Most rose varieties are not adapted to harsh winters, but there are species that can withstand harsh climates, but they require the help of a gardener.
Do roses require pruning?
Pruning roses in the fall is necessary for several reasons. Pruning ensures:
- a riot of rose blooms next year;
- full wintering of the bush without numerous shoots that will weaken the bush during wintering;
- giving the bush a compact appearance for more convenient shelter for the winter;
- facilitating the task of the roots in providing shoots with nutrients;
- removal of weak and diseased branches with faded buds and pests that have settled on them;
- plant rejuvenation;
- the bush subsequently acquires a beautiful appearance.
If you don't prune roses, the top may die off with age, and root shoots that aren't removed in time will fill the center and make the bush look untidy.
Basic rules of pruning
It's customary to leave no more than seven shoots on a bush for the winter. The process of removing and shortening stems begins when the outside temperature reaches a stable temperature of around -2 degrees Celsius. In temperate climates, this occurs in late October or early November.

Pruning tools
The primary tool for thinning bushes is pruning shears, but experienced gardeners also use a sharp knife. A handsaw may be needed to cut thick branches larger than 2.5 cm in diameter.
Preparing for pruning
By the end of September:
- Stop watering and loosening the soil under the roses to slow down the growth of shoots.
- Late buds are not allowed to bloom by pinching them.
- If there is heavy rain, a canopy is stretched over the rose garden.
- The bushes are hilled to a height of 10-20 cm.
Pruning technique
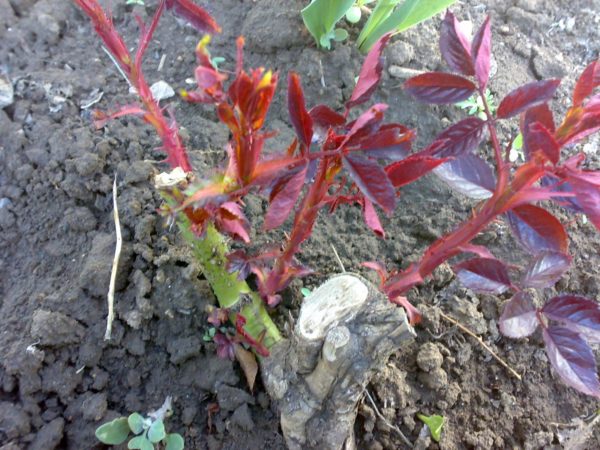
How to prune a shoot correctly? To begin the process, in addition to pruning shears, you'll need the following: garden pitch, heavy gloves to protect your hands from thorns, and a pink solution of potassium permanganate to disinfect the tools. Basic rules:
- the cut is made 1-1.5 cm above the bud at an angle of 45 degrees;
- the cut is made in one movement, without burrs;
- Do not make a cut above a bud facing inside the bush.
The cut wound should be immediately sealed with garden pitch to prevent infection and bush rot. After pruning, remove not only excess branches but also fallen leaves and other debris around the rose bushes, which pests could use for overwintering. After pruning, treat not only the plants but also the soil beneath them with fungicides.

Types of pruning
There are several types of pruning. These are:
- Sanitary pruning, in which the bush is thinned evenly so that one shoot does not shade another.
- A rejuvenating treatment that leaves stumps with 2-3 buds each. It's used on older bushes.
They also produce pruning the bush in autumn When planting, the shoots are shortened, leaving three buds. If the root system is exposed, the roots are also shortened by 3-5 cm to stimulate lateral root growth.
Pruning times vary by region
Pruning times vary across regions. Autumn in the Leningrad region is known for its rain and wind. A dry, clear day in mid-October is chosen for pruning branches and removing excess shoots. High-quality tools are essential for achieving smooth, even cuts on the bushes. Wounds are immediately treated with garden pitch or sprinkled with ash. After a few weeks, the plants are covered with sawdust, peat, or covering material.
In Siberia and the Urals, winter comes quickly and is characterized by sharp temperature drops. Therefore, roses grafted onto wild roses will better withstand extreme conditions in these regions. A gentle pruning of shoots is done at the end of September, and the rose bushes are covered after two weeks.
Pruning methods
In the fall, perform gentle pruning to minimize damage to the plant. Beginner gardeners may find various methods of pruning interesting.
Traditional pruning
This method is suitable for pruning all types of roses. Remove:
- young root shoots;
- unripe shoots;
- weak branches;
- dried stems;
- branches with visible signs of disease.
After thinning, the plant has 5-7 healthy shoots that require minor shortening.

Severe pruning
This involves cutting the bush almost to the base, leaving only a few stumps with 2-3 buds. In the spring, vigorous shoots form, blooming 1-1.5 months later than with light pruning.
Moderate pruning
When using this method, the stems are shortened by half. Four to five buds remain on the stem. The following summer, the plant produces long stems suitable for cutting, and the bushes bloom slightly later than with light pruning.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Light pruning
In this case, the rose bush stems are trimmed back by 1/3, leaving up to 10 buds. This method is not suitable for rose varieties that grow quickly. The following June, the bush will delight you with abundant blooms, but the short branches that have grown will not allow you to create a bouquet.
Pros and cons of fall pruning
The positive aspects of shortening shoots in the fall include:
- profuse flowering;
- bush rejuvenation;
- accumulation of nutrients by the plant;
- strong root system.
The disadvantages will appear in the following cases:
- if the shortening of shoots took place from the beginning of August, and unripe shoots froze;
- After the frosts, the warmth returned and the buds began to grow.
Methods for pruning different varieties of roses
Abundant flowering of roses is ensured by different pruning methods, which vary depending on the plant variety.
How to prune a climbing rose for winter
Many gardeners have a question: is it necessary? trim the shoots of climbing plants roses before covering them for the winter?
Climbing roses can be divided into two groups: once-blooming and repeat-blooming. Stem pruning methods differ for each group. For climbing roses, 3-4 replacement shoots are left in the fall, and faded and dried stems are pruned. For large-flowered roses, stems are shortened by 1/3. The cuts are then treated with pitch or ash.
Before removing the roses from the support, the ground is covered with spruce branches or a wooden board is placed on it, the roses are placed on the substrate and covered with spruce branches, roofing felt, and covered with earth or sand.
How to prune a floribunda rose
Floribunda rose varieties are the result of repeated crossing of different rose varieties. They produce bushes of varying sizes, from large to compact. They bloom with single, semi-double, and double flowers. Floribundas are recommended for inexperienced gardeners for creating hedges, as they will delight with their long-lasting blooms.
Floribunda roses require pruning for rejuvenation. Both severe and moderate pruning are based on this group's ability to quickly recover and send up shoots with flower stalks from the base of the bush. However, such drastic pruning is more suitable for spring work. In the fall, all diseased, dry, and immature stems are removed, leaving a few of the strongest ones and trimming them back to a height of about 50 cm. Light pruning is not suitable for these varieties.
How to prune groundcover varieties
Popularly known as carpet roses, they form a carpet of flowers. They are widely used in landscape design. They can be grown without pruning, but pruning groundcover roses in the fall increases flowering the following season and gives the bush a more decorative shape. Here are step-by-step instructions:
- the cut is made at an angle of 45 degrees, 0.5-1 cm above the bud;
- the bud should be on the outside, the cut goes away from it, and not towards it;
- unripe, dried and diseased branches are cut out with sharp pruning shears;
- Strong stems are shortened by 15-20 cm.
The wounds are treated with a disinfectant.
How to prune park shrub roses
Park shrub roses are a beautiful addition to any park or garden. They grow up to 1.5 m tall and bloom continuously for a month. In autumn, the leaves are removed from the bushes and under them. Small shrub roses are pruned to 10 cm, removing the blooms, while taller shrubs are pruned to 30 cm.
How to prune hybrid tea varieties
These varieties were developed through selective breeding in the mid-19th century. They are prized by gardeners for their variety of colors, flower size, and resistance to temperature fluctuations. These varieties are suitable for cut flowers, producing one flower per stem. Pruning hybrid tea roses for the winter is done to facilitate protection during the cold season. Shortening of shoots is moderate or gentle, as the main pruning will be done in the spring to remove frozen and damaged stems.
How to prune polyanthus roses
These varieties are the result of selective breeding. Their parents are the Chinese tea rose and the Japanese dwarf rose. Polyanthus roses are low-growing shrubs, approximately 50-70 cm tall. They are used as border decorations in flower beds and to create group flower arrangements. Polyanthus roses are pruned as follows:
- remove diseased and young shoots;
- for varieties with small flowers, 2-3 buds are left on strong stems and 1-2 on weak ones for the winter;
- For flowers with large flowers, the mature shoots of the current year are removed by 1/3, for older ones, light pruning is performed.
How to prune miniature roses
These groups of roses require the least pruning. Before going into hibernation Diseased and unripe branches, flowers and dried inflorescences are removed from the bushes.

How to prune standard roses
Standard roses are created by grafting onto wild roses. Hybrid tea, floribunda, climbing, and groundcover roses are used as grafting material. In the first year of planting, flowering branches are pruned in the fall, removing any green new growth. In subsequent years, pruning follows the pruning pattern of the grafted variety.
When is it better to prune roses: in spring or autumn?
Branch pruning can be done in both seasons. In the fall, gentle corrective pruning is performed, while in the spring, the procedure is more drastic. All rose bushes are inspected in early spring. Dead branches are completely removed or cut back to healthy tissue.
Care after pruning
Two weeks after pruning, the plants are fed with phosphorus and potassium fertilizers to help them gain strength and endure the harsh winter. The bushes do not require watering; they gradually begin to go dormant.
Rose bushes should be covered when temperatures reach -5 degrees Celsius. Oak leaves, spruce branches, sawdust, and peat can be used as covering materials. Small bushes can be covered with arches and covered with lutrasil or spunbond.

You need to remove the leaves if they haven't fallen off yet.
Some rose growers are categorically opposed to forced leaf removal, believing that this procedure weakens the plant, and that roses without foliage do not stock up on the necessary set of microelements for successful wintering.
Storing cuttings until spring
When shaping a bush, it's necessary to remove not only weak and diseased branches, but also healthy stems if the bush becomes overly dense, which can later be used to grow a cultivar. There are several ways to store cuttings over the winter:
- Storing in moss. Cuttings approximately 12-15 cm in size with 2-3 buds are soaked in a rooting stimulant solution. Sphagnum moss, pre-treated with phytosporin, is laid out on newspaper, followed by the cuttings, and then more moss on top. Wrap them in newspaper or a plastic bag and store in a cool place until warmer weather arrives. This could be a refrigerator shelf or a basement.
- You can preserve cuttings until spring by rooting them in potato tubers. The plant will develop rapidly, receiving the necessary nutrients from the potato. To do this, select a healthy, medium-sized tuber, remove the eyes, and disinfect it with potassium permanganate. Soak the tips of the cuttings in the same solution for a while. Make holes in the tubers the size of the branches and insert them. The tuber itself is planted in a pot with soil, covering the plant with a jar until the cutting is fully rooted.
- The cut cuttings are stored together with the bush, which is covered for the winter.
None of the methods guarantee 100% survival, but with desire and experience, you can propagate different varieties from cuttings.
The rose is a capricious and finicky plant, which, with proper care and tender attention, will reward you with a decorative appearance, fragrant blooms, and beautiful flowers.

 Roses: Varieties and Types, Photos with Names and Descriptions
Roses: Varieties and Types, Photos with Names and Descriptions How to water roses so they bloom profusely
How to water roses so they bloom profusely How to care for a potted rose at home after purchase
How to care for a potted rose at home after purchase Rose Cordana Mix: care at home after purchase and can it be planted outdoors?
Rose Cordana Mix: care at home after purchase and can it be planted outdoors?