Philodendrons are plants in the Araceae family that grow in the form of herbs, vines, and shrubs. They are native to Brazil, the Americas, and the Antilles. NASA has listed the philodendron as one of the most effective air purifiers. The plant gets its name from its special fondness for trees. In its natural habitat, it uses them as support to reach closer to the sun.
The plant is characterized by a wide variety of species. They differ not only in appearance but also in their environmental preferences. Therefore, different species require specific care. You can appreciate the diversity of philodendron by examining its species, including their names and photos, and choose the ones that best suit your needs.
Characteristics of Philodendron and names of species with descriptions
Philodendron is an evergreen perennial. Some species are capable of flowering. The inflorescence consists of a spadix and a spathe, characteristic of all Araceae. The plant's flowers have no ornamental value. Moreover, when grown indoors, they bloom deformed.
The root system is complex. It consists of underground and aboveground roots. Aboveground roots, in turn, are divided into two types. Some help the plant attach to its supports, while others provide additional nutrients.
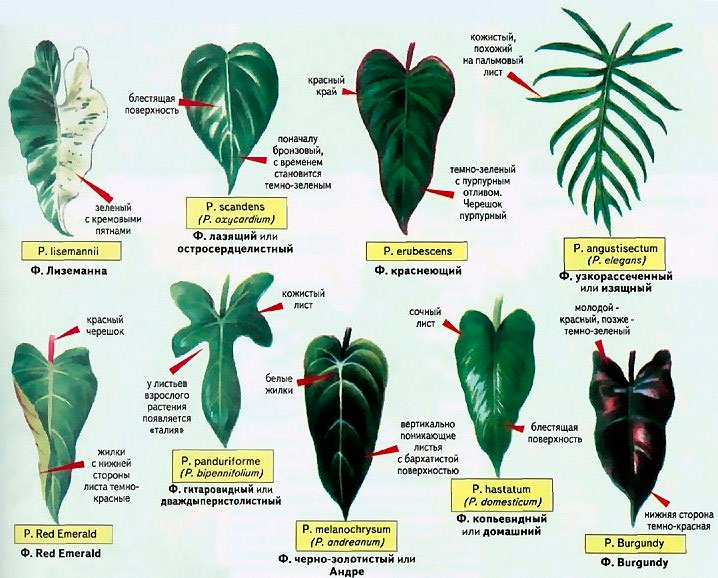
The stems are fleshy and climbing. They usually become woody at the base. The leaves are large and leathery. Color and shape vary depending on the species. They appear thick, but are actually easily damaged.
Climbing
Philodendron climbing is a variety of Philodendron spp. It is distinguished by its long, slender stem, reaching over 3 meters. The leaves are heart-shaped with a sharply pointed tip. The surface of the blades is glossy. In young leaves, the surface is bronze, but with age it becomes bright green. The leaves are attached to elongated petioles.
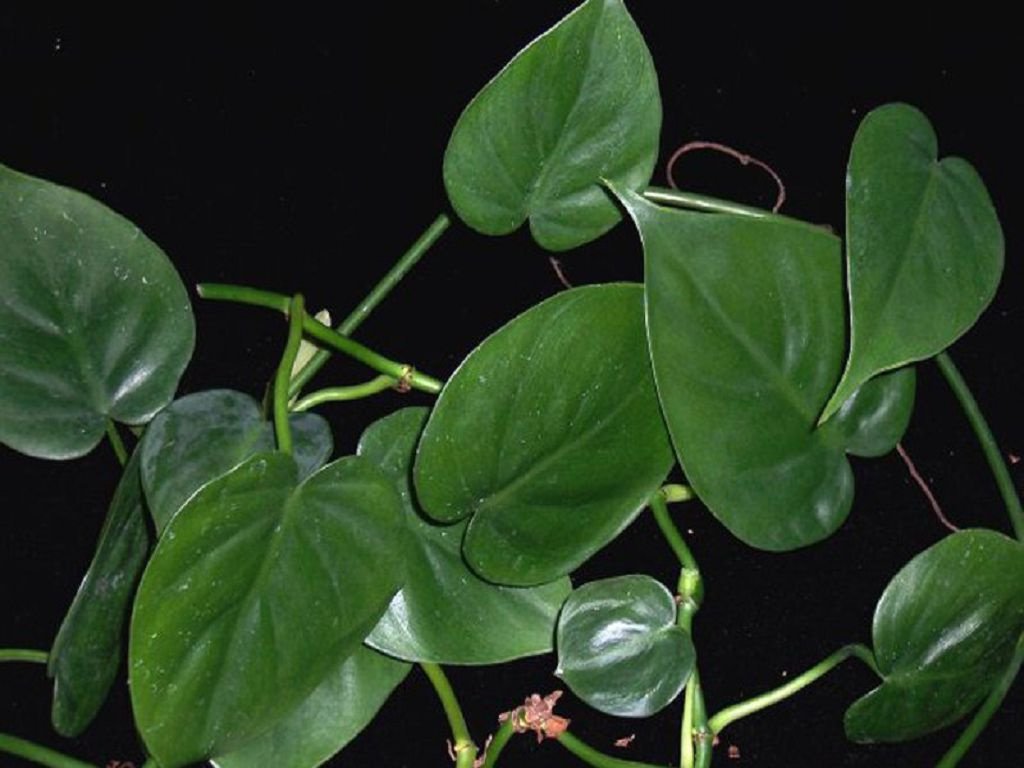

This variety became the progenitor of many hybrids. Many cultivars have a metallic sheen on the leaf surface or a brownish tint. Climbing philodendrons are considered beautiful bloomers, but it is impossible to achieve their flowering in a home environment.
Sello
This species is also known as the bipinnate and bipinnate philodendron. Young plants have entire, heart-shaped leaves, a delicate light green. As they mature, the leaves change shape, becoming pinnately dissected and dark green.
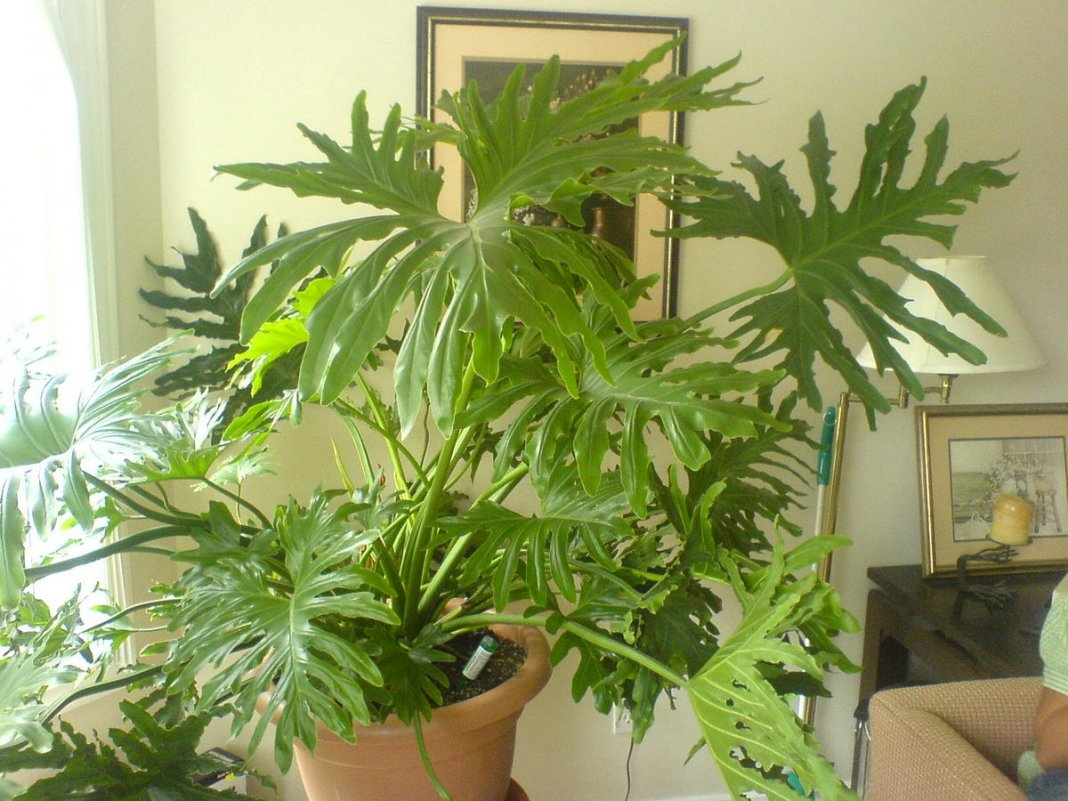

Sello is a flowering species. During flowering, the plant has a unique ability to increase the air temperature around it. Sello flowers emit a pleasant, sweet aroma. In some countries, the fruits of this species are used as food, and the juice from the leaves is used for medicinal purposes.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Scandense Brazil
Scandens Brasil is a variety of Climbing Philodendron. It differs from the original only in its leaves.
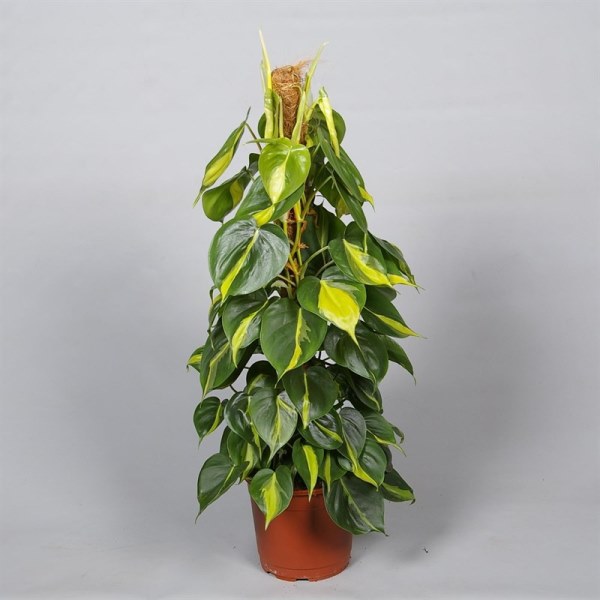

Scandens Brasil varieties have larger leaflets. They are also heart-shaped, but the leaf edges are more rounded. A distinctive feature of this hybrid is its coloring. It combines dark green and yellow-green hues. The lighter shade can appear as a narrow stroke or a diffuse spot. Each leaf pattern is unique. Some growers manage to achieve a uniform yellow-green coloration on individual leaves.
Blushing
Philodendron blushensis is a compact vine with an unusual coloring. Its name comes from the reddish hue that appears on the petioles, internodes, and, in some varieties, even on the leaves. Unlike other philodendrons, this species is relatively unbranched. The plants are resilient to adverse environmental conditions and have a high vitality.
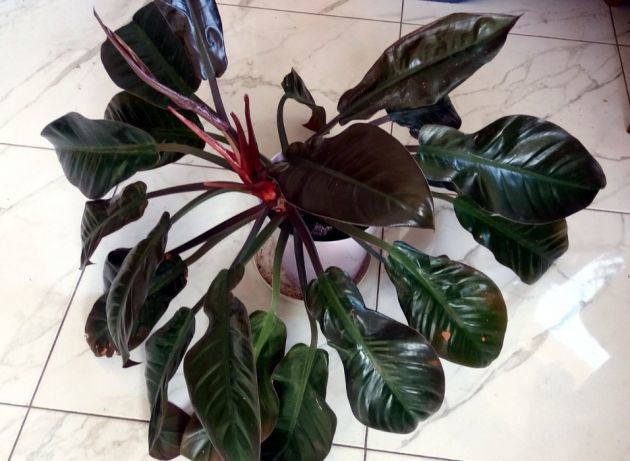

Numerous hybrids have been developed from the Reddening variety. They vary in leaf color, from bright green to purple. Some varieties feature marbled foliage.
Caring for Philodendron at Home
Home care involves creating a microclimate as close as possible to the plant's natural conditions. To avoid potential growing problems, it's important to follow the advice of experienced specialists.
Soil and pot for planting
The plant is grown in light soil. To prepare the substrate, mix the following ingredients:
- leaf soil – 3/5;
- turf soil – 1/5;
- sand – 1/5.

A philodendron's pot must be well-ventilated and moisture-draining. Therefore, it's best grown in a clay or ceramic pot. The plant shouldn't feel cramped. Each time you repot, use a pot that's 10% larger than the previous one. The pot should have drainage holes in the bottom. A drip tray to collect excess moisture is essential.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Location and lighting
It's commonly believed that this flower isn't fussy about lighting conditions. This isn't entirely true. Only the Philodendron splendens and Philodendron rufensum (Blushing Philodendron) don't require intense light. Other species can tolerate partial shade, but experts recommend growing them in bright, filtered light.
On a south-facing side, it should be placed in the back of the room, away from the window. Direct sunlight is harmful to the plant. A lack of light also affects its appearance: the leaves become smaller, the stems become elongated, and variegated varieties lose their decorative pattern.
Temperature
The optimal temperature range for growing this flower is considered to be between 22°C and 30°C. In conditions of high humidity, the plant tolerates higher temperatures well.

Around January, it enters dormancy, which lasts until mid-March. During this time, it's best to lower the temperature to 15°C. However, the transition should be gradual, so the plant doesn't experience any discomfort.
Philodendrons do not tolerate cold very well, especially the Golden-Black, Wrinkled, and Warty varieties. The critical minimum for these species is 18°C (64°F). For other species, the critical minimum is 13°C (55°F).
Watering and air humidity
The plant's native habitat is tropical forests, so it requires high humidity. To achieve this, the plant should be misted regularly (except during periods of stagnation). It's a good idea to place a container of damp pebbles or expanded clay under the pot.
Philodendrons are watered frequently and with ample amounts of water. In summer, water every two days. In autumn, gradually reduce the frequency to once a week by winter. However, don't reduce the amount of water; even during the dormant period, the soil should not dry out.
For irrigation, use soft, settled water. Bring it to room temperature before use.
Over time, the philodendron will need support. It's advisable to purchase a special trunk made of coconut fiber with moss inside. By moistening the moss, you can provide the plant with additional moisture.
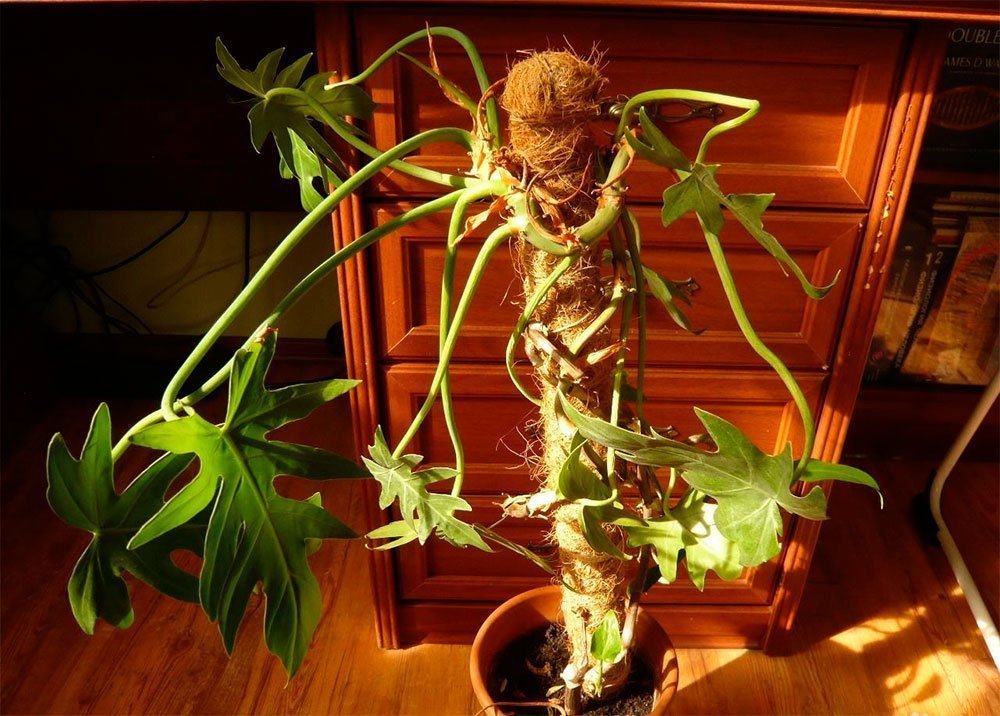

Regular hygiene procedures also help increase humidity. Dust should be regularly removed from the plant's leaves and stems with a damp cloth. Some gardeners recommend periodically placing the plant under a warm shower. A fine-mist spray can be used to clean the velvety leaves.
Fertilizers and feeding
Fertilize the plant in spring and summer, during the active growth period. If the dormant period is not observed, fertilizing is acceptable year-round. However, in autumn and winter, fertilization frequency should be reduced by half.
Transfer
Scheduled repotting is carried out in the spring. Young plants should be repotted annually. Mature philodendrons are repotted every 3-5 years, but the topsoil should be replaced annually.
Unscheduled transplants are carried out in the following cases:
- roots growing through the drainage holes of the pot;
- high concentration of salts in the soil, which is expressed by a white coating on the surface;
- severe soil compaction;
- moss on the surface of the substrate.
Potential problems when growing philodendron
When growing a philodendron, a gardener may encounter the following difficulties:
| Problem | Cause |
|---|---|
| Drying of leaf tips and edges | Low humidity, dry air or exposure to drafts. |
| Brown leaf edges | Overwatering. |
| Small, dull plates | Insufficient lighting. |
| Dry beige spots on leaves | Sunburn. |
| Folding the edge of the sheet down | Excess fertilizer. |
| Yellow and small upper leaves | Not enough fertilizer. |
| Blackening of leaves | Low temperature. |
Yellowing and shedding of lower leaves is a natural process that accompanies the aging of a flower. Philodendrons, like other members of the Araceae family, are prone to guttation—the appearance of droplets of liquid on the stems.
Methods of propagating indoor flowers
There are several ways to propagate the flower. At home, philodendrons can be propagated by cuttings, leaves, seeds, and air layering.
Cuttings and leaves
The material for cuttings is apical or lateral shoots with 2-3 full leaves. Stem parts with aerial roots root much faster.
The cuttings are placed in a moist mixture of sand and peat. They are kept in conditions of high humidity and warm temperatures until they are fully rooted. The cuttings are then replanted like mature philodendrons.
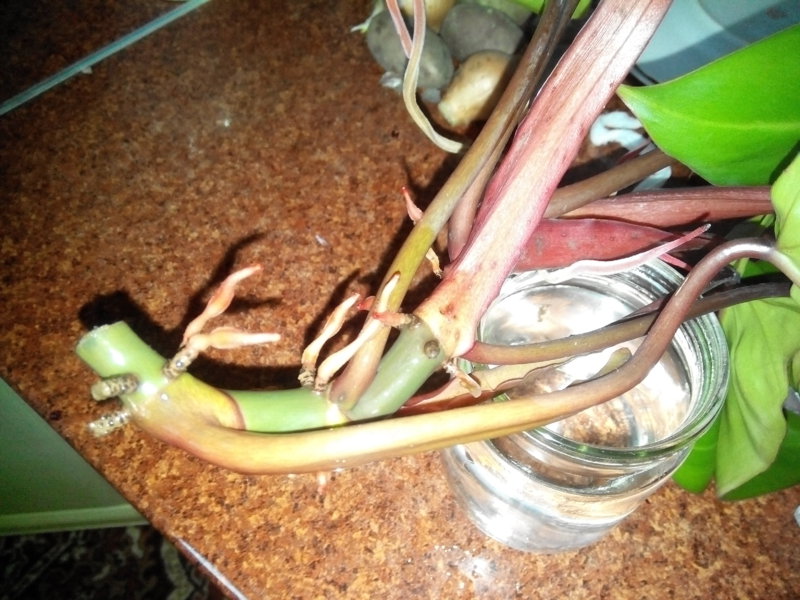

Leaf propagation isn't the most popular method because it often rots before it has time to root. However, if other propagation material is unavailable, you can try growing a philodendron from a leaf.
The planting material is a large leaf with a heel, cut from a mature, healthy plant. The rooting process is similar to rooting cuttings.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Air layering
Air layering is suitable for philodendrons with vertical stems. This method is very simple and considered the most effective.
Place a flowerpot filled with suitable soil near the philodendron. Then select a stem, preferably one with aerial roots, and root it in the additional pot. The base of the stem should remain on the parent plant, the middle should be buried in the substrate, and the tip should remain above the soil surface. For security, the stem can be pinned to the soil with a staple.
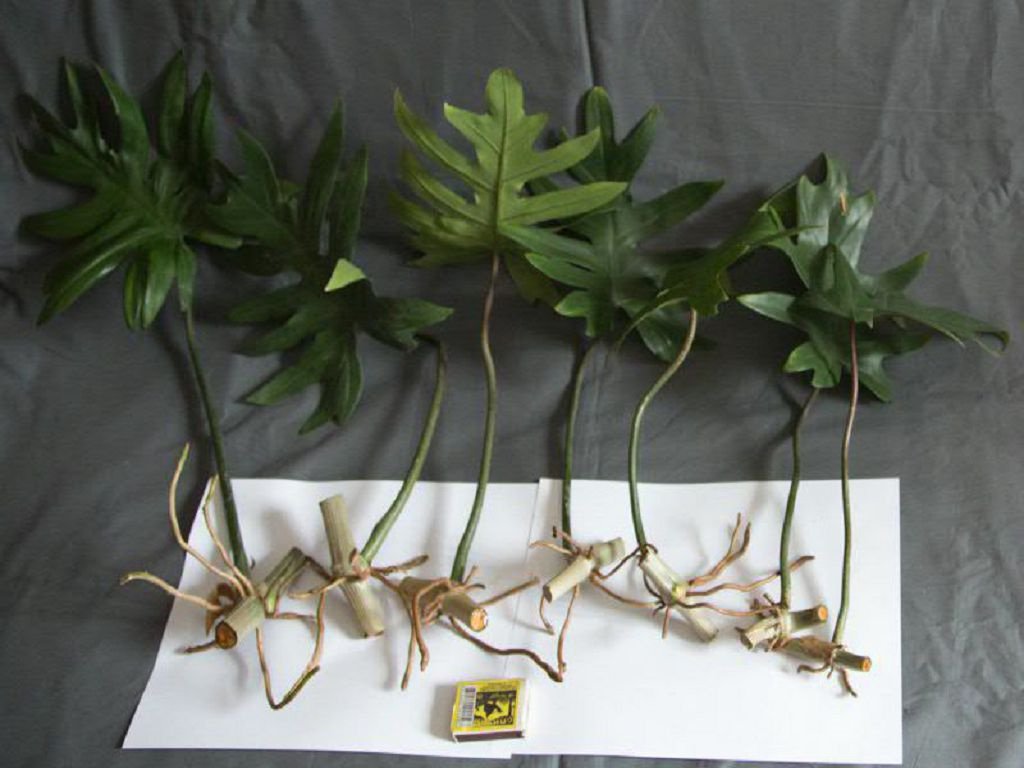

The cutting requires no additional care, as it draws its nourishment from the main plant. Once the stem is well-rooted, it is cut from the mother plant.
Seeds
Tree-like plant species are propagated by seed. Fresh seeds germinate within a week of sowing. They are germinated in peat-sand soil after being soaked in water for 12 hours.
For successful germination, seeds are germinated in greenhouse conditions: at high temperatures and under glass. The seedlings are not buried deep, but simply sprinkled onto the soil. The seeds are sprayed daily with a fine mist spray, and condensation is removed from the glass.
After germination, the glass is removed, but the flowers continue to grow under the same conditions. When the seedlings produce a couple of true leaves, they are pricked out into individual containers. Once established, the philodendrons are replanted in the spring.
Frequently Asked Questions
Philodendron is a creeping houseplant used for interior decoration. Care for different varieties and species of this flower varies. Since the vine can take up a large amount of space over time, this should be taken into account before planting.

 The most fashionable flowers of 2025
The most fashionable flowers of 2025 Large ceramic pots and planters: what's the difference and how to choose the right one for your plants?
Large ceramic pots and planters: what's the difference and how to choose the right one for your plants? Beauty and Ease of Care: Top 10 Most Beautiful and Easy-to-Care Indoor Flowers
Beauty and Ease of Care: Top 10 Most Beautiful and Easy-to-Care Indoor Flowers Top 15 Flowers That Last Long in a Vase
Top 15 Flowers That Last Long in a Vase