Currants are berry bushes that delight with their generous and healthy harvest. Currants contain a large number of nutrients and vitamins. Gardeners love currant bushes not only for their beneficial properties but also for their ease of care and propagation. A single bush can bear fruit for 15 years and yield up to 4 kg of berries per season. However, there comes a time when it's necessary to propagate black currants.
Preparing cuttings
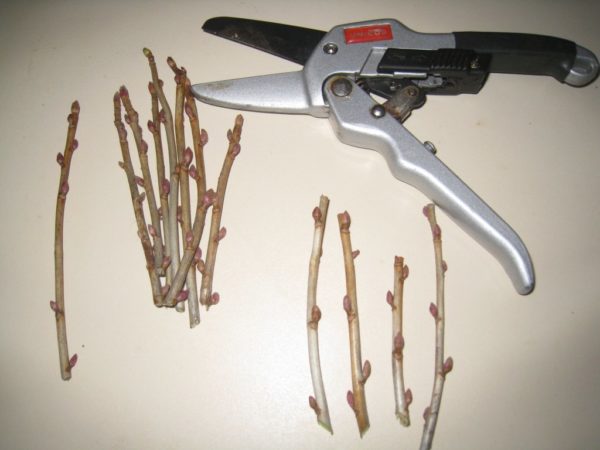
To black currant I got a good harvest from cuttings in the fall, but it's important to know how to harvest them properly. To propagate currants, it's important to prepare the cuttings in advance. To obtain cuttings, you need to select a healthy bush that's 3-5 years old.
The harvesting time is selected depending on the type of currant:
- Black currant – in the warm autumn period: the end of September and the whole of October.
- Red currant propagation occurs between the end of August and mid-September.
- White and golden are propagated by spring layering.
Autumn is considered the optimal time to prepare cuttings. This is because at this time, the plant loses less moisture and sap flow is reduced. In spring, thanks to the moisture, cuttings take root more quickly and develop a strong root system.
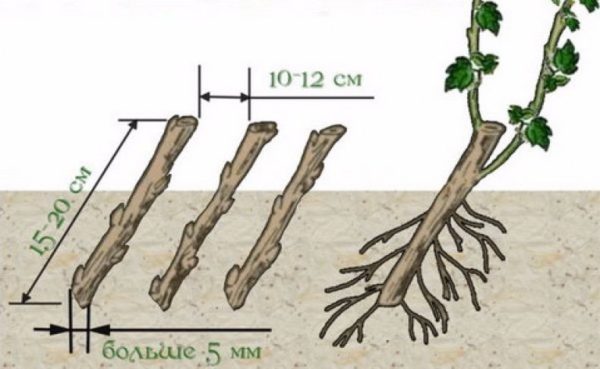
Suitable shoots are cut with pruning shears, then divided into 20-30 cm long seedlings using a sharp knife. The top of the seedling is cut at a 90-degree angle, and the bottom at a 60-degree angle. The bottom cut is made 0.5 cm from the top bud, and the top cut is made up to 1 cm from the bottom bud. It is not recommended to use the ends of the shoots for harvesting, as they tend to dry out.
The cuts are then treated to retain moisture. Hot paraffin or beeswax is used for this purpose. The cuttings are planted in the fall. When planting, the bottom bud is covered with soil, and it is from this bud that the roots will emerge in the spring.

Pros and cons of propagation by cuttings
Taking currant cuttings in the fall is very popular among gardeners. It has several advantages:
- one bush produces a lot of planting material;
- if conditions are comfortable, the bush can be planted immediately;
- the seedling receives all the characteristics and positive qualities from the mother bush;
- the plant can be grown at any time of the year;
- this method renews the variety;
- there is no need to replant the seedlings, they take root perfectly in the planted area;
- almost all seedlings take root;
- the root system is not damaged.
However, propagating currants by cuttings also has its negative aspects:
- the impossibility of predicting the survival of a bush;
- danger of freezing due to severe frosts.
To avoid being left without young seedlings in the spring, it is recommended plant currant cuttings in the fall in large quantities.
Rules for preparing cuttings
The best time to perform this procedure is after the summer heat has subsided, but the first frosts have not yet arrived. This period is from late August to the first half of October.
In spring, melting snow will have a beneficial effect on the development of the root system, helping them to establish roots. The shoots should be at least 6 mm thick. The shoot should be cut off at the root to avoid leaving stumps on the bushes. This negatively impacts the further development of the shrub. All leaves are removed from the shoot.
When choosing a shoot, it's important to consider the bud's shape. A healthy bud should be elongated. If it's swollen and round, it's infested with mites.

Selecting soil
Before planting a particular currant variety, it's important to consider the soil type in your area. Light soil is suitable for white and red currants. Loamy soil is also suitable. Neutral soil is best for black currants.
Once the seedlings have been prepared by the gardener, they can begin preparing the site for planting. First, the area must be leveled. Then, the area must be cleared of any weeds that have taken root. These weeds hinder the normal development of the planted seedlings.
After clearing the area, you can begin fertilizing the soil and then digging it. Compost or humus can be used as fertilizer. Phosphorus-potassium fertilizers can also be added.
If a gardener decides to plant cuttings directly in a permanent location in the fall, the holes are dug in advance, two weeks before planting. When planting seedlings in the spring, the holes are also prepared in the fall.
How to propagate black currants by cuttings in autumn
Before propagating blackcurrants with cuttings in the fall, it's important to understand the specifics of their cultivation. For example, planting density will depend on the soil's fertility. If the soil doesn't contain the required amount of nutrients, it's best to space the bushes further apart to ensure they have enough of the essential nutrients for healthy growth.
It's also important to consider the level of light in the area, as the plant prefers full sun. The shape of the future bush also plays a significant role – if dense foliage is planned, the distance between the plants should be wider.
There are two ways to propagate currants in autumn:
- With green cuttings.
- Lignified cuttings.
Both methods have advantages and disadvantages, as well as peculiarities during reproduction.
Green cuttings
A green cutting is a shoot from this year. It is typically used when woody shoots have not been prepared in advance. There is a specific sequence for planting these shoots.
First, select a healthy mother plant from which to take a shoot no more than 0.8 mm thick. This procedure is performed in the morning, and the shoot is divided into cuttings of 15-20 cm each.
Plant at a depth of 2-3 cm, with at least 20 cm between each new plant. Fertilize and loosen the soil well. Cover the planted seedlings with a plastic bottle or glass jar. This will maintain a consistent humidity level, speeding up the rooting process.
Water the cuttings thoroughly for two weeks. The soil should not dry out, as this will kill the plants. After another two weeks, gradually uncover the cuttings for short periods, gradually increasing the duration. Once the cuttings have become accustomed to the open air, the jar can be removed completely.

Lignified cuttings
Woody cuttings are shoots from the previous year. This is a more effective method, as it results in a higher survival rate.
The cutting should be planted no more than 15 cm deep, with a 12 cm gap between shoots. It's important to leave 2-3 buds above the surface to prevent the plant from dying. This is the only way the cutting will take root and grow.
The mother plant must be healthy. The resulting cuttings are placed in a trench with compost and nutrients.
How to propagate red currants by cuttings in autumn
Propagating red currants by cuttings in the fall is possible if the region experiences a mild winter. In regions with cold winters, it's best to start the cuttings in pots and then transplant them into the ground in the spring.
There are two ways to propagate red currants using cuttings:
- Growth stimulation solution. Place the end of the shoot in this solution for 7 days, then plant it in the ground. The room temperature should be at least 20 degrees Celsius.
- Mix peat and humus in a pot with soil and sand. Place the end of the shoot in the pot, leaving the buds above the surface.
However, for those who don't want to plant red currants in the fall, there's the option of freezing cuttings. The cuttings are placed in burlap, then wrapped in plastic, and stored in the refrigerator. Throughout the winter, the cuttings are periodically removed and aired.
Methods for rooting currant cuttings
Before planting cuttings, they must first root. This is necessary to ensure they establish quickly in the open soil. There are three ways to root seedlings:
- in a special substrate;
- use of growth promoters;
- keeping the cuttings in water until they take root.
The last method is classic and considered the most accessible and simple. The finished shoots should be placed in clean water for two weeks.
As a rule, roots begin to appear after a week and a half, and after another 4 days the cutting can be transferred to the ground.
Using a growth stimulant involves adding any special preparation. There are a fair number of these available commercially today. They help roots grow faster and become even stronger.
The substrate is made from turf soil and alder or pine sawdust. The two are mixed in a 1:3 ratio. The cutting is placed in this substrate. To prevent the seedling from dying, it's important to maintain high humidity both in the substrate and in the room where the seedlings are located.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Planting cuttings in the ground
As soon as the seedlings emerge, they can be planted. The site where the seedlings will be planted should be sunny and protected from the wind. Although currants thrive in moisture, they should not be overwatered. To prevent root rot, it's important to find a site with deep groundwater. A site on a slope is considered ideal.
Before planting the seedlings, the area is fertilized. This requires organic matter, at a rate of 5 kg per square meter. Dig holes in the soil at least 20 cm deep, shaping them into cubes with sides measuring 40 cm.
Before planting seedlings, it's important to carefully inspect the root system. Any roots that are dry or broken should be removed. cut offTo avoid root burn, add a nutrient mixture to the hole before planting and fill with water at a rate of 8 liters per hole.
The seedling is placed in the hole at an angle, allowing the root system to penetrate 10 cm deep. This will result in several shoots forming in the spring, which will form the bush itself. At least 20 cm of shoot should remain above ground, with at least 1 meter between the seedlings.
Caring for currants
The survival and development of seedlings depends on how well they are cared for after planting and again in the spring. If not cared for properly, they may die or produce a poor harvest.
Immediately after landing
As soon as the seedlings are planted, they are watered thoroughly. It's important to maintain consistently high humidity to prevent the seedlings from dying. After three weeks, the roots begin to establish, so the watering intensity is significantly reduced. After this, begin fertilizing the plants.
It's important to mulch shrubs with peat, straw, or compost. Apply a 10-cm layer on the surface. This will reduce moisture evaporation from the soil. Some gardeners use plastic film, covering the entire area except for the holes where the seedlings are planted.
In the spring, to speed up the bushes' awakening, all coverings are removed and the plants are uncovered. After a year, the seedling grows into a full-fledged currant bush, which will delight you with a bountiful harvest.

In the second year
In the second year after planting, the seedlings are transplanted to a permanent location, if necessary. This is best done in the fall, when the bush has already gained strength and energy.
The main care for a currant bush in its second year is fertilizing and protecting it from pests. At home, special fertilizers can help the seedling gain strength and become stronger for growth. Superphosphate is a good choice for this purpose.
Among pests, the bud mite is particularly dangerous to currant bushes. This pest attacks the buds themselves. Powdery mildew is also dangerous to the plant, particularly affecting red currants.
Conclusion
Reproduction in autumn black currant cuttings – this is an opportunity to get a good harvest of healthy berries without significant expenditure of effort and energy. The key is preparing the planting material. This requires a healthy mother plant. Then, proper rooting of the cuttings and their subsequent care are crucial.
Cuttings can easily increase the yield of rare currant varieties. A harvest can be obtained as early as the following year after planting.

 How to propagate black and red currants with cuttings in autumn: planting features
How to propagate black and red currants with cuttings in autumn: planting features Features of planting currants in autumn
Features of planting currants in autumn Blackcurrant: pruning in autumn, rejuvenating an old bush, preparing for winter
Blackcurrant: pruning in autumn, rejuvenating an old bush, preparing for winter Currant pruning scheme in autumn for beginners
Currant pruning scheme in autumn for beginners