
Post-emergence potato care is crucial, as it determines how the plant will develop and bear fruit. If preparatory measures are not taken correctly, the potatoes will fail to germinate or will lag in development.
Why are potatoes failing to germinate, and what should you do if the plant isn't growing properly? Below, we'll cover all the specifics of potato planting and the reasons why potatoes may stop growing.
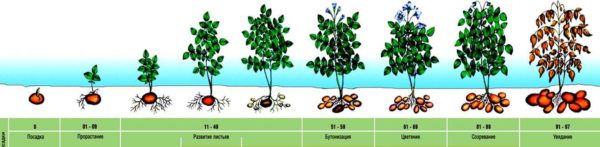
Normal development of potatoes
How many days does it take for potatoes to sprout after planting? This depends on the temperature conditions in the region. Typically, the tubers take about 10 days to sprout after planting. Twelve days is also acceptable. A longer period indicates the plant is lagging behind in its development. But is this true in all regions? No, only farmers living in the south of the country should be alarmed after 13 days without sprouting. In northern regions, sprouting takes at least 15 days, and sometimes as long as 25.
Potato germination time depends on the variety. How long does it take for southern potato varieties to sprout after planting? In warmer climates, they germinate quickly, in less than 10 days. However, if you mistakenly buy potatoes for planting in the north, the plant may die altogether. Northern varieties, on the other hand, are not susceptible to such problems and develop steadily within 15 to 25 days, regardless of the planting location.

Any deviations in the crop's development are a reason to check the growing conditions. All the problems that can arise when growing potatoes are discussed below.
Problems that may appear early in development
Potatoes are sensitive to frost, temperature fluctuations, drought, and nutrient deficiencies. Therefore, even the slightest deviation from proper care can cause the crop to stop growing or even die.
The main problems that may arise immediately after planting seeds:
- Sprouts aren't appearing. This indicates a lack of nutrients in the soil or insect damage to the tubers. Another common cause of failure to sprout is the wrong variety or seed selection.
- The potatoes have sprouted but aren't growing. This is typical in cold regions with sharp temperature fluctuations between day and night. The soil may retain heat at night, but the air is detrimental to the young sprouts, preventing them from growing. The lack of growth may also be due to inadequate care.
- The plant develops only in soil. Why aren't the potatoes sprouting, but the tubers are growing? Most likely, the variety is a southern variety and can't thrive in cold conditions, but the soil temperature and nutrient content are sufficient for tuber development. Simultaneously with the emergence of sprouts, the tuber begins actively "whelping"—developing numerous small roots, which hinders the growth of the stem. Why are the potatoes "whelping"? It could be a poorly selected or weak potato variety, or unfavorable outdoor conditions. Or the potatoes may have been planted too deeply.
- Sprouts often appear, but in small numbers—only half or even a third sprout. The remaining tubers sprout later, after 10-15 days. Why do potatoes sprout unevenly? This can be due to poor seeding or uneven fertilizer distribution. Sometimes farmers confuse varieties, planting early and later varieties together.
Germination problems can be easily prevented by providing proper care for your potatoes. How to do this is described below.

What causes abnormal growth?
The above list doesn't cover all the root causes that can slow or stop potato growth. There are many more factors that influence crop growth.
Potatoes don't sprout - reasons:
- Small seed material. Do not plant tubers that weigh less than 25 grams. The exception is potato varieties with small tubers.
- Poor-quality seed material. If the tubers have black spots, cuts, or serious deformations, they are unlikely to produce shoots.
- Seeds purchased at grocery stores. Vegetables in supermarkets are treated to extend their shelf life. Preservatives reduce the viability of the tubers, making them less likely to sprout than potatoes purchased at a grocery store.
- Pest attack. Mole crickets and some other insects (and their larvae) bore holes in tubers and can destroy the entire crop.
- Nutritional deficiencies. Minerals must be supplied to the plant regularly. Fertilizing and fertilizing the soil before planting are necessary. If these measures are not taken, growth will slow or stop.
Weather conditions have the greatest impact. If drought sets in, the plant dies. Even if the buds are well-nourished, they cannot function properly because nutrients cannot reach the root system without moisture. Excess moisture during heavy rains is also dangerous. It can cause the tubers to rot, preventing them from sprouting at all.

If frosts or nighttime cold spells occur suddenly, potato germination will be slower. They may die if the soil temperature is too low or stop developing, entering "dormant"—a state in which tubers remain dormant during winter storage.
Once you understand why your potatoes are sprouting unevenly, you should move on to fixing the problem.
How to eliminate plant growth retardation
Potatoes aren't sprouting—what should I do? Even if the potatoes have already been planted, you can still improve their germination conditions by watering and fertilizing them properly. Replanting the tubers is also possible, although it takes a lot of time and effort and doesn't always resolve the root cause.
It's best to begin actively fertilizing the soil, hilling it, and covering the seedlings with a tarp made of a special material. Covering the crop is especially important. Covering the plantings should be done at night, before the evening chill sets in. This is especially important in spring and during the colder periods of summer. Covering reduces the risk of frost damage to the seedlings and allows them to develop normally even during very cold spring nights.

Don't overdo it with fertilizing. Watering with fertilizer dissolved in water once every two weeks is sufficient. The water used for dilution should be warm, and don't pour too much into one spot.
All weeds should be removed from the soil, as they can drain nutrients and hinder plant growth. If the plants haven't been treated for pests and diseases yet, they should be treated as well. Until the seedlings have sprouted or are two weeks old, you can safely cultivate the soil.
The last resort is to dig up the beds and remove any bad tubers. Unsprouted, rotten, or pest-infested tubers will only harm their neighbors by rotting. If the seeds were planted too close together, some will need to be removed and others thinned out. Then, development can begin with renewed vigor.
If, even after these measures, the potatoes haven't sprouted, what should you do? Replace the seed completely. Potatoes that don't sprout, even after proper planting and consistent care, are simply defective and unviable.
How to properly prepare crops for planting
By understanding why potatoes aren't sprouting properly, you can easily prevent delayed potato growth. You should begin preparing the tubers a month before planting.
The seed material needs to be selected.
The following are removed:
- small tubers;
- seeds with damage;
- rotten units;
- specimens affected by diseases.
It's crucial to plant the seeds correctly. Planting the seeds too deeply is the main reason why potatoes don't germinate and instead produce tubers in the ground. The tubers should be 10 cm above the soil surface. The tubers can only be planted when the soil temperature reaches 10 degrees Celsius (50 degrees Fahrenheit). Soil warming is measured with a separate thermometer; soil and air temperatures are not the same. The soil warms up to 10 degrees Celsius in late spring, when the air temperature is around 20 degrees Celsius (68 degrees Fahrenheit).
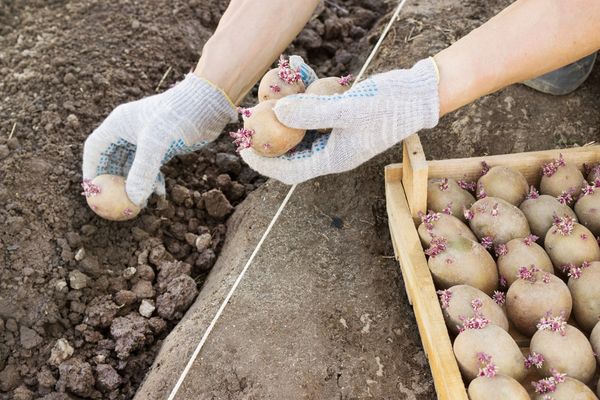

Before planting, it's advisable to treat the tubers with copper sulfate. This will reduce the crop's risk of disease.
After planting, you need to regularly:
- water the sprouts;
- hilling up the bushes;
- feed the plants;
- carry out procedures aimed at pest control.

Reviews
Dmitry K., 39 years old, farmer:
"Before sowing seeds, I select the affected tubers, treat them with copper sulfate, and plant them as soon as the soil warms up to 10 degrees Celsius. This is enough for the sprouts to emerge simultaneously and on time. Further development depends on care. Less-treated areas develop poorly. Priority areas, where my workers constantly mound, water, and cultivate, naturally yield more, and the plants there are more developed."
Anastasia F., 78 years old, vegetable grower:
"My potatoes used to sprout poorly because I barely followed the planting guidelines. I planted the tubers 'on a hunch,' but it turned out I was too deep. Once I learned all the planting guidelines and put them into practice, the plants grew much faster: they sprouted twice as soon, yielded several times more, and there were almost no unsprouted tubers."
Georgy N., 52 years old, vegetable grower:
"I always take good care of the tubers I plant. I water, fertilize, and treat them regularly and timely for pests. I highly recommend treating the soil for insects beforehand. They can destroy the entire harvest at the end of summer or the entire seedlings in the spring if they aren't protected. Even if all planting instructions are followed, half the tubers may die."
If you follow simple rules for planting and caring for potatoes, germination problems will disappear completely. Much knowledge comes with experience, so if the tubers don't sprout the first time, don't give up on vegetable gardening right away. With time, anyone can learn to properly care for the crop.
 Potato planting dates according to the moon for 2021 in the Moscow region
Potato planting dates according to the moon for 2021 in the Moscow region Potato varieties: names with photos, descriptions, and characteristics
Potato varieties: names with photos, descriptions, and characteristics When to dig up potatoes in 2020 according to the moon and how to best store them
When to dig up potatoes in 2020 according to the moon and how to best store them List of potato varieties with names, descriptions, and photos
List of potato varieties with names, descriptions, and photos