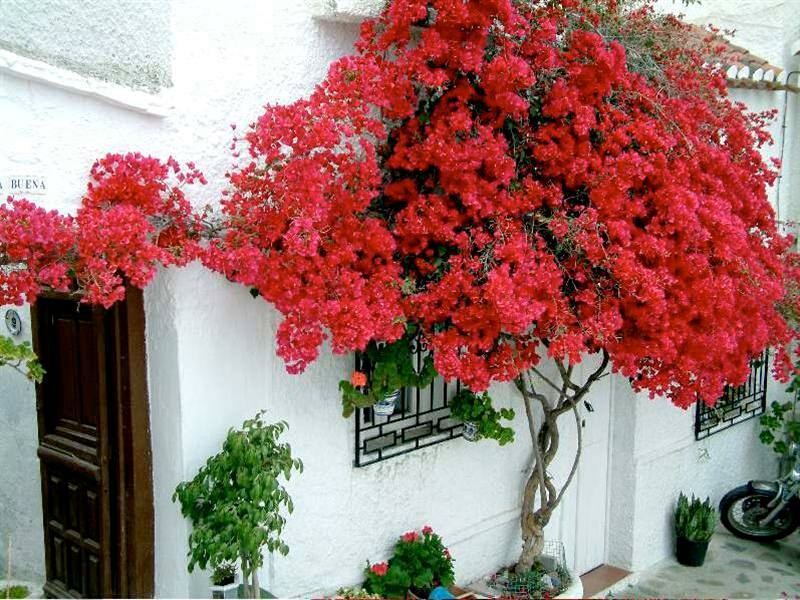
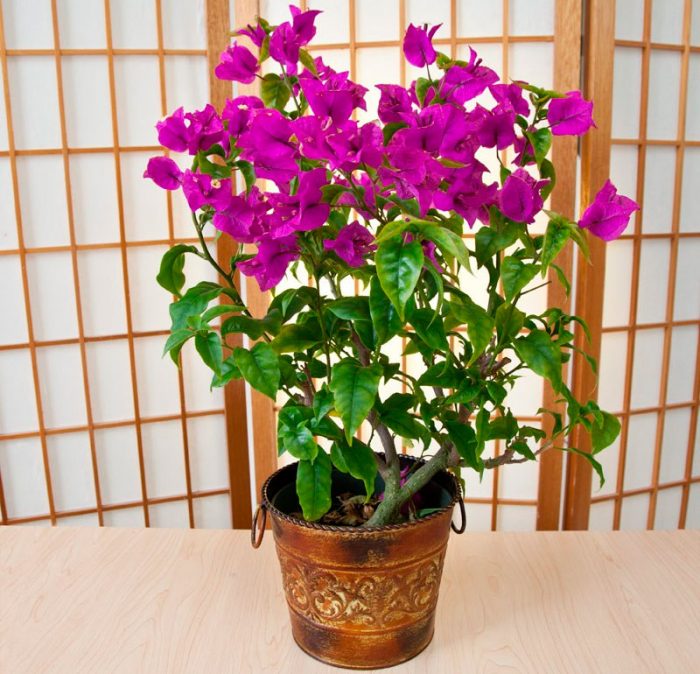
Bougainvillea is a vibrant Brazilian beauty that thrives in bright light and spacious conditions. Currently, there are approximately 14 wild species and approximately 300 cultivated varieties. Bougainvilleas include shrubs with climbing stems, reaching less than half a meter in height, and small trees.
Despite its beauty and diversity, this flowering plant isn't particularly popular among domestic gardeners and is rarely seen in homes. Bougainvillea is unfairly considered a capricious plant that struggles to thrive indoors, but in reality, simple care following a few simple rules will help you grow a healthy plant.
Characteristics of bougainvillea and species diversity
Bougainvillea is a small genus of evergreen plants belonging to the Nyctaginaceae family and named after the French explorer L. A. de Bougainville. The flower's native land is Brazil. The plant grows as shrubs and low trees with twining, vine-like branches. The shoots are covered with long, thorny, but sparse spines, which help them anchor themselves to supports.
As the vine grows, its stems become covered with dark brown bark, which takes on a grayish tint in mature vines. Petiolate, ovate leaves are arranged alternately across the entire surface of young shoots. The small, bright green leaves have smooth edges and a predominantly smooth surface, although some cultivars have pubescent leaf blades.
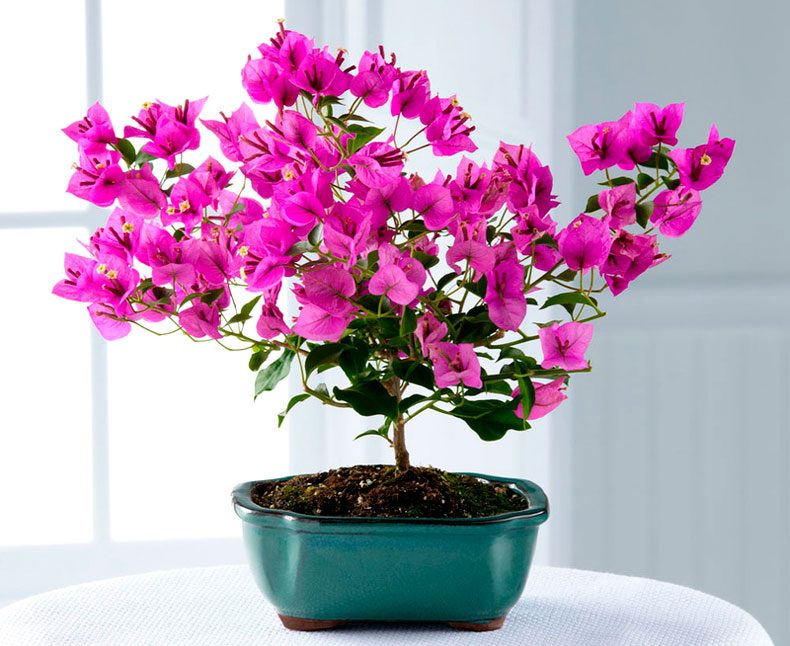
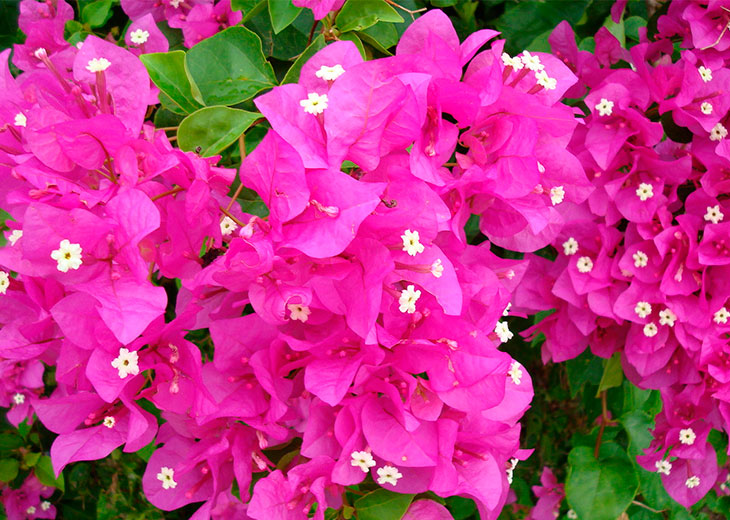
The shrub's small tubular flowers, gathered in racemes, have no ornamental value and fall off quickly. However, the vine's vibrant bracts, which surround the inconspicuous yellow-white flowers, are striking in their beauty and variety. Each flower is surrounded by three large, papery bracts, through which fine veins are visible. The shape and color of the bracts depend on the plant variety. The bracts retain their ornamental value for quite a long time. You can appreciate the beauty of the vine in bloom from the photo.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:There are approximately 14 species of bougainvillea in the wild, but only three varieties and their cultivars are suitable for growing as potted plants. These species include:
- Bougainvillea glabra. The most popular indoor bougainvillea, it gets its name from its bare, heavily branched stems. The shrub's branches are covered with glossy, oval leaves with pointed edges. Varieties with crimson, purple, yellow, orange, and red bracts are available, which retain their decorative appeal for a long time.

Bougainvillea Napa - Bougainvillea Resplendent. A fast-growing vine with long, flexible stems densely covered with numerous sharp spines. The dark green, heart-shaped leaves have a velvety surface and a fairly dense structure. The vine's bright red bracts fade gradually, eventually turning white.

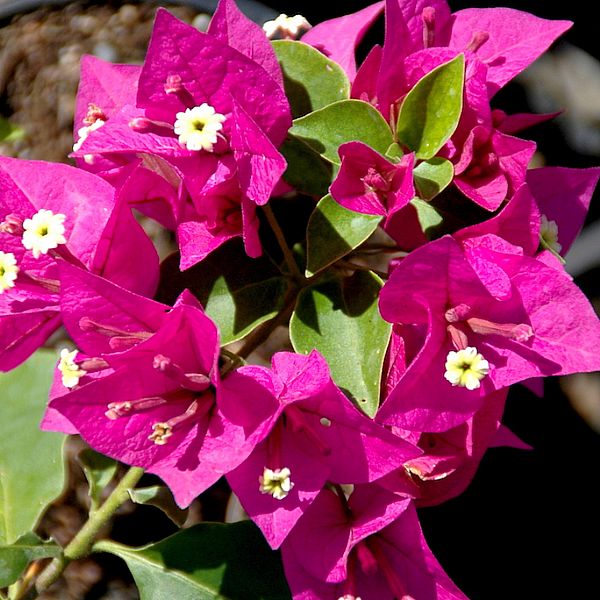
Bougainvillea Remarkable - Bougainvillea Peruviana. A variety with long, loosely climbing stems that do not produce side shoots. The branches of the bush are covered with narrow, ovate leaves with a pointed tip. Double, pink or purple, rounded bracts surround small, white-yellow flowers.

Bougainvillea Peruviana
Caring for bougainvillea at home and apartment maintenance rules
Bougainvillea is an easy-to-grow flowering plant that's ideal for apartment living. When growing this tropical flower indoors, remember that it requires plenty of light and doesn't tolerate cold air currents well.
Lighting
Bougainvillea is quite demanding when it comes to light. The quality and duration of its blooms depend on the amount of light the shrub receives.
Only during particularly hot periods does the plant require protection from the midday sun. A thin curtain can be used for light shade. Insufficient light can result in pale leaves and a complete lack of flowering. A south-facing windowsill is an ideal location for this plant.
Temperature and humidity
During the active growing season of spring and summer, this heat-loving shrub is recommended to be kept at temperatures between 22 and 25°C. In winter, it is recommended to keep the shrub in a cooler room, with temperatures between 12 and 16°C. This overwintering stimulates further flowering.
For normal growth, the shrub requires high humidity. Placing a container of water next to the plant will help alleviate dry air. During the non-flowering period, you can moisten the leaves with a spray bottle. Avoid misting the flowering shrub, as water splashing on the bracts will cause them to wilt quickly.
Watering and fertilizing
During the spring and summer, the plant requires regular and abundant watering. Gardeners recommend watering the plant immediately after the top layer of soil dries out. The soil in the pot should always remain slightly moist. In winter, the frequency and intensity of watering should be reduced to a minimum. Lightly moistening the soil is sufficient to prevent it from drying out completely.
From spring until mid-autumn, the plant requires additional feeding. Liquid fertilizers for ornamental flowering plants are best. It is recommended to feed the shrub once every 14 days. The dormant plant does not require additional feeding.
Care during the flowering period
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Blooming bougainvillea requires frequent and abundant watering with well-settled water. Dry soil can cause the bracts to wilt quickly. Regular application of complex fertilizers also promotes long-lasting blooms.
A pot with a blooming bougainvillea should not be moved, since a sudden change in location can lead not only to the cessation of flowering, but also to the complete exposure of the bush.
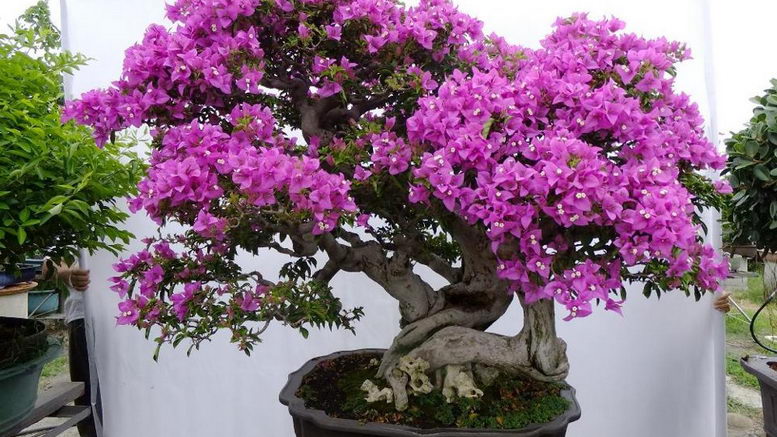

Pruning and pinching
Regular pruning not only helps control the shrub's growth but also improves its appearance. It is recommended to prune three times a year:
- The first pruning is done in early spring before active growth begins. During spring pruning, damaged, dried, and weakened branches are removed.
- In summer, only cosmetic pruning of the plant is carried out, during which wilted inflorescences are cut off.

Pruning rules - In the fall, immediately after the shrub has finished flowering, pruning is also recommended. During the autumn months, before the dormant period begins, young shoots are shortened. After pruning, two-thirds of the original shoot length and 6-8 buds on each shoot should remain. Excess and abnormally growing shoots are trimmed off completely. It is not recommended to trim old branches older than 3 years.
Preparing for winter
Preparing a bush for cold wintering plays an important role in its cultivation. Starting in mid-autumn, the plant must be prepared for the dormant period. To do this, gradually reduce the amount and frequency of watering, and completely stop fertilizing.

This is because a cool room and the absence of foliage significantly slow down the evaporation of moisture from the soil surface. If the bush still has some foliage, watering once every 15-20 days is sufficient to maintain optimal soil moisture.
Diseases and pests
This tropical beauty is quite resistant to various diseases and pests, but improper care significantly reduces its protective functions:
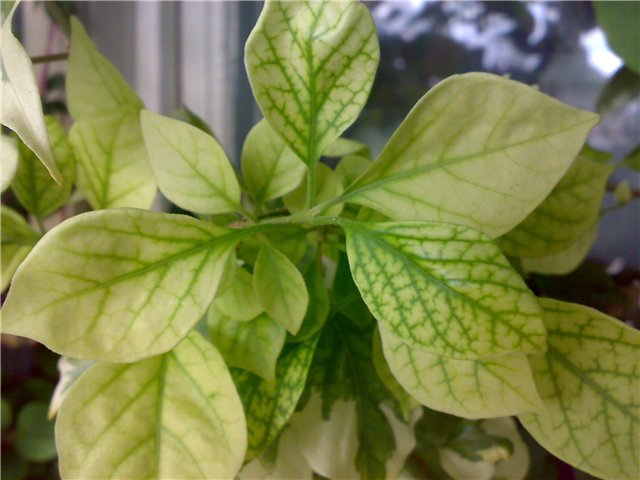
- A lack of iron and other nutrients in the soil causes chlorosis. The disease can be identified by the plant's pale leaves. Applying a complex fertilizer and treating the foliage with an iron chelate solution will help eliminate the disease.

Chlorosis - Stagnant moisture in the soil can cause root rot. The plant can only be saved if the disease is detected early, when the rot has only affected a small portion of the roots. To do this, remove all rotted roots, treat the plant with antifungal agents, and completely replace the soil.
- The plant can also be attacked by harmful insects such as aphids, spider mites, and mealybugs. Double treatment with insecticides will rid the plant of aphids and mealybugs, and acaricides will combat spider mites.
Propagation, cultivation and transplantation of indoor bougainvillea
Indoor bougainvillea can be propagated in three ways: cuttings, seeds, and air layering. However, most gardeners prefer cuttings, avoiding any other propagation methods. Growing bougainvillea from cuttings is a fairly easy and reliable method, suitable for even a novice gardener.
- Propagation by cuttings is recommended to be carried out in late spring or early summer.
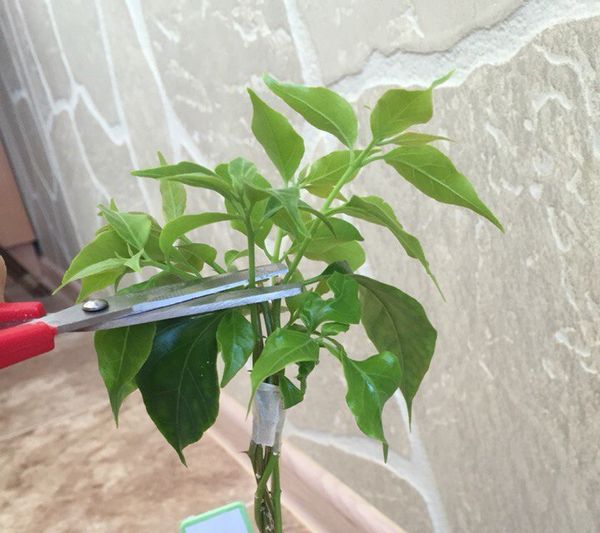
- Cuttings are taken from sections of young semi-lignified shoots 10 cm long, on which at least 1 bud remains.

Pruning cuttings - The lower leaves of the cuttings are cut off, and the rest are shortened by half to reduce the area of moisture evaporation.
- The cutting must be prepared for planting in soil. To do this, place the cutting in a container filled with warm water for several hours, and treat the cut site with charcoal powder and a growth stimulant.
- It is recommended to root the cutting in a soil mixture of sand and peat, taken in equal quantities.

Rooting cuttings - To create greenhouse conditions, the container with cuttings is covered with plastic film.
- The greenhouse with cuttings must be kept in a well-lit place at a temperature of at least 25 °C.
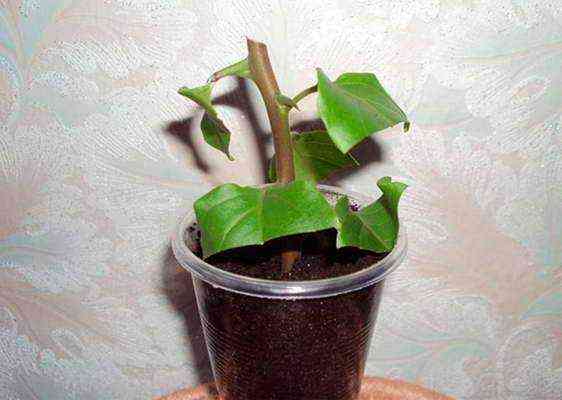
- With regular ventilation and watering, the cutting will take root in 6-8 weeks, after which it can be transplanted into a small pot for further growth.
- Transplanting a young plant into a permanent container is carried out after its roots have filled all the space in the previous one.
This procedure is best performed in the spring, immediately after the dormant period ends. It's best to choose small but deep containers for planting the bush. The diameter of each subsequent pot should be a couple of centimeters larger than the previous one. Suitable soil for the bush can be purchased at a specialty store or mixed yourself using equal parts of turf, humus, sand, and peat.
Transfer algorithm:
- Moisten the soil in the pot well for further extraction of the bush.
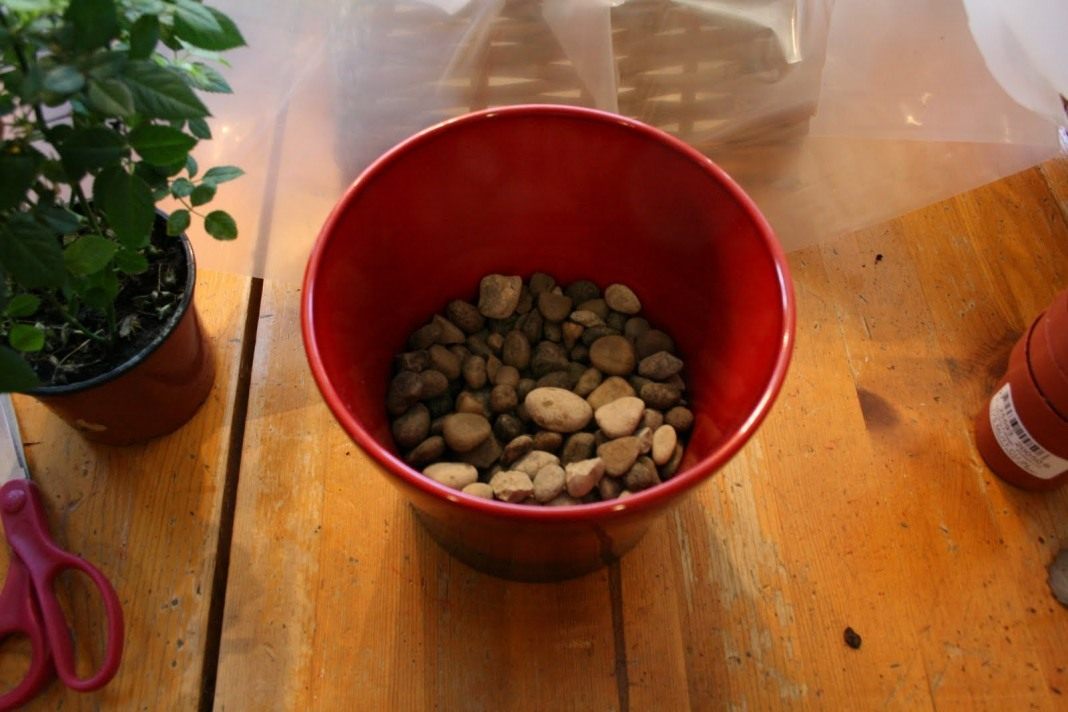
- Fill the bottom of the new container with a 2-4 cm thick drainage layer. Expanded clay, small pebbles, or broken brick can serve as drainage.

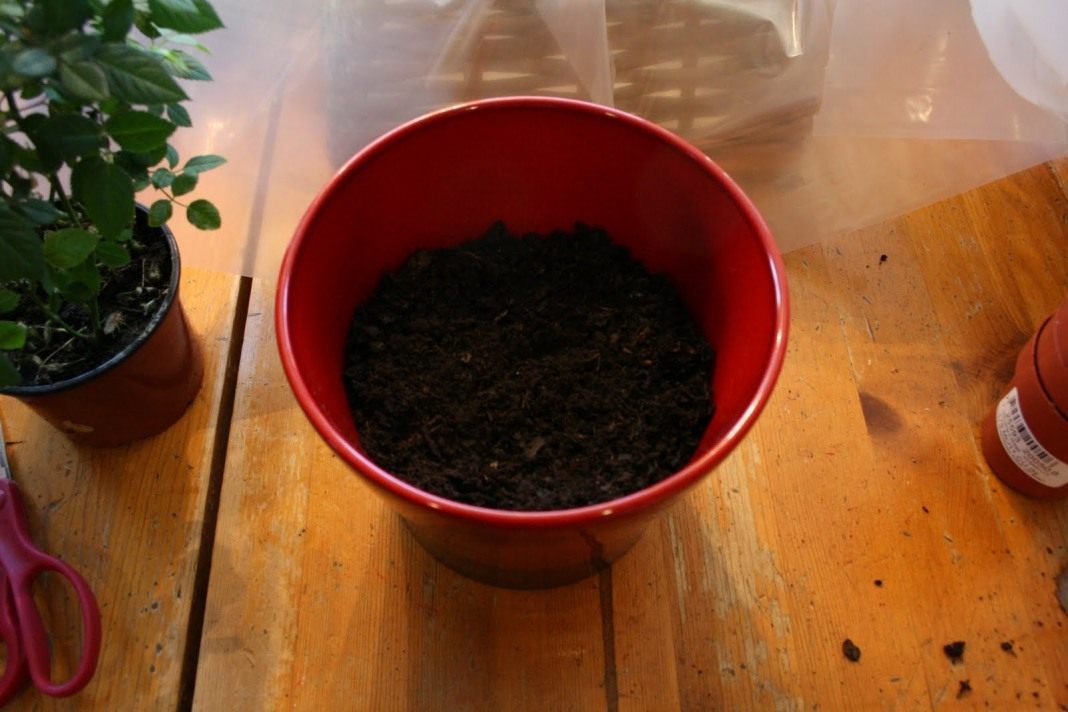
Drainage - Place a layer of potting soil on top of the drainage layer. The width of the soil layer should be approximately equal to the drainage layer.

Priming - Carefully remove the plant from the old container and inspect its root system for diseases, trying to disturb the root ball as little as possible.
- Place the bush into a new pot along with the lump of soil.
- Fill the voids of the pot and lightly press the soil around the flower.
- Moisten the soil.
For several days after transplanting, the plant should be kept in the shade to allow it to adapt more quickly to the new soil substrate.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Frequently asked questions about growing
Bougainvillea is only now gaining popularity among gardeners, so its response to certain growing conditions is not well known.
If the soil where the cutting is planted is dry, you can moisten it, but don't overwater. After two weeks, the cutting will be ready for transplanting into a new potting mix. It's best to use store-bought soil when repotting.
Bougainvillea is an unpretentious indoor plant that always thanks you for creating conditions close to the climate of its tropical homeland with lush and long-lasting flowering.













 The most fashionable flowers of 2025
The most fashionable flowers of 2025 Large ceramic pots and planters: what's the difference and how to choose the right one for your plants?
Large ceramic pots and planters: what's the difference and how to choose the right one for your plants? Beauty and Ease of Care: Top 10 Most Beautiful and Easy-to-Care Indoor Flowers
Beauty and Ease of Care: Top 10 Most Beautiful and Easy-to-Care Indoor Flowers Top 15 Flowers That Last Long in a Vase
Top 15 Flowers That Last Long in a Vase