 Due to iodine's antiseptic properties, it is often used to treat plants. It helps kill pests in garden plots. It can also be used to treat greenhouse tomatoes against late blight, root rot, and powdery mildew.
Due to iodine's antiseptic properties, it is often used to treat plants. It helps kill pests in garden plots. It can also be used to treat greenhouse tomatoes against late blight, root rot, and powdery mildew.
The prepared working composition is used to feed seedlings to increase yield.
What is late blight?
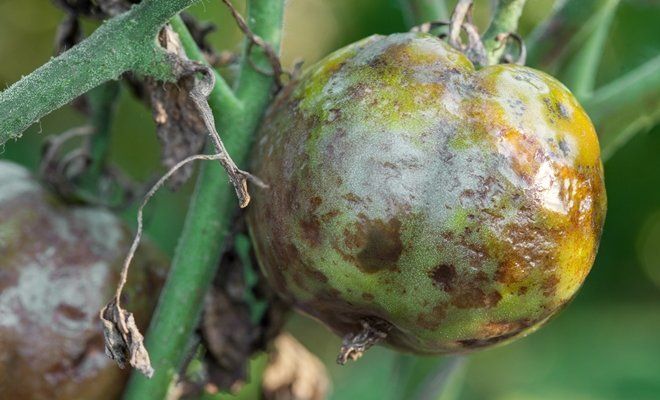
Late blight (phytophthora) is a dangerous fungal infection that causes plant death. Once the blight has taken hold, the microorganisms completely destroy vegetable crops. The disease is especially dangerous to crops from the nightshade family, but other vegetation also suffers from the spreading infection.
Late blight develops due to high humidity or contaminated seeds. To prevent the fungus, gardeners treat the seed and soil. The infection also begins to spread at low temperatures. The fungus attacks both outdoor and greenhouse crops.
Signs and causes of the disease
Late blight appears on plant foliage as early as three days after infection. In damp weather, the fungus spreads more rapidly. Dirty-brown spots appear on the leaves, followed by a grayish coating (spores). In dry weather, the foliage dries out quickly; in damp weather, it rots. Late blight is spread by asexual spores (zoosporangia), which are resistant to environmental factors, allowing the fungus to persist in the soil and air for a long time. Favorable conditions promote increased zoospore production:
- humidity;
- fogs;
- watering;
- rains;
- dew.
Spores spread through plant tissue. If moisture remains on the leaves and stems, they germinate within 4 hours. Soil moisture promotes faster infection, as moisture remains in contact with the roots for longer.
Iodine deficiency in tomatoes reduces their resistance to disease. Iodine deficiency occurs due to a lack of the element in peat and podzolic soils. Deficiencies are also observed in light sandy loams and substrates with a lack of organic matter. Acidic soils are unfavorable for iodine, as it penetrates deeper layers where the tomato root system cannot reach. Iodine deficiency in plants causes the following negative changes:
- fruit sets poorly;
- the ovaries are rotting;
- red and yellow vegetables do not have a bright color;
- the vegetative mass is pale;
- stunted growth;
- flowers, fruits and seeds are poorly formed;
- Tomatoes have weak protective functions against fungal diseases.
Late blight affects the entire plant – the fungus spreads through the root system, leaves and seeds.
The beneficial properties of iodine against disease
Iodine is a natural antiseptic. This trace element normalizes plant physiological processes, including respiration, photosynthesis, and nitrogen-water metabolism. Iodine is involved in the synthesis of certain proteins and amino acids (it is a constituent).
The preparation normalizes the development of garden crops, budding, and fruit set. Iodine supplements are used to support the vital functions of:
- flower crops;
- strawberries;
- potatoes;
- tomatoes;
- eggplants;
- cucumbers;
- beets;
- cabbage;
- Luke;
- corn;
- sunflower;
- salad greens.
The following are treated with iodine solution:
- Seed material - to stimulate germination.
- Seedlings - to strengthen the immune system.
- Crops during vegetation - disease control, increasing yield.
Thanks to this product, plants become more resistant to diseases and their nitrogen absorption is improved.
Fertilizing tomatoes with iodine solution
For preventative purposes, universal iodine fertilizers are recommended. This is especially important for cabbage, cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, and garden greens. Iodine is used both in greenhouses and in open fields.
Preparation of fertilizer:40 drops of iodine are dissolved in a 10-liter container with water.
Usage:Apply 500 ml of the product to each bush that has developed its first bloom. Repeat treatment after a month.
Iodine and brilliant green
Brilliant green contains copper compounds, meaning it has an antiseptic effect on tomatoes. Brilliant green is an excellent fertilizer with a rich microelement composition. To combat root rot on tomatoes or cucumbers, it's necessary to harvest the crop first.
The bushes are watered with a prepared solution: half a teaspoon of brilliant green is dissolved in a 10-liter container of water.
For preventative purposes, use an iodine solution: dissolve half a teaspoon of iodine in a 10-liter container of water. The solution is applied through a sprayer.
Mixing one part iodine or brilliant green with two parts water creates a healing solution for treating plant stems. Apply the solution to the stems 5 cm above the ground with a brush or cotton swab. The fungal infection is killed after the second treatment. A total of three treatments, performed weekly, are recommended.
Downy mildew on tomatoes can be eliminated with a prepared solution containing brilliant green. Add the following to a bucket of water:
- whey or milk - 2 liters:
- brilliant green - 10 ml;
- urea - 50 g.

During the season, garden plants are treated three times (at 7-day intervals) from the beginning of flowering. For preventative purposes, the solution is suitable for cabbage, onions, shrubs, cucumbers, and other crops.
Preparing a remedy to combat powdery mildew:
- milk - 100 ml;
- iodine - 3 drops;
- water - 1000 ml.
The components are mixed, and the resulting mixture is used to spray greenery. Treatments are carried out once a week.
The following solution helps against late blight:
- 10 liter container with water;
- 40 drops of iodine;
- 1 tbsp. hydrogen peroxide.
Spray the leaves and stems of plants (keeping the foliage and soil moist). Apply four times per season, once a week after flowering. The prepared mixture not only kills fungal infections and diseases but also rejuvenates plants and prevents yellowing of the foliage.
You can fight late blight with a prepared solution containing brilliant green:
- brilliant green - 40 drops;
- ten-liter container with water;
- The components are mixed and sprayed through a spray bottle.
The composition is sprayed generously on plants (once a week, 4 times per season).
Spraying and fertilizing are carried out in cloudy weather or in the evening.
Iodine and ash
Ash-iodine treatment is used to prevent late blight on tomatoes and other garden crops. It's especially important in warm but damp weather. To prepare the solution, you need:
- 10 liters of water;
- a glass of ash;
- 10 drops of iodine.

Before applying the prepared solution to the crops, water them thoroughly. This ensures the solution is absorbed quickly and does not burn the roots. After mixing the mixture, water the soil around the plants. The iodine disinfects the soil, destroys spores, and the ash provides the plants with beneficial micronutrients and strengthens their immune system.
Preventive measures
To prevent the disease, begin by disinfecting the seeds before planting. Dissolve a drop of iodine in one liter of settled water. Soak the planting material in this solution for seven hours. Afterward, dry the seeds and sow them in greenhouses or garden beds.
Seedlings are also watered with an iodine solution. Small sprouts are fertilized with a mixture made from:
- 3000 ml of water;
- 3 drops of iodine.
The prepared solution is used to strengthen the immune system, form lush bushes, abundant flowering and fruiting. When the seedlings are already planted in open ground and a sudden cold snap with rain comes, each sprout is watered with one liter of the prepared solution for fungal infection.
Recipe: Add 20 drops of iodine to a 10-liter bucket of water. The plants will withstand inclement weather. Twenty-one days after the preventative watering, spray the tomatoes with an iodine solution to prevent late blight.
When treating and preventing late blight with iodine, it's important to adhere to the recommended dosage and timing of treatments. Excessive amounts of the product undermine the health of plants. Excessive amounts of the element lead to foliar dieback.


 Fertilizing tomatoes with salt
Fertilizing tomatoes with salt How to fertilize vegetable seedlings with regular iodine
How to fertilize vegetable seedlings with regular iodine When and how to sow tomato seedlings in March 2024 – simple and accessible for beginners
When and how to sow tomato seedlings in March 2024 – simple and accessible for beginners Catalog of black tomato varieties
Catalog of black tomato varieties