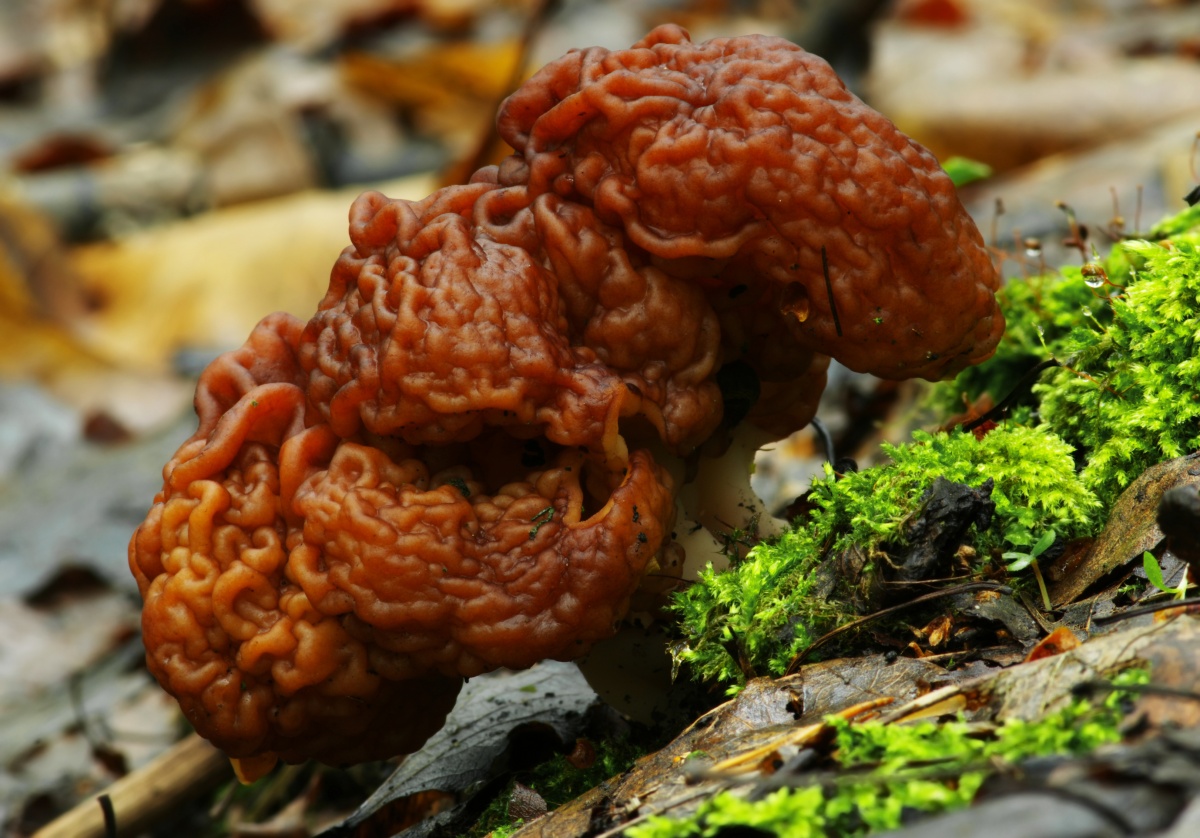
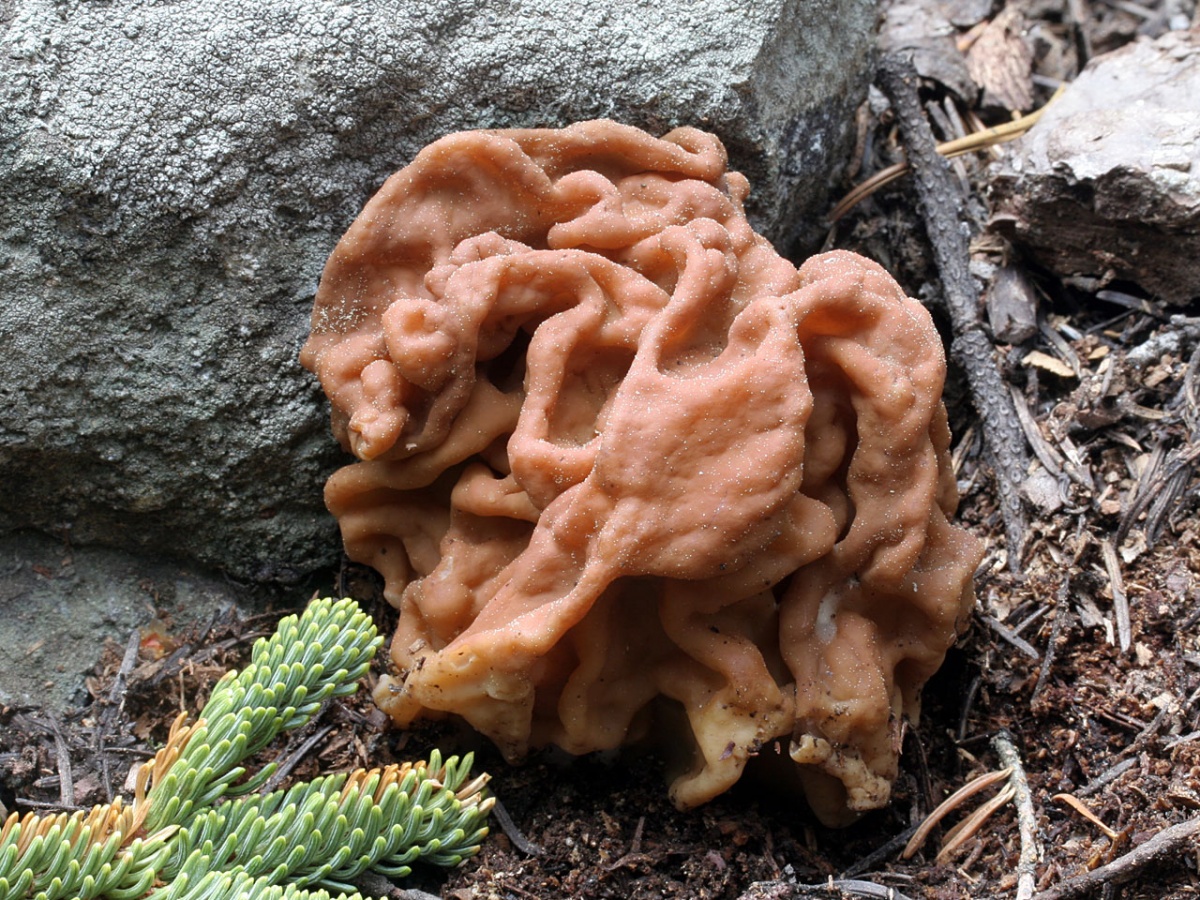
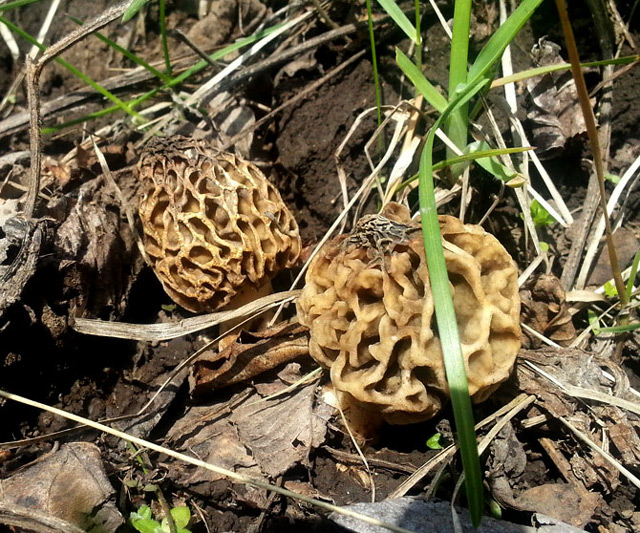
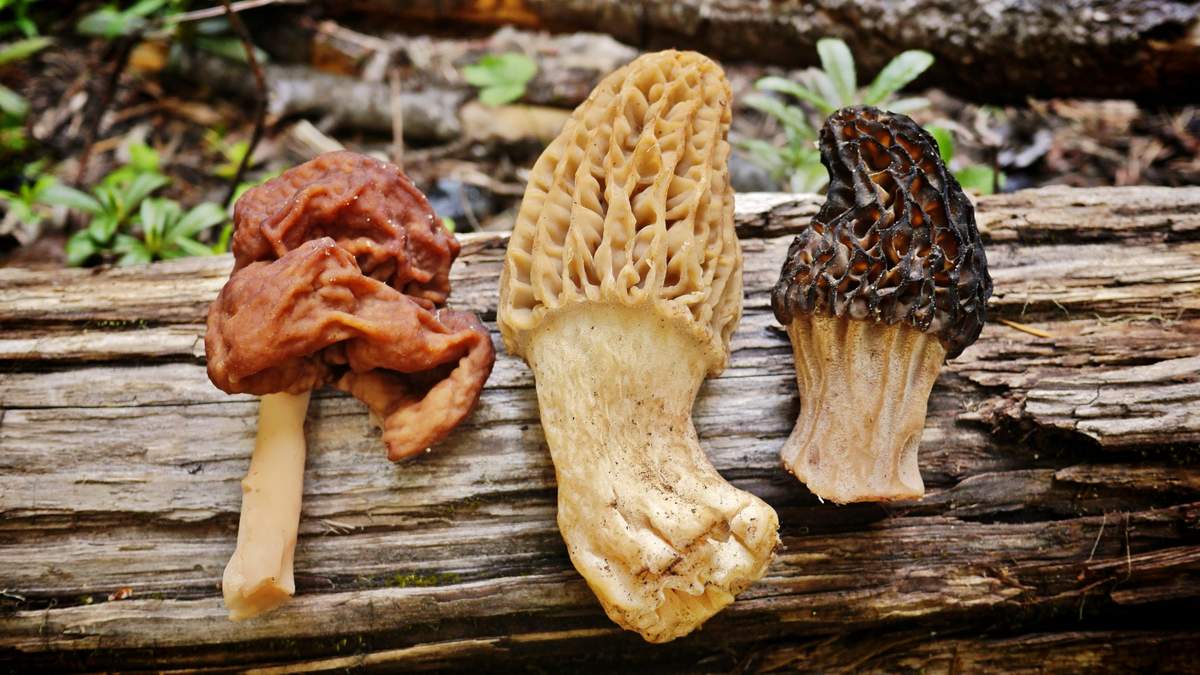
Advice!A more reliable method of treatment is prolonged drying at high temperatures or at least 6 months in the open air. This will completely evaporate the toxin. - The giant morel. This species is very similar to the common morel and grows at the same time of year. The giant morel's cap is less wrinkled, has a lighter color, and reaches a size of about 30 centimeters.
They also have different spore structures. Giant morels grow in both coniferous and deciduous forests. The method for processing this mushroom is the same as for the common morel. This mushroom is often used to make mushroom powder.
-

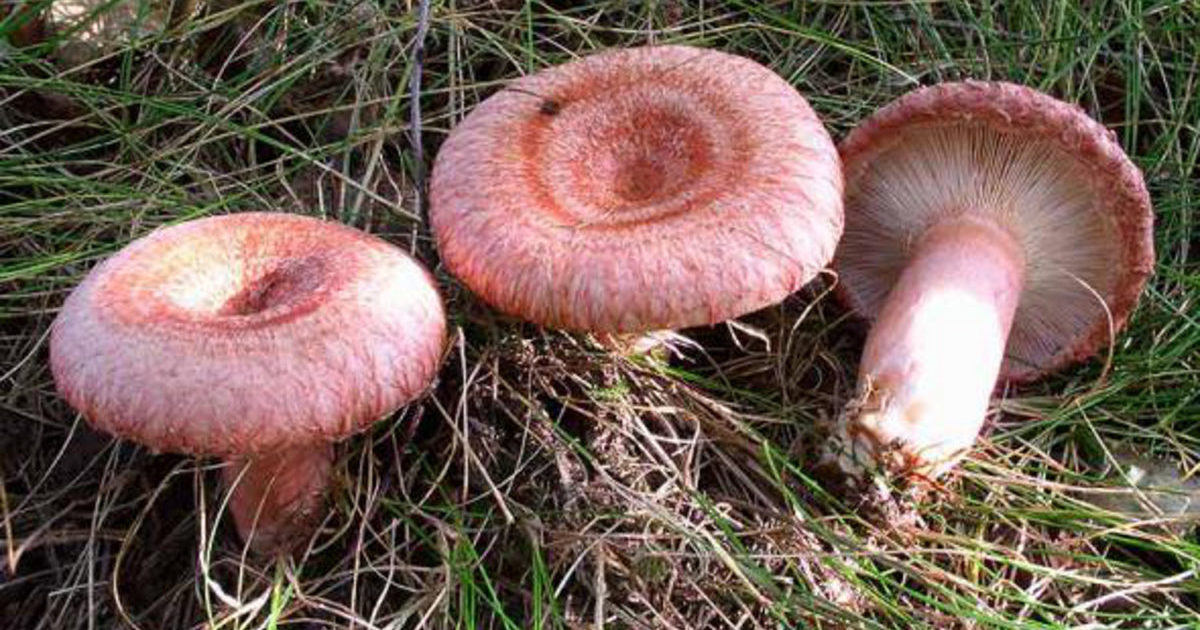
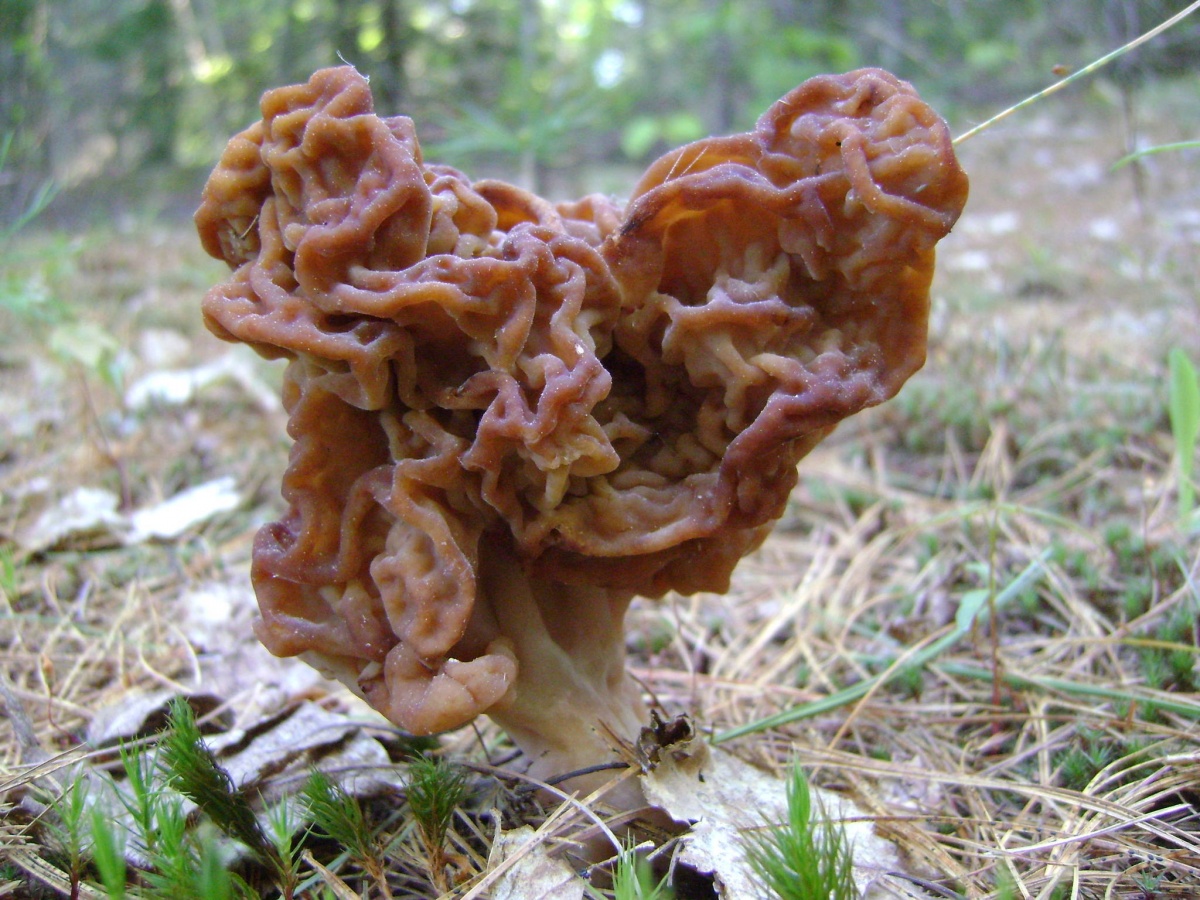
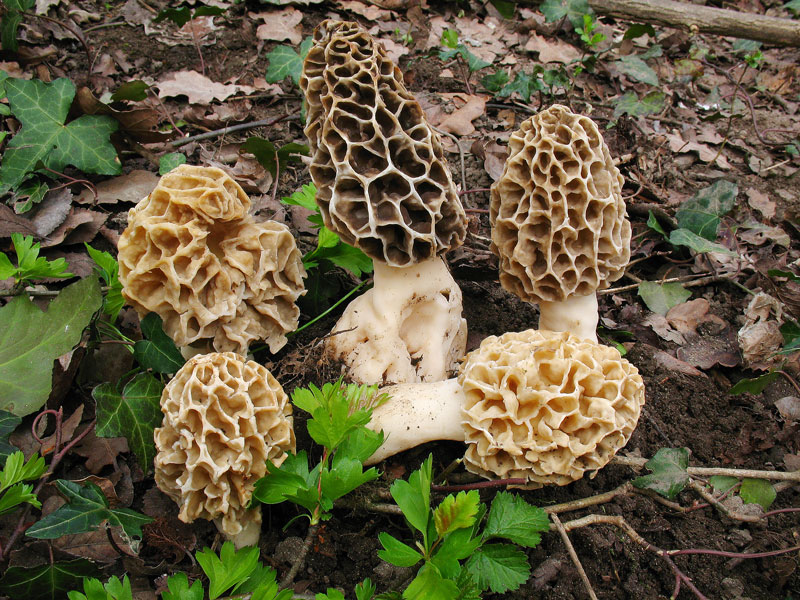
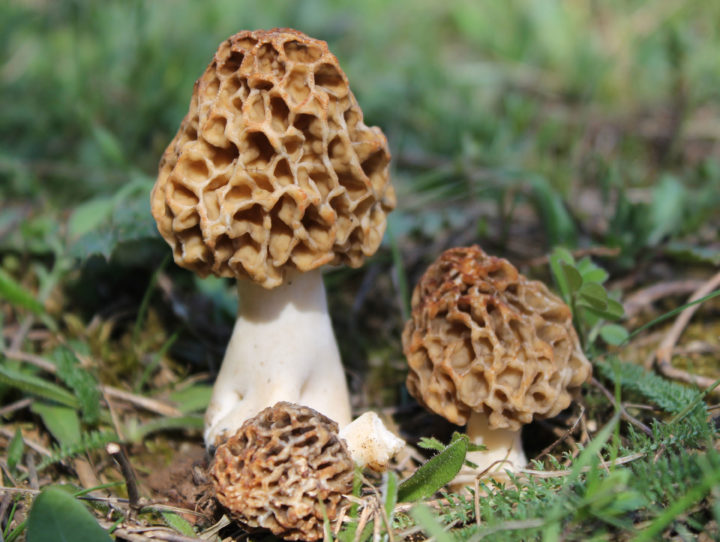
Giant morel - Morel mushroom. This species is completely safe and edible, unlike similar gyromitra mushrooms. Morels may contain a small amount of toxin, which is easily removed completely during processing. They are lightweight due to their hollow interior. The cap is elongated and ovoid, sometimes flattened or spherical. The cap can reach 8 centimeters in diameter. As the mushroom matures, its color darkens.
The morel cap's structure is uneven, consisting of wrinkled, rounded depressions (cells) of varying sizes. The stem is irregular, thickened at the base, and cylindrical in shape. The stem is 5-8 centimeters long and 3 centimeters wide. Its color is light beige, but darkens with age.
Morels can be found starting in late April in mixed or deciduous forests, primarily in warm, bright locations. This species typically grows in clumps. Morels have a light mushroom aroma and light, crisp flesh. They don't require long cooking—15-20 minutes is sufficient. They have a delicate flavor and are suitable for any dish.
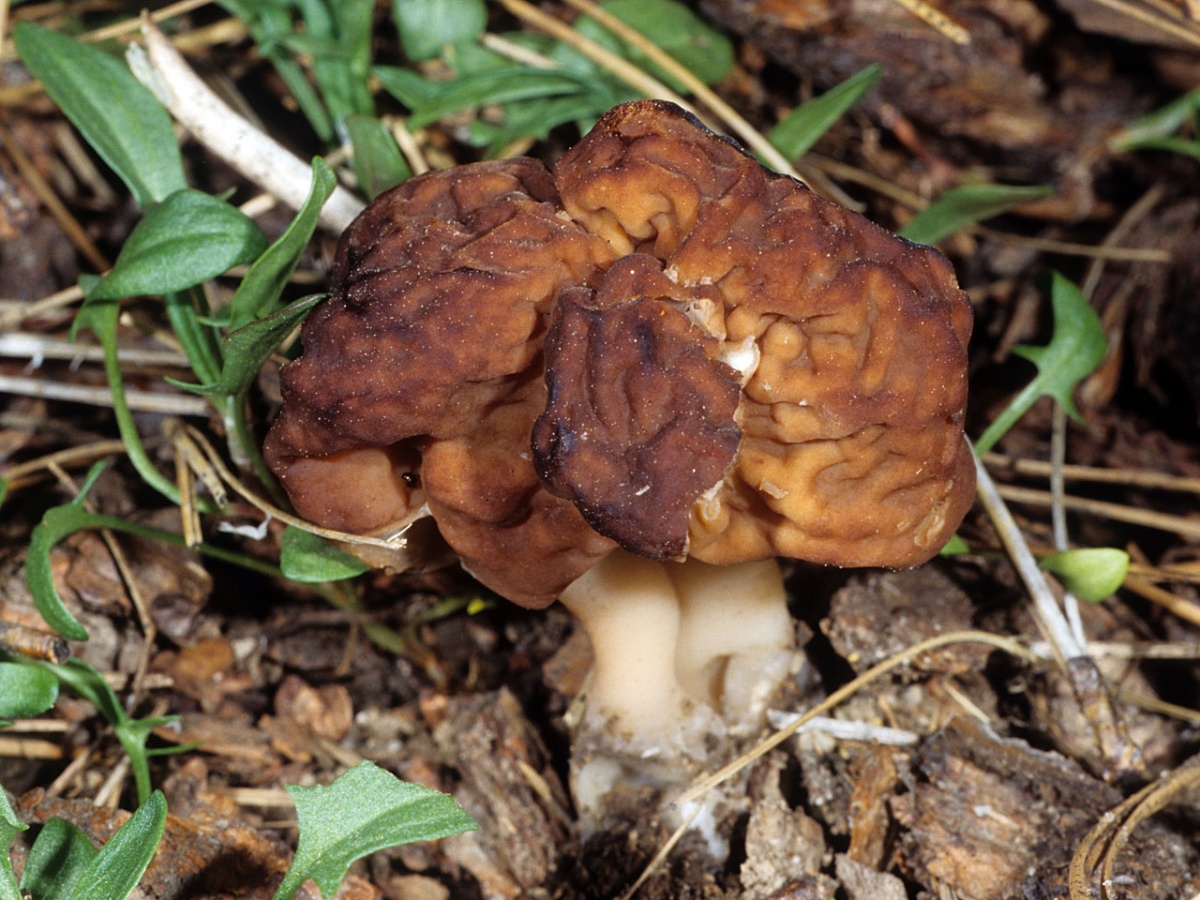
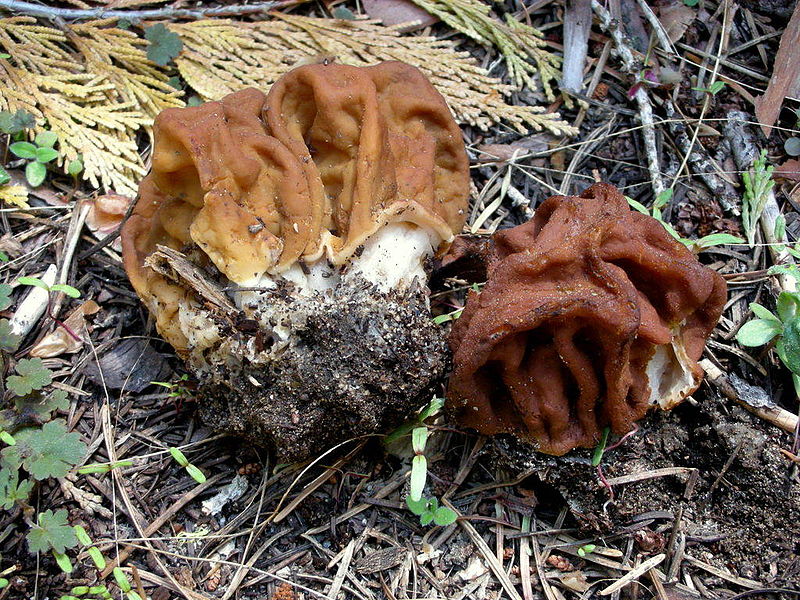
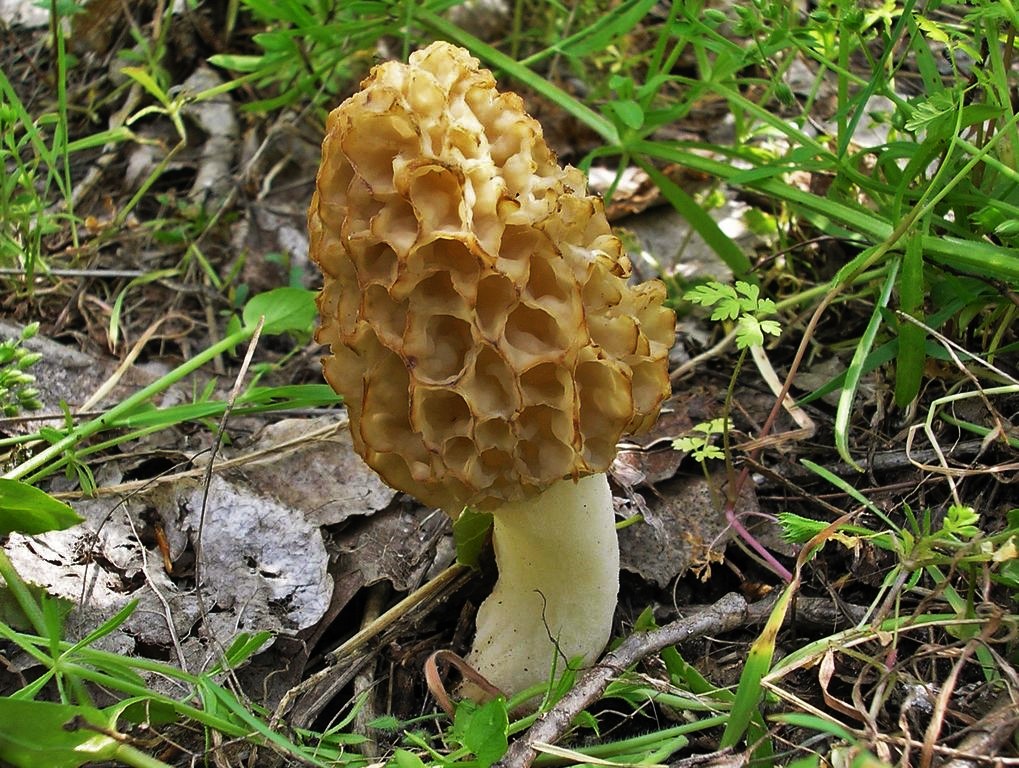
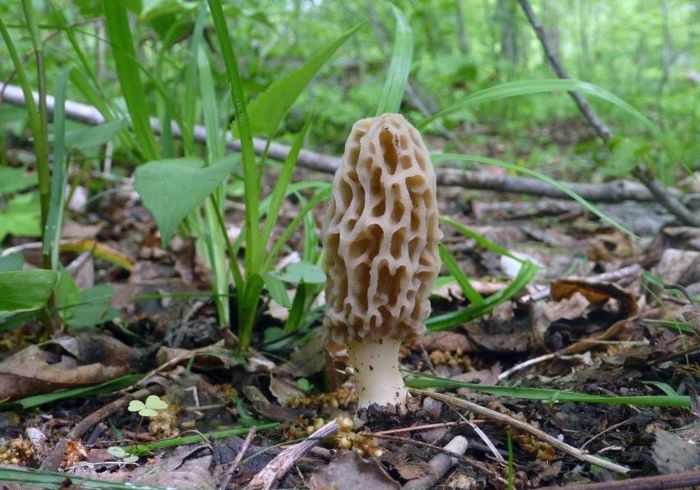
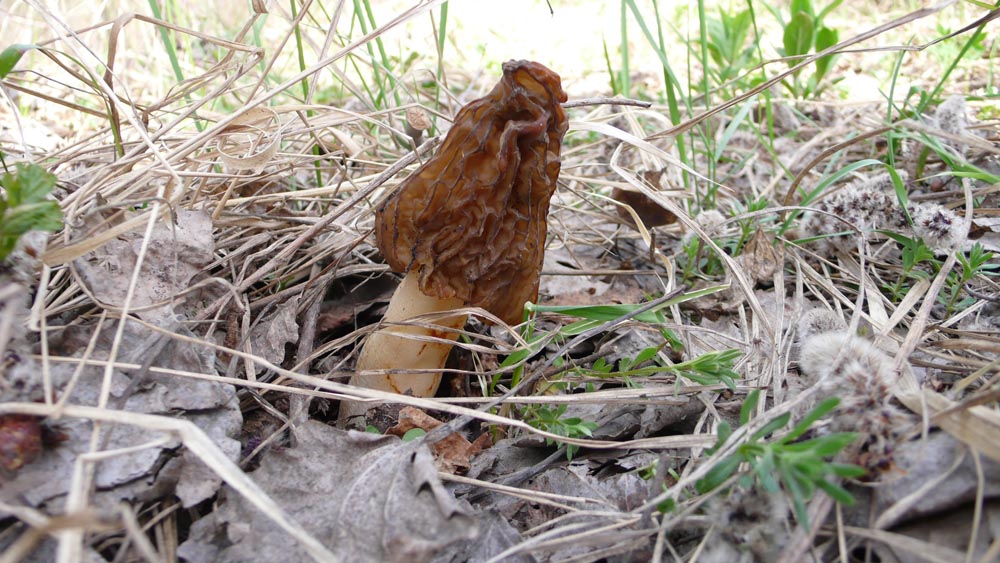
- Morel Cap. In early spring, as soon as the snow melts, you can encounter the morel cap mushroom in the forests of Belarus. It usually appears in mid-April. This morel prefers deciduous forests with good lighting. It is conditionally edible and requires boiling before consumption. The boiling water must be discarded, and the mushrooms are rinsed under running water.
The morel cap is very similar in appearance to the common morel, but differs in that the cap is attached to the stem as in most species—at the apex. The common morel attaches differently, along the lower edge. Morels grow to about 16 centimeters in height. The cap is about 5 centimeters wide and 3-5 centimeters high. The stem is fairly tall and slender, pale yellow in color, reaching 10-13 centimeters in length and 2 centimeters in width. The flesh does not have a strong mushroom aroma.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Summer mushroom species in Belarus
Belarus's climate is suitable for the growth of a variety of mushrooms, even in the dry summer months. The forest soil is rich in essential nutrients and well-hydrated. In summer, the forests harbor a variety of edible, semi-edible, and poisonous mushrooms.
The most popular edible species are:
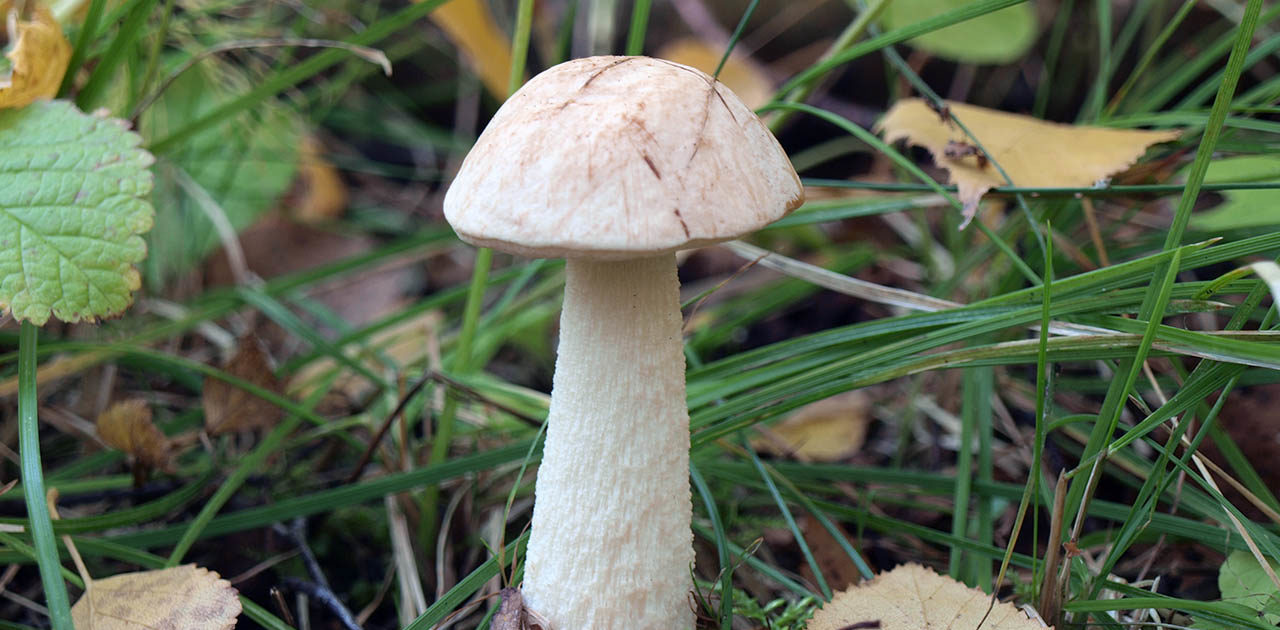
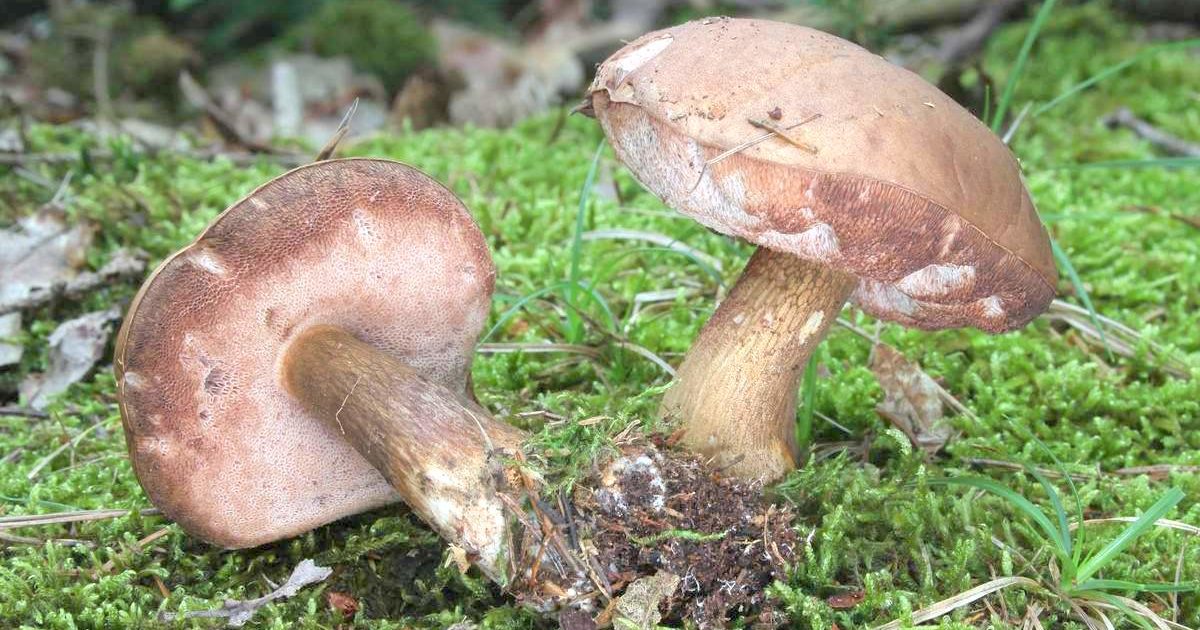
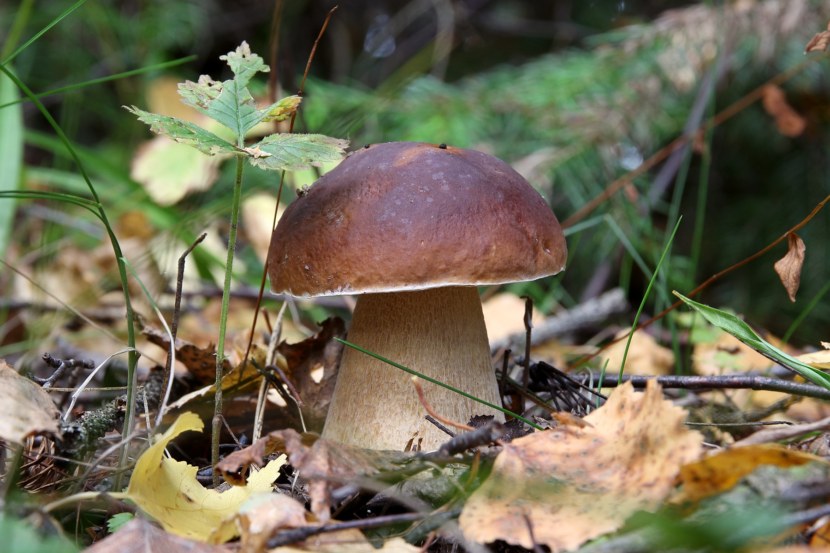
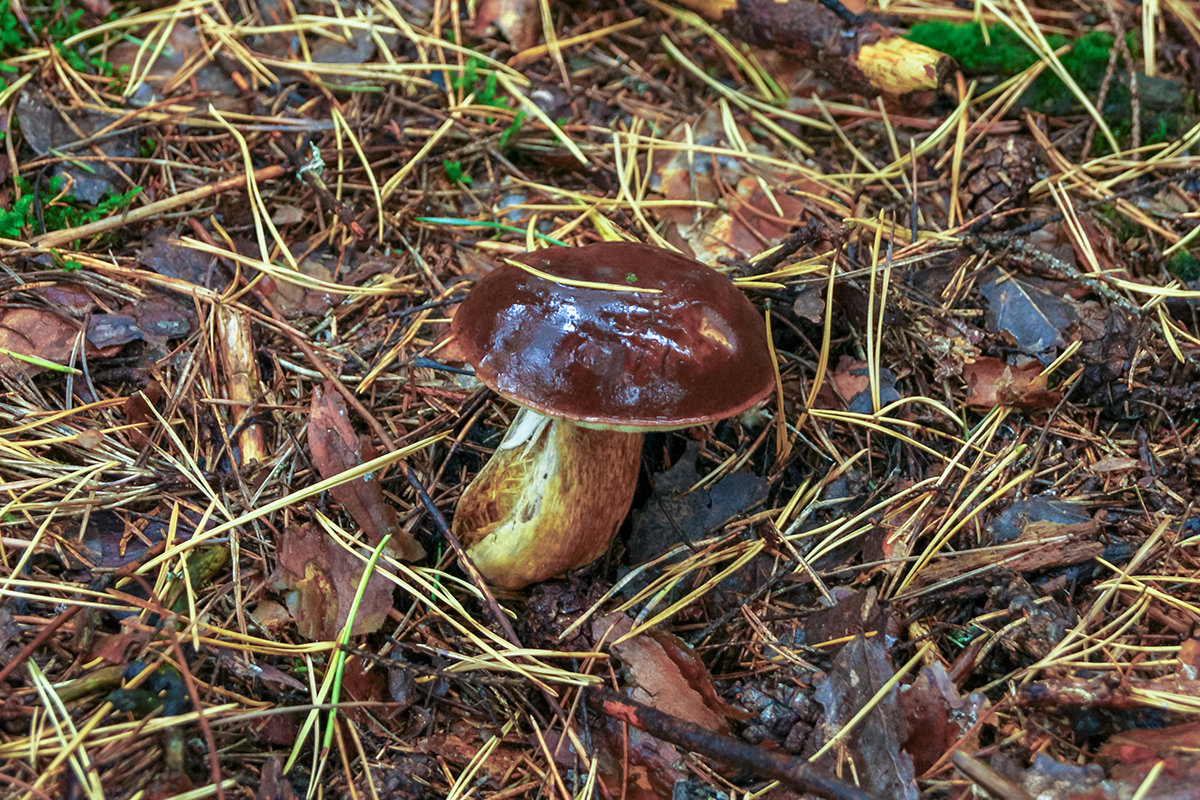
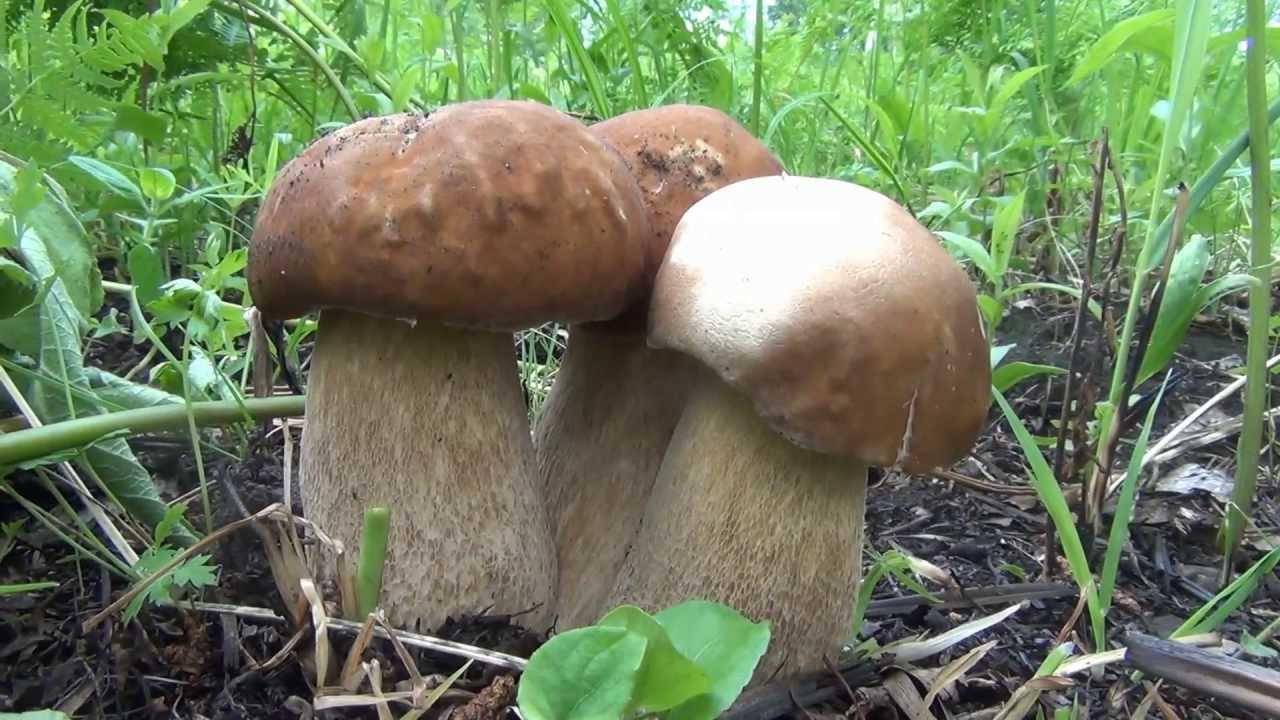
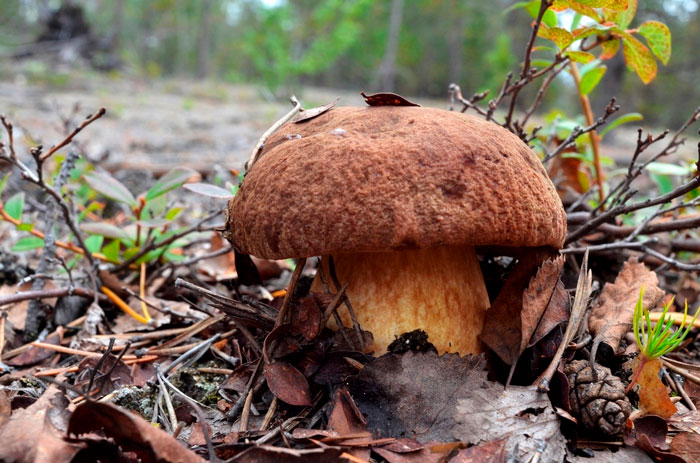
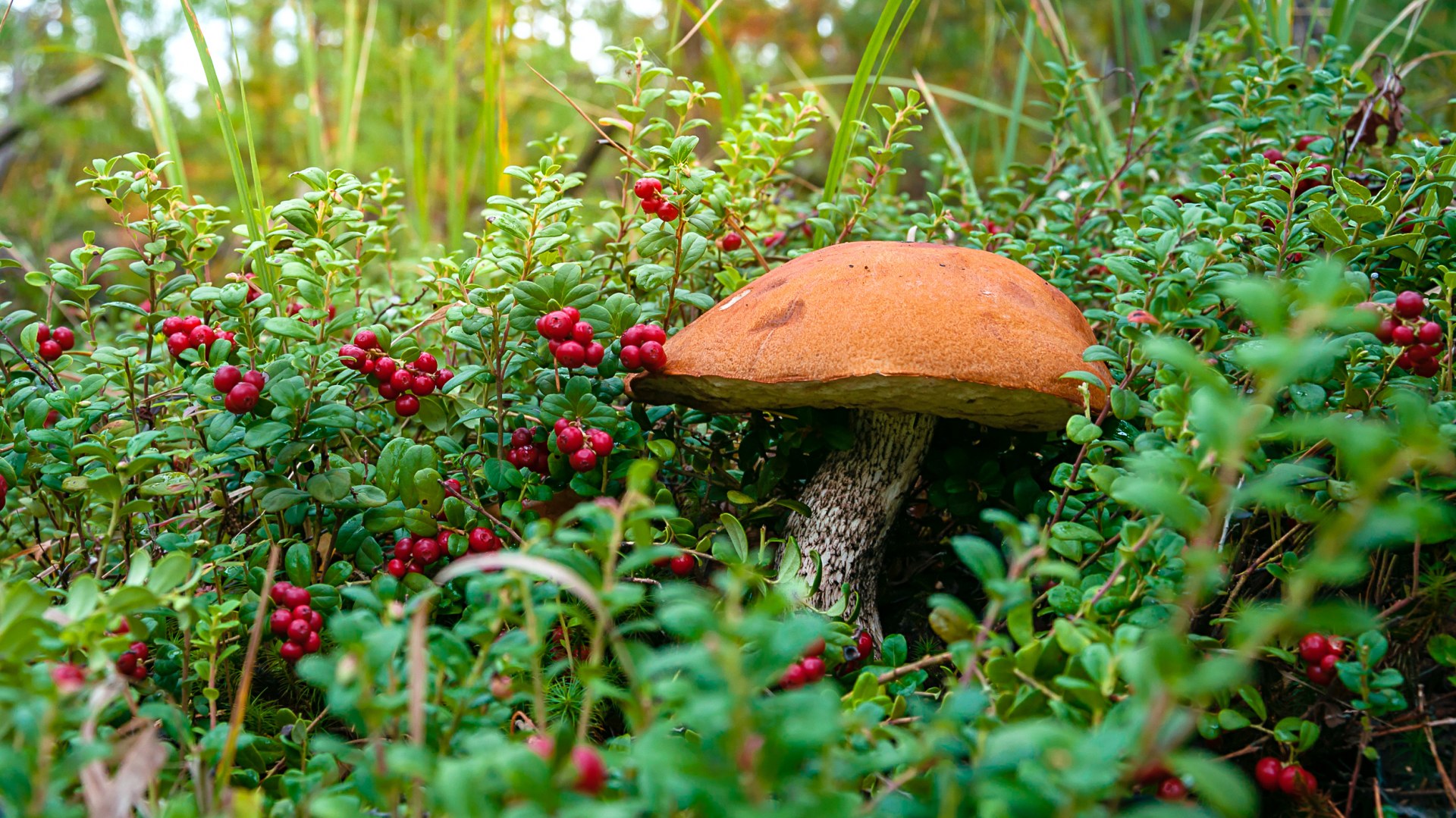
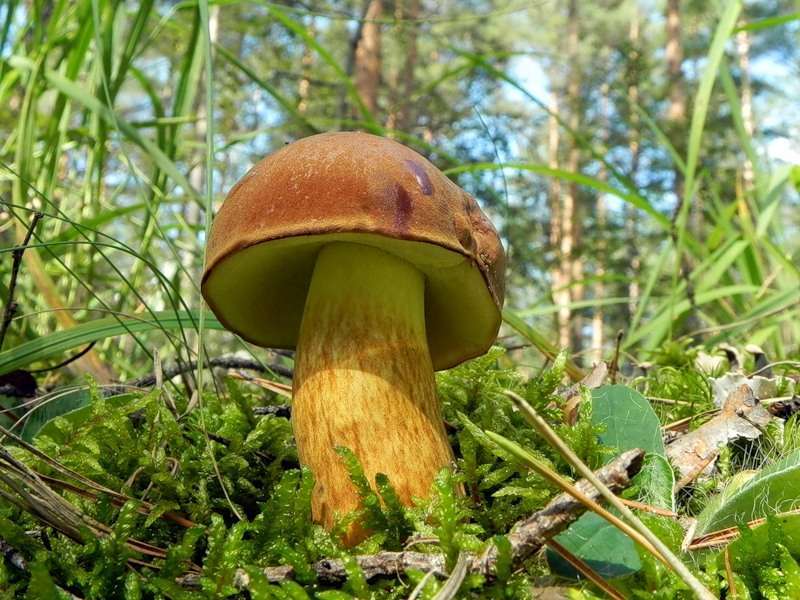
- The well-known white mushroom, also known as the boletus, boasts excellent taste and beneficial properties. Boletus mushrooms begin to grow from late May to early June and continue until the end of November. They thrive in coniferous, deciduous, and mixed forests. Marshy soils and peatlands are exceptions. Boletus mushrooms typically grow in clumps. Their caps are brown and russet, and they grow up to 8-35 centimeters long.
When young, the cap is convex, later becoming flatter. The cap surface is rough, dense, and virtually inseparable. In rainy weather, a layer of mucus forms on the cap. The underside of the cap is dense, light yellow, and sponge-like in texture. The flesh is white, fleshy, and firm, with a wonderful mushroom aroma.

Pine porcini mushroom The stem averages 12-14 centimeters in length, sometimes reaching 25 centimeters. Its diameter averages 8 centimeters and it's barrel-shaped. Its texture is firm, and its color is white or brown. It contains numerous nutrients, minerals, and vitamins, yet is low in calories. Cooking methods vary. Dried, it retains its aroma and white color.
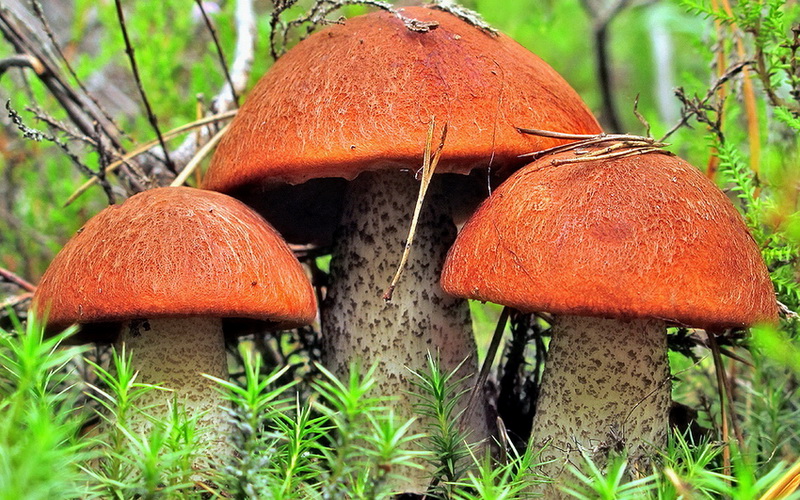
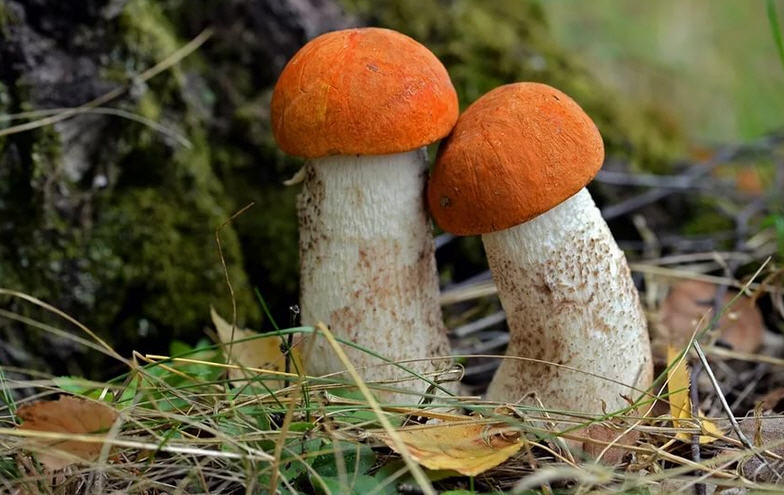
- The aspen boletus. This member of the mushroom kingdom is slightly smaller in size than the porcini mushroom. It begins growing from late May or June until October. The aspen boletus is characterized by a brightly colored, domed cap. The cap is reddish-orange in color and velvety to the touch. The body is quite dense and juicy. A distinctive feature of the aspen boletus is that its flesh quickly turns black when cut.
The stem is white-gray and covered with small scales. Although the aspen mushroom has a mild aroma, it has excellent flavor and is suitable for any cooking method. Aspen mushrooms spoil quickly, so they require prompt preparation. The skin is removed from the cap and boiled for up to 30 minutes.
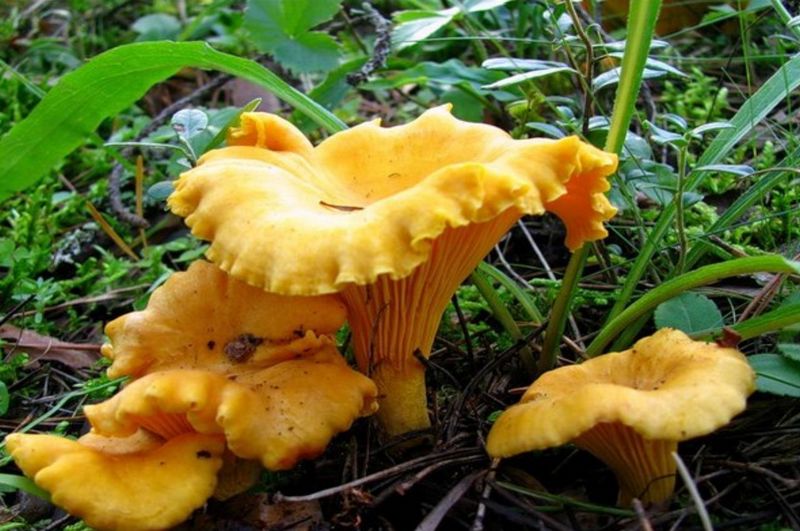
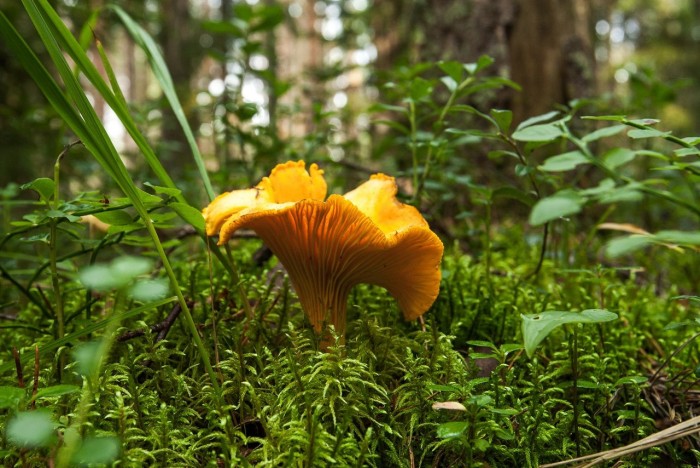
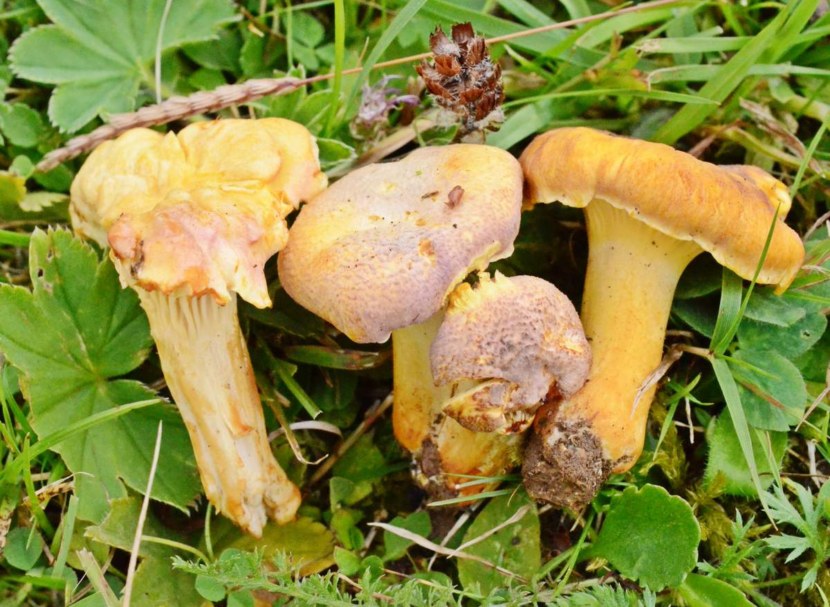
- Chanterelles. The chanterelle's shape is bizarre and unusual. These mushrooms reach 10 centimeters in height and 8 centimeters in width. The cap and stem form a single fruiting body. Chanterelles come in a variety of colors, from light yellow to bright orange. Chanterelles are quite popular in Belarus, as the climate is ideal for them.
They grow in large clusters, often on tree stumps. Chanterelle caps are funnel-shaped and smooth to the touch, with wavy edges. The cap's base consists of thin, closely spaced gills. The stem has a fibrous structure and is soft to the touch. Chanterelles have a delicate fruity aroma and a pleasant flavor. They are not susceptible to parasites. They are delicious when pickled.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Autumn mushrooms of Belarus
Autumn is the peak of mushroom picking season. Those that began growing in the summer are already gaining strength. Many mushrooms appear with the last warm days. The following species typically appear in autumn:
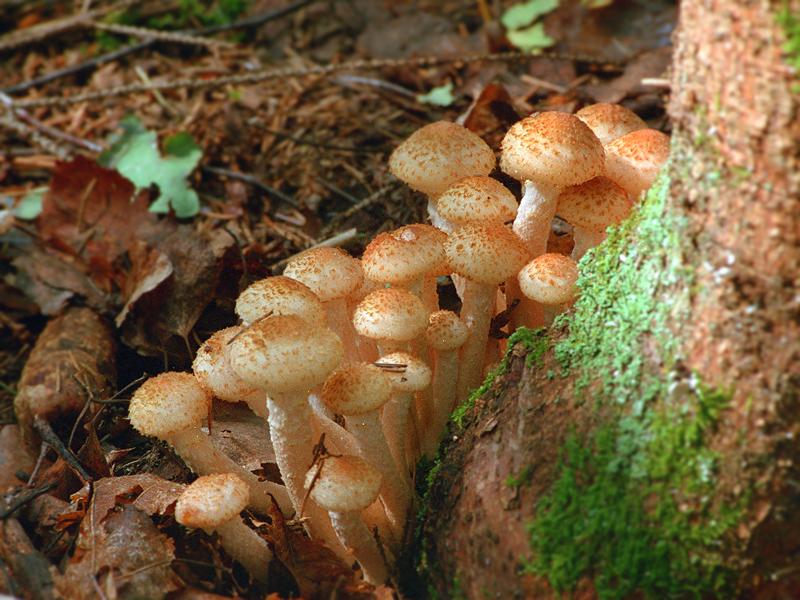
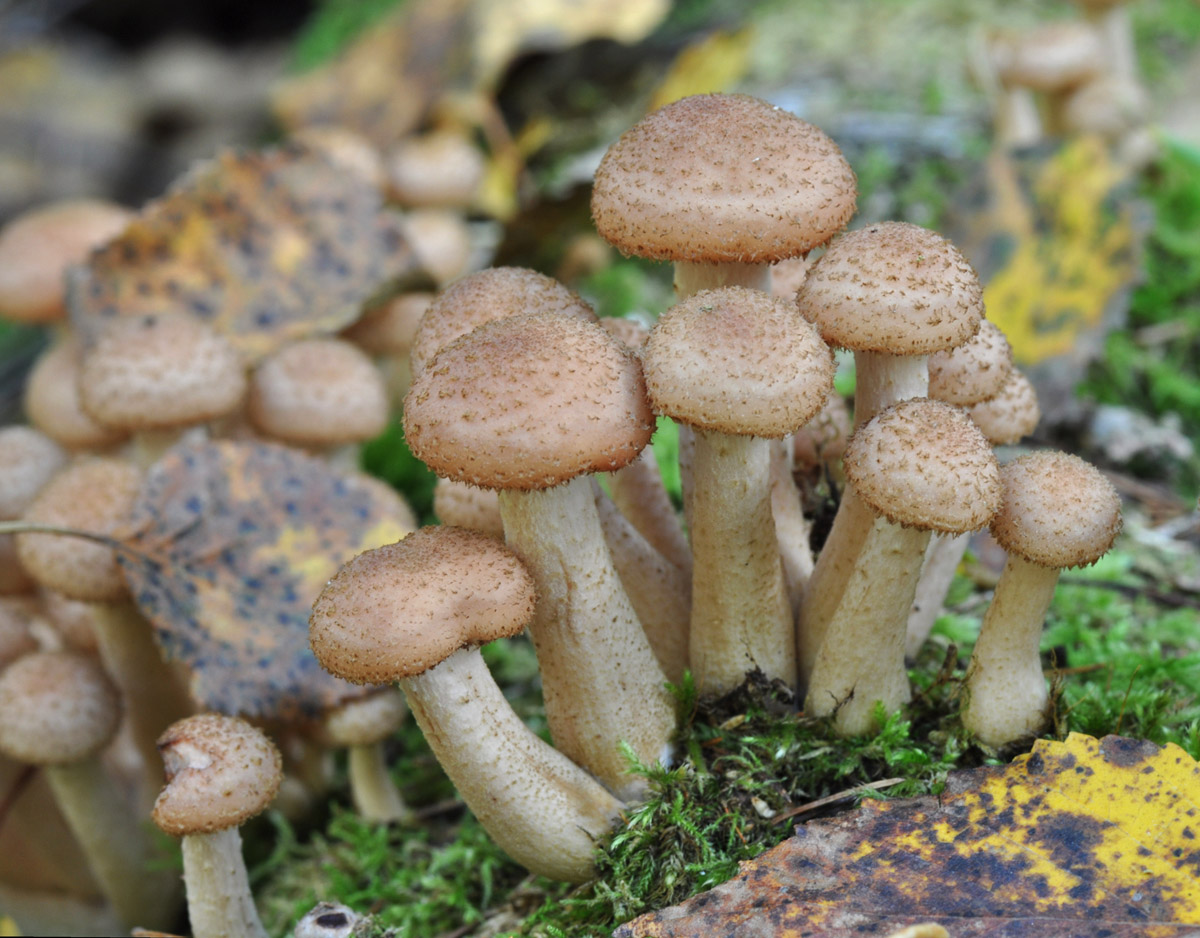
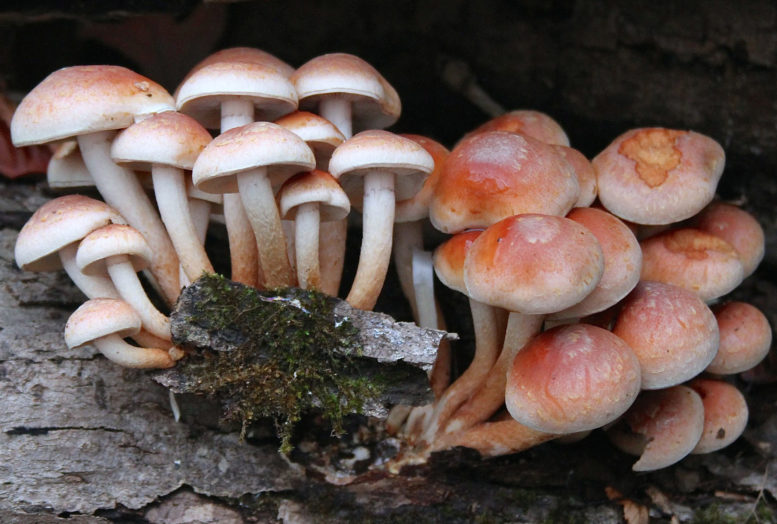
- Autumn honey fungus. Also known as the honey fungus, they appear in early autumn. They reach sizes from 11 to 23 centimeters. Their stems are thin, about 2 centimeters in diameter, and yellow-brown in color. Because honey fungus grows in large numbers close together, their stems are fused at the base.
The autumn honey fungus has a yellow-brown cap, approximately 15 centimeters in diameter. The cap is hemispherical and covered with small brown scales. A thin ring connects the cap to the stem, which breaks as the mushroom grows but remains in fragments on the stem. Autumn honey fungus is delicious pickled or prepared in any other way.
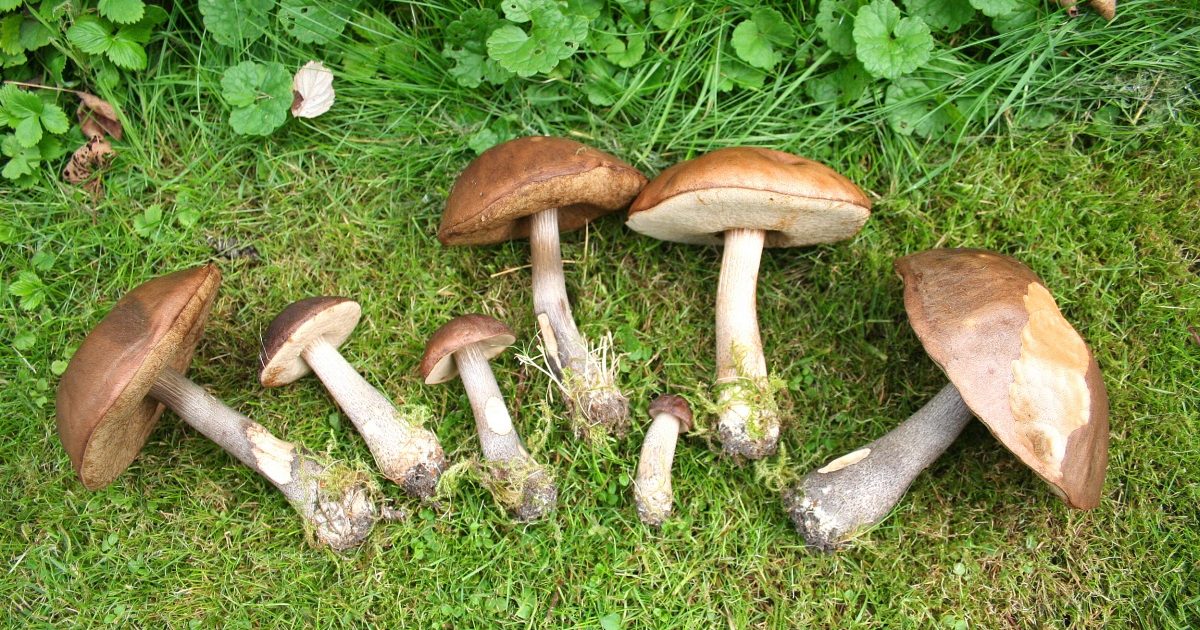
- Boletus. Autumn mushrooms like boletus are quite common in the forests of Belarus and have an excellent aroma and flavor. The cap of the boletus is dry and slightly rough to the touch, covered with barely noticeable cracks. The caps can reach up to 12 centimeters in size. During rainy periods, the cap can be sticky. The cap color is yellow or reddish-brown.
The boletus mushroom's stem is thick and can be yellow or red. The stem averages 10 centimeters long and is cylindrical. When cut, the stem may take on a blue tint. When harvesting boletus mushrooms, be careful to ensure they are free of the mold characteristic of them, as it is toxic. Boletus mushrooms should not be dried. The best cooking methods are roasting or pickling.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:The most dangerous inedible and poisonous look-alikes
To ensure a satisfying mushroom picking experience, it's crucial to remember that Belarusian forests are full of poisonous mushrooms, not just edible ones. Carefully study the characteristic features of dangerous inedible and poisonous look-alikes. The following poisonous species are distinguished:
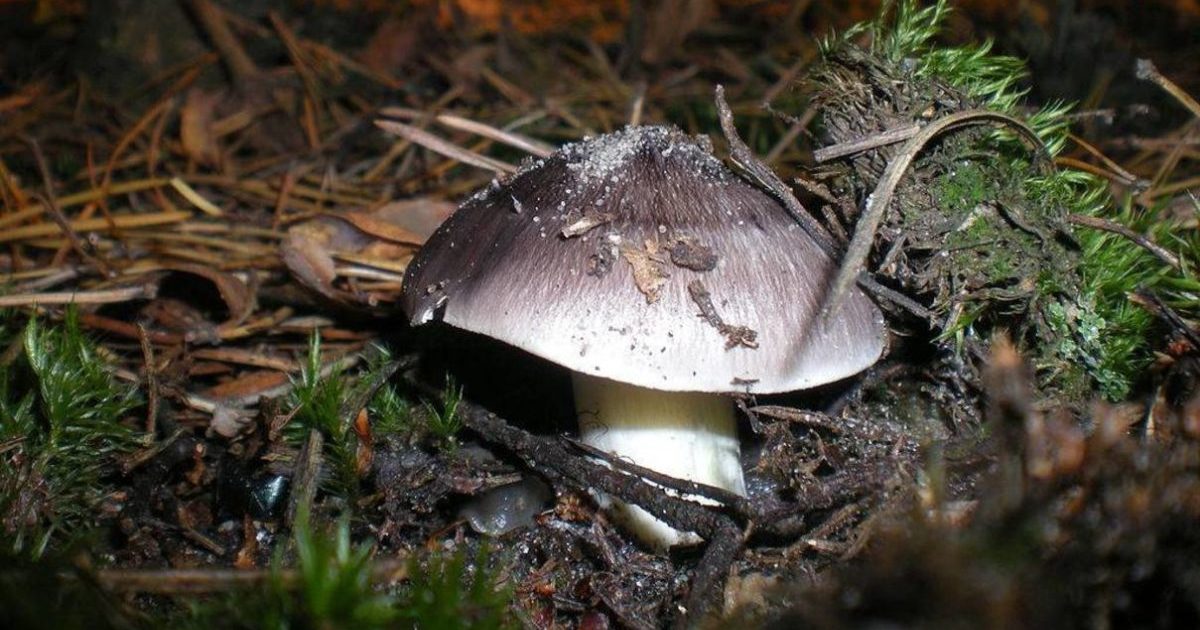
- Death Cap. Everyone knows that this mushroom is poisonous and deadly to humans. Death caps can be fatal. The death cap's cap is slightly convex and gray or olive-colored. The flesh is white, odorless, and neutral in taste. The death cap's stem is white and has a distinctive thickening at the base.
- False honey fungus. The first thing to notice is the lack of a characteristic ring on the stem. False honey fungus has a dome-shaped cap, reddish-yellow or orange in color, with a darker zone in the center. The stem is hollow and fibrous. The flesh is yellow and has a pungent odor, and the taste is bitter.
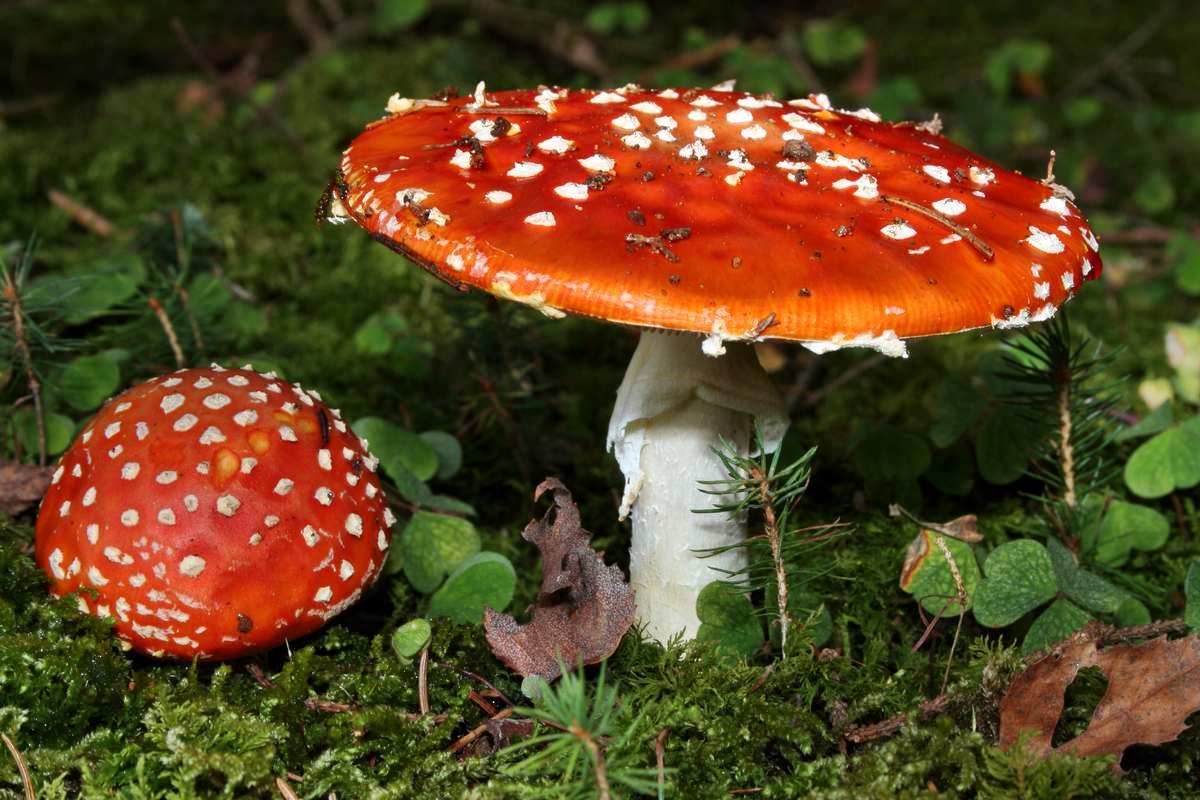
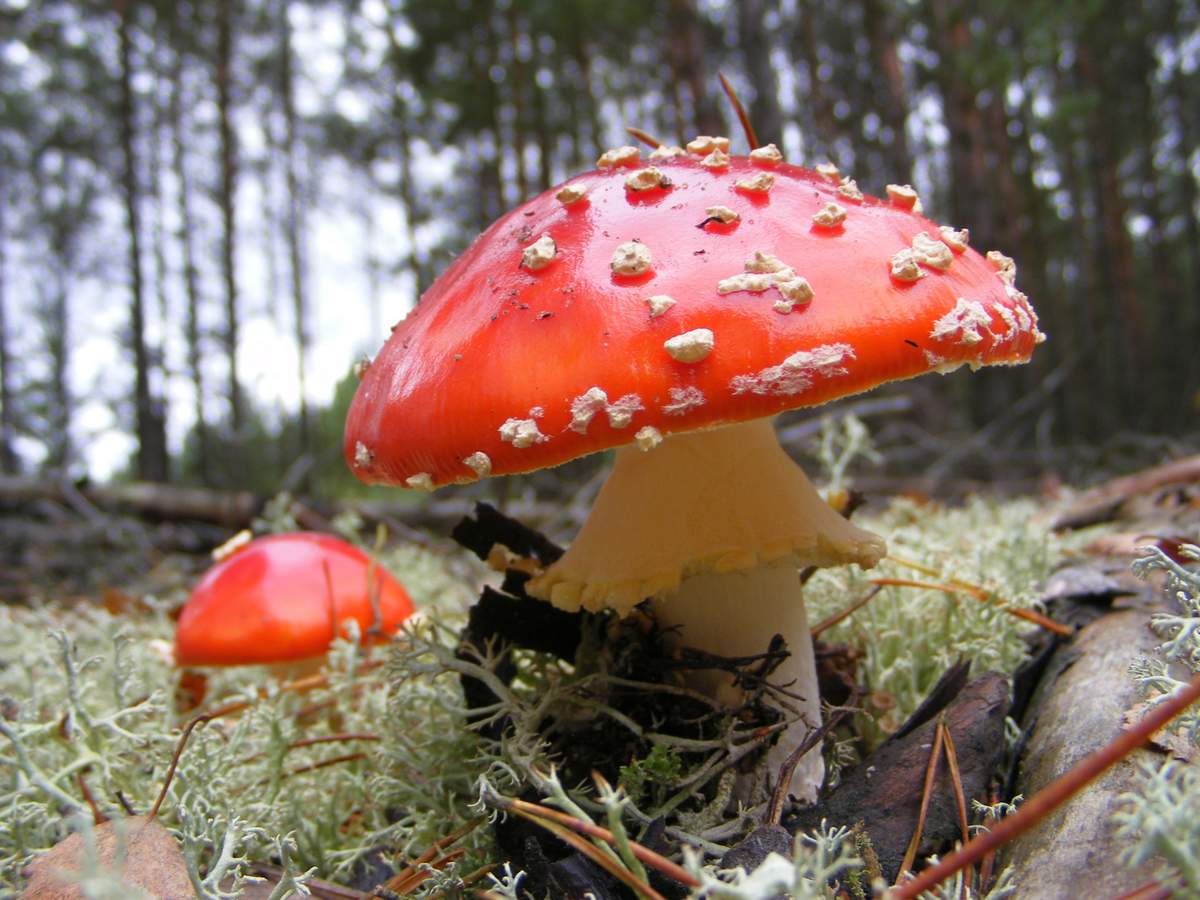
- Red fly agaricThe very bright and easily recognizable red fly agaric is also considered a dangerous species for humans. Its bright red cap is covered with white scales, and its white stem is cylindrical and has a characteristic thickening at the base.
Best gathering places
Mushroom picking is possible almost anywhere in Belarus. There are many different maps and sources indicating which species grow in abundance and where. For boletus, the best places to go are the Borisov, Minsk, and Smolevichi districts.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Chanterelles can be found in abundance in the Berezinsky, Volozhinsky, and Stolbtsy districts. Honey mushroom enthusiasts should definitely visit the Logoisk, Minsky, and Volozhin districts. Boletus mushrooms are best found in the Lyubansky and Vileika districts.
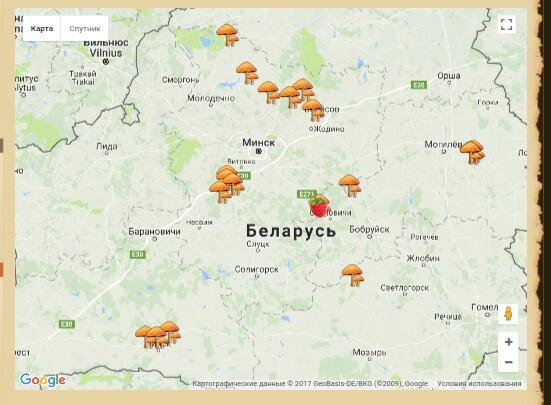
The best places for collecting are considered to be mixed forests that are well-lit and ventilated. Since Belarus is quite large and rich in forests with a variety of tree types, everyone can find a species to suit their taste.
Answers to frequently asked questions
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:This article lists only the main and most well-known types of edible and inedible poisonous mushrooms. In the forests of Belarus, even a seasoned mushroom picker won't leave empty-handed. Remarkably, the climate allows for their collection almost year-round.







































 What are the benefits and harms of oyster mushrooms for humans (+27 photos)?
What are the benefits and harms of oyster mushrooms for humans (+27 photos)? What to do if salted mushrooms become moldy (+11 photos)?
What to do if salted mushrooms become moldy (+11 photos)? What mushrooms are considered tubular and their description (+39 photos)
What mushrooms are considered tubular and their description (+39 photos)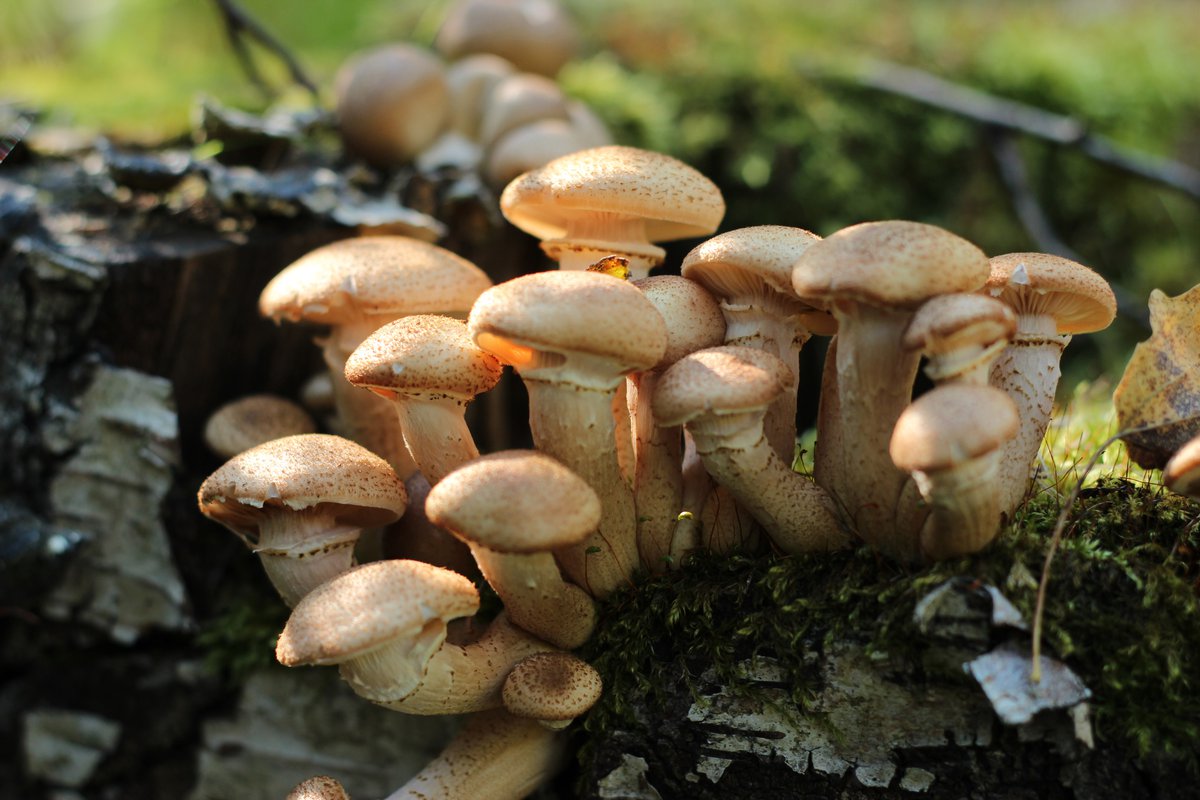 When and where can you start picking honey mushrooms in the Moscow region in 2021?
When and where can you start picking honey mushrooms in the Moscow region in 2021?