Grapes ripen in mid-autumn. At this time, it's time to prepare planting material. This will allow you to enjoy sweet berries next year. However, not everyone's seedlings survive the winter. It's important to follow these rules. storing grape cuttings In winter, the future harvest depends on their quality. They should be treated like any living organism.

Autumn works
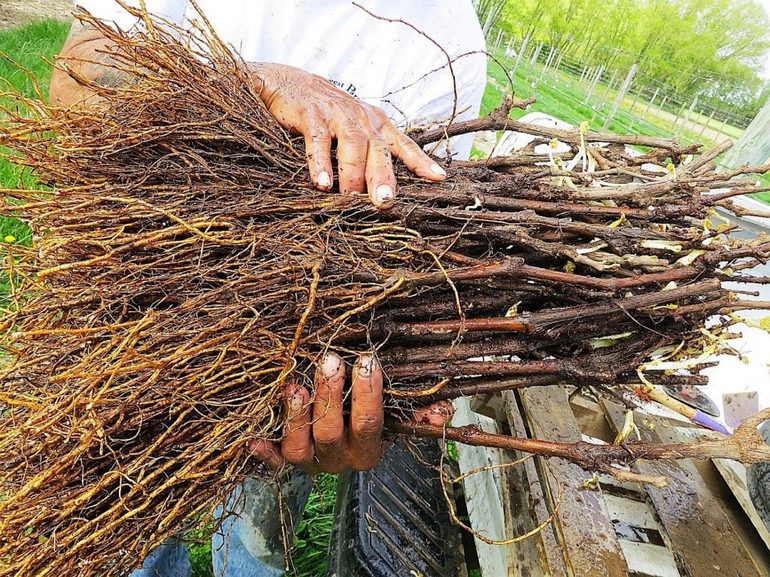

Gardeners prepare for the next planting season differently. Some believe that seedlings should be harvested in the first months of autumn before frost, while others harden off seedlings in freezing temperatures. It's best to consider the climate of a particular region. Planting material should be suitable for surviving the winter and establishing roots after spring planting.
It is also necessary to choose the right vine. There are several recommendations for this:
- Only those varieties that are needed next year will be suitable;
- You shouldn’t choose fat and shoot branches, it’s better to cut off fruit-bearing ones;
- optimal thickness - up to 1 cm;
- The length depends on the number of buds.
The thickness of the vine is importantThin material won't survive the winter; it will simply freeze. Thick branches will become overgrown, making them unsuitable for cuttings. Therefore, cuttings of 0.5 to 1 cm are suitable. Choose long vines with 5-6 buds. In the spring, they can be trimmed to a suitable size. However, 3-4 buds are sufficient for planting cuttings. Then grape cuttings are being prepared for winter storage.
Preparation for storage
After selecting suitable branches, they are cut and cleared of tendrils, leaves, and lateral shoots. The cuttings should be labeled immediately, as they are virtually indistinguishable after cleaning. All varieties will look identical. Experienced gardeners suggest storing grapevines in winter by gathering them into bundles, tying them with rope, and labeling them with the names of the berries.
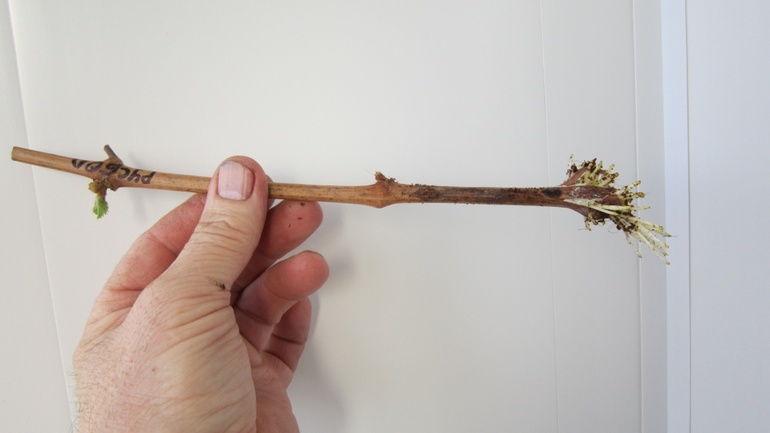

Paper labeling should not be used. This material can cause mold and rot. Therefore, it is recommended to make labels from foil, plastic, or other synthetic materials. Use a marker to write the variety name and number of seedlings on them.
Immediately after marking, the cuttings should be laid out in a storage area. If this is not possible, wrap the cuttings in a plastic bag or bury them a few centimeters in the ground. It's best to treat the cuttings within 24 hours of pruning, otherwise they may spoil before the planting season begins. This will ensure they retain maximum moisture. If a fifth of the moisture is lost, the vine will not take root.
Basic methods
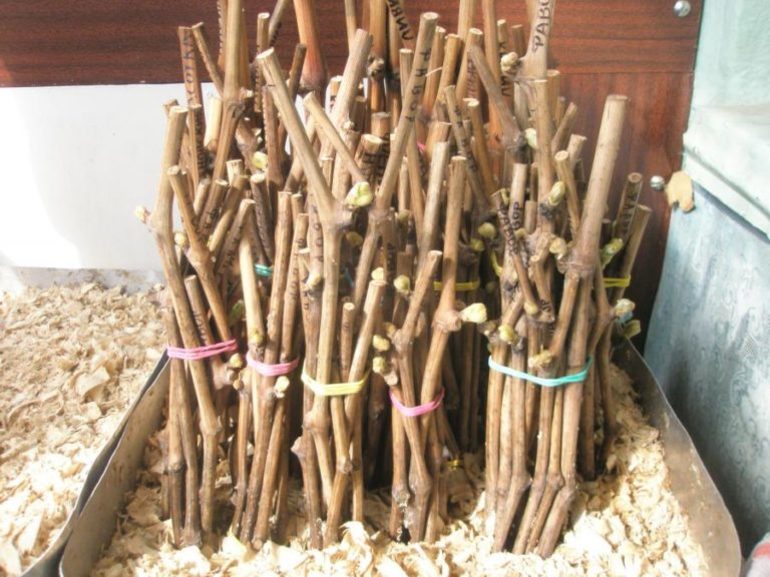

There are several ways to store grape cuttings in winter.
They are conventionally divided into two types depending on the result.:
- guaranteeing their preservation;
- suitable for home conditions.
The first method requires strictly maintaining a specific temperature and humidity level. Nutrients and moisture will be fully retained at a temperature of 0.4 degrees Celsius. However, it's difficult to create and maintain such a temperature at home. Therefore, the second, simpler option is used. The pruned vines are wrapped in bags with damp pine sawdust and placed in a cellar.
Using the refrigerator
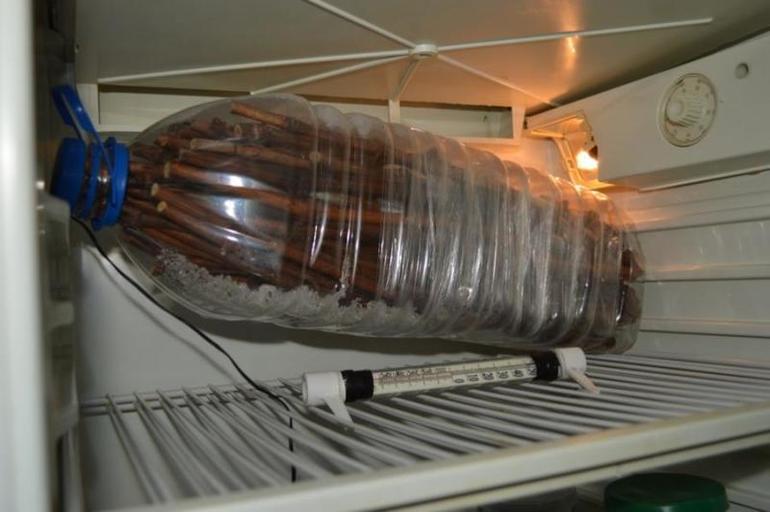

At home they use method of storing cuttings in winter Grapes in plastic bottles. This requires a large working refrigerator with ample shelves. If you don't have the space, you'll have to trim the vines to a minimum length and store them in a regular grocery refrigerator.
The branches are trimmed, a large piece of natural fabric (cotton or linen) is soaked in a copper sulfate solution, and the cuttings are wrapped in it. Then, they are placed in a sturdy plastic bag or a five-liter plastic bottle, capped, and placed on the middle shelf of the refrigerator. Household appliances don't always maintain a consistent temperature, so for the first few weeks, a thermometer should be placed on the shelf along with the cuttings. The gardener should monitor the readings and adjust the refrigerator temperature if necessary.
The material should not be disturbed frequently; it should be checked no more than twice a month. The cuttings can dry out quickly, in which case they should be moistened. If mold or mildew develops on the branches, the vines should be removed, wiped with a cloth, and treated again with copper sulfate. The prepared cuttings should not be cleaned with other chemicals.
Cuttings in the basement
If you have a cellar or basement, it will be much easier to preserve grapevines over the winter. However, even in these rooms, you need to monitor the temperature. To ensure the cuttings survive the winter, the thermometer should always read above zero. However, if it rises above 8 degrees Celsius, they will become overweight and will not produce shoots in the spring. The higher the temperature, the more moisture should be in the basement.
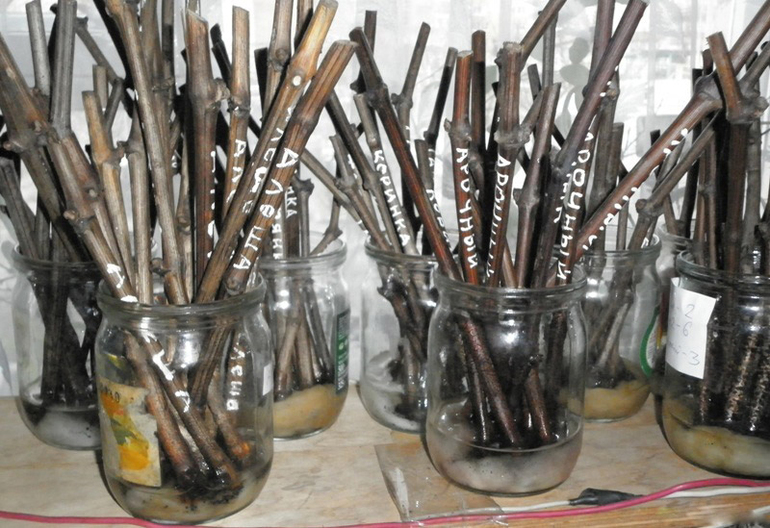
After preparation and treatment with copper sulfate, the cuttings are placed in a bag with fine, damp sand or wood shavings. The plastic bag is opened regularly to allow the cuttings to breathe fresh air. Check to see if the ash has dried out or become moldy. If this has happened, remove the cuttings from the bag, clean them, and treat them with copper sulfate. Then, air-dry them, repack them, and store them in a cellar or basement.
Grapes in the ground
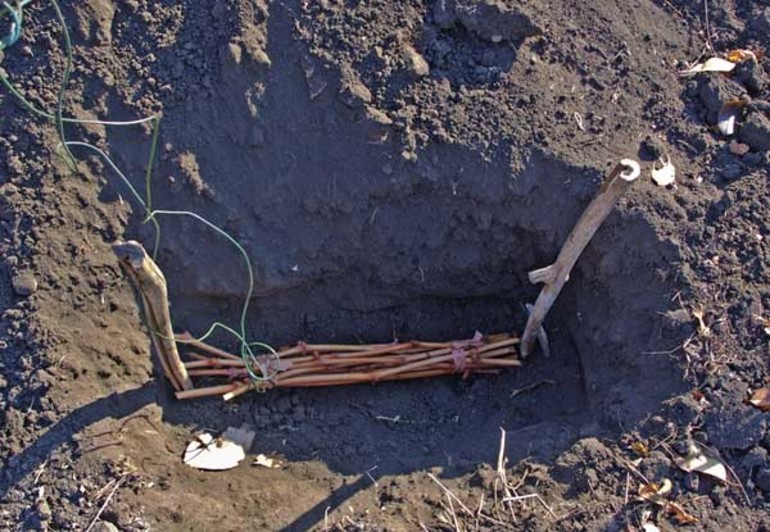

There's another effective way to store grape seedlings over winter. It's used by gardeners who don't have a cellar or basement, and whose refrigerators aren't large enough to hold bags or bottles of vines. Minimal effort is required to preserve grapes in the ground.
First, dig a shallow trench. Choose a site with a slight elevation to prevent water from stagnating during the spring snowmelt. If moisture covers the cuttings, they will rot or become moldy. If a flat area is chosen, dig a small ditch near the cuttings, heading toward the slope, where the liquid will accumulate.
The width of the trench directly depends on the number of branches. The more branches there are, the wider the trench should be. The depth is usually no more than 50 cm. Before placing the cuttings in the ground, sort them and label them. A thin layer of sand is poured into the bottom of the hole, and the cuttings are placed on top, leaving almost no space between them. Then they are covered with 6-7 cm of damp sand, and the trench is filled in. Do not wrap the vines in plastic or cloth, otherwise the planting material will rot or become moldy.
Features of rooting
Once gardeners have learned how to store grape cuttings over winter before planting, they need to learn the intricacies of rooting them. The cuttings are removed from storage and tested for suitability. To do this, make longitudinal cuts through the buds of one vine of each variety. If the branches are green inside, they are ready for planting. Dry or rotten cuttings will have black or brown cuts.
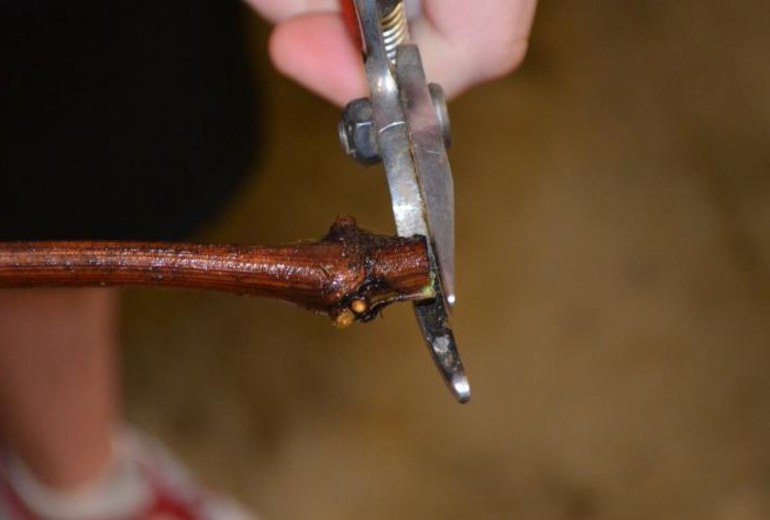

Then, the oblique cuts at the ends of the seedlings are renewed; this will improve root formation. Additionally, the cuttings need to undergo several more procedures.:
- soak;
- furrow;
- to kilchevat';
- stratify;
- stimulate.
For the first stage, use melted or rainwater. Each branch is immersed in it up to two-thirds of its length and soaked for three days. If the vine has been overdried, this time is extended. After this, make cuts in the lower part with a sharp knife. The vines need to be exposed to different temperatures. One option for this procedure is to dig a trench, place the lower part of the branch in it, leave the upper part exposed to the air, and cover the top with plastic film to create a greenhouse.
The next step is stratification. The cuttings should be placed in a warm place, where the temperature reaches 20-24 degrees Celsius. This will awaken the vines from their winter dormancy, and healthy seedlings will open their buds. They are then treated with special growth-stimulating agents.
Planting in the ground
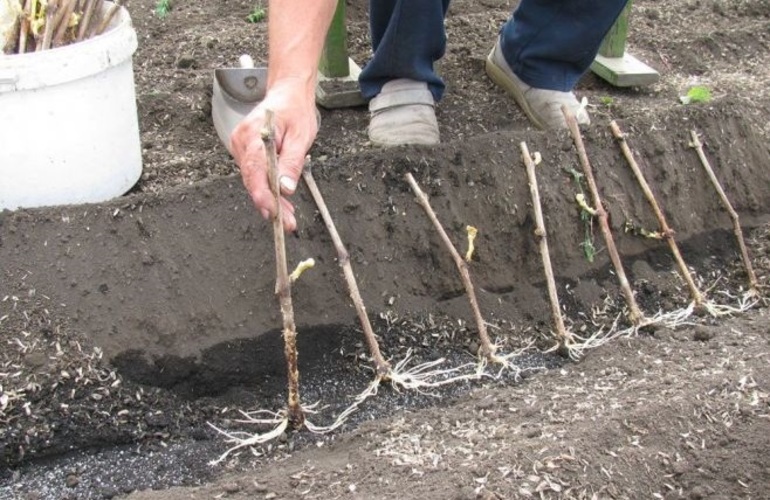

After preparation, the cuttings are planted in the ground. You'll need to purchase special containers—pots—in advance. You can make them yourself from cut-off bottles, milk cartons, and juice cartons. Separately, prepare the soil, consisting of soil, sand, pine sawdust, and humus. Make several holes in the bottom of the container, add drainage, and fill with soil. Lightly moisten the soil, insert the cutting, and fill the container to the rim. Water generously and place the pot in a sunny, warm spot.
Periodically, cuttings fed with a solution of water and wood ashThe use of chemicals is not recommended yet. If shoots are growing rapidly, they should be pinched back. When warm, dry weather sets in in early April, the vines can be transplanted into open soil. It's important to remember to water and fertilize the plant regularly. After planting, liquid fertilizer can be applied sparingly.
Preserving grapevine cuttings over the winter is a laborious process. However, buying new cuttings each year is more expensive than growing them yourself. Therefore, many gardeners learn to care for vines during the cold months. If all the necessary conditions are met, strong, healthy shoots can be obtained in the spring.
 General cleaning of the vineyard: a list of mandatory activities
General cleaning of the vineyard: a list of mandatory activities When to harvest grapes for wine
When to harvest grapes for wine Can you eat grapes with seeds? Health benefits and risks
Can you eat grapes with seeds? Health benefits and risks Grape seed oil - properties and uses, benefits and contraindications
Grape seed oil - properties and uses, benefits and contraindications