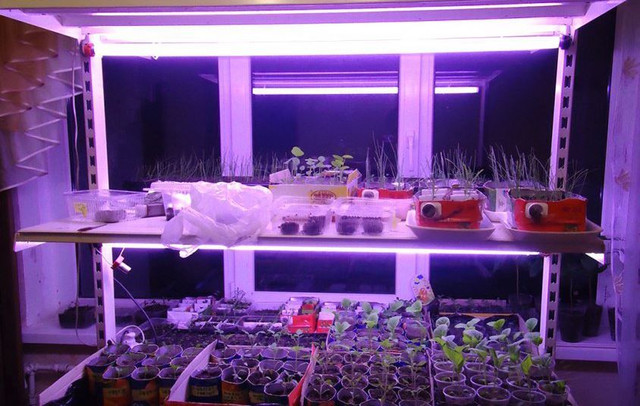
During the cold season, the amount of light in apartments and other rooms where indoor plants are grown is significantly reduced, which negatively impacts the plants' proper development. Experienced gardeners understand the importance of good lighting and therefore prefer to use additional light sources. A special lamp for indoor plants is an excellent solution to this problem, as some plants require supplemental lighting not only in winter but also in autumn.
When is a lamp needed for indoor flowers?
Newbies, having learned about the possibility of installing supplemental lighting, often expose their flowers to illumination 24/7. As a result, the plants begin to weaken and wilt. The fact is, they also need darkness, as vital processes occur during the dark hours.
Light-loving varieties
Light-loving plants deserve special attention, as they require adequate light more than any other plant. These include species that naturally grow in open areas, steppes, and deserts: amaryllis, kalanchoe, abutilon, and azalea. Hibiscus, ficus, and eucalyptus also belong to this group, as in the wild, they inhabit the upper canopy of tropical forests.

Variegated varieties also require good light, which helps the foliage maintain its vibrant, attractive appearance. Some variegated flowers also thrive in shade, so it's important to know the exact variety of your houseplant and its preferences.
How to determine the need for additional lighting
A lack of sunlight will inevitably affect the plant's appearance: growth and development slows, and leaves or the entire above-ground part become deformed.
It is easy to determine the lack of light by the foliage:
- the petioles of the leaves will begin to bend in search of a light source and stretch out significantly;
- after the deformation of the petioles, the stem becomes curved;
- the leaves will begin to fall, and young leaves will form far from each other;
- the leaf blade takes on a curved shape, often with curled edges;
- the foliage loses its brightness and color saturation, and in variegated varieties the pattern fades;
- the foliage at the base will begin to wilt.
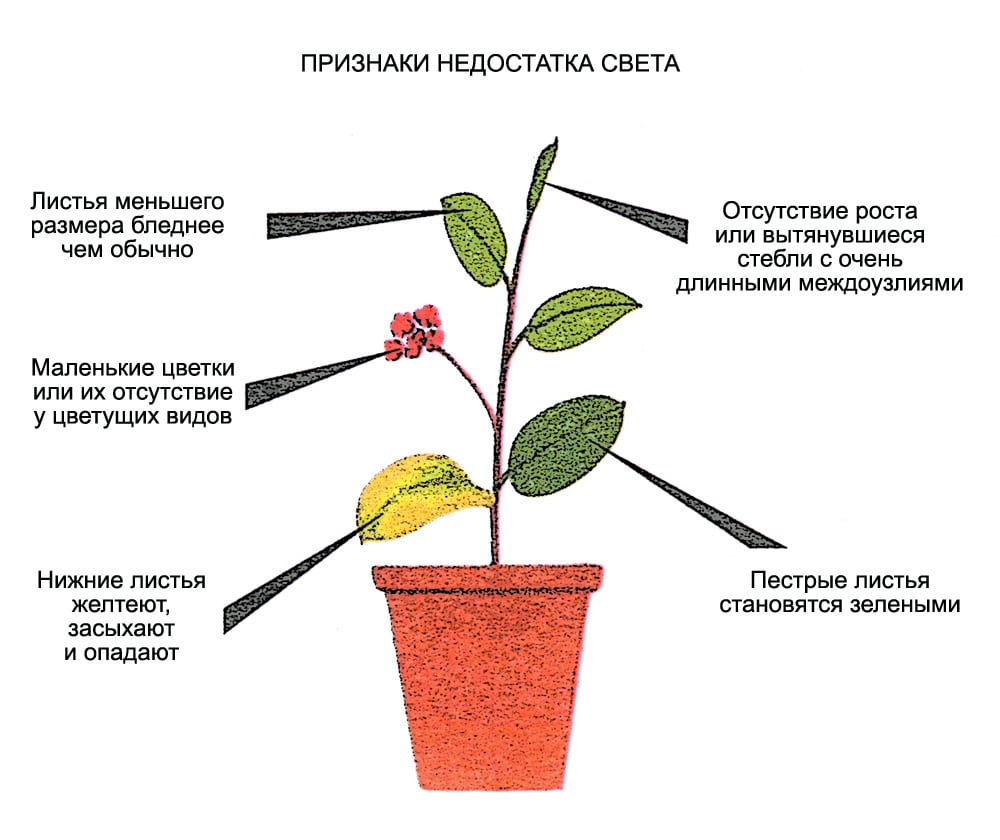
If the cold season is the flowering period of a houseplant, then the lack of light can be determined by the flowers.
Flowering plants signal a problem in the following ways:
- During the flowering phase, only a very small number of inflorescences are formed, and it is possible that flowering will not occur at all;
- If the problem is not addressed in time, the formed buds may fall off;
- If flowering has occurred, the flowers will be small and faded.
As is well known, chlorophyll absorbs water and carbon dioxide from the environment and, under the influence of ultraviolet rays, converts them into glucose and oxygen, which plants need. Phytolamps can replace sunlight, so their use will have a beneficial effect on photosynthesis.
Types of lamps for indoor plants
A wide variety of grow lights can be used for supplemental lighting, each with its own advantages and efficiency. Before purchasing, determine which flowers and how much supplemental lighting is needed.
Energy saving
Energy-saving lamps are a type of fluorescent grow light. Their distinctive features include compact dimensions and a longer lifespan of approximately 15,000 hours. Energy-saving lamps have a built-in ballast and a practical E27 bulb base.
Despite all the advantages, experienced gardeners prefer to use linear fluorescent lamps. This is because energy-saving lamps have low light output. Their tightly wound glass tube creates a self-dimming effect.
Neodymium
A neodymium lamp is an incandescent bulb. According to gardeners, this isn't the best choice because its light intensity is low and it generates significant heat. Its spectrum contains a large amount of red light, which is detrimental to plants. A neodymium lamp can provide good brightness with a low light output. This is due to the use of a special glass made with neodymium.
Incandescent lamps are most often used to heat greenhouse plants. When using a neodymium lamp, keep the following disadvantages in mind:
- it gets very hot, which often leads to burns of the above-ground part;
- there is no blue color in the spectrum of the device;
- The device has a relatively low radiation output.
In addition, using such a device is very expensive, because it has a high consumption of electrical energy.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Fluorescent
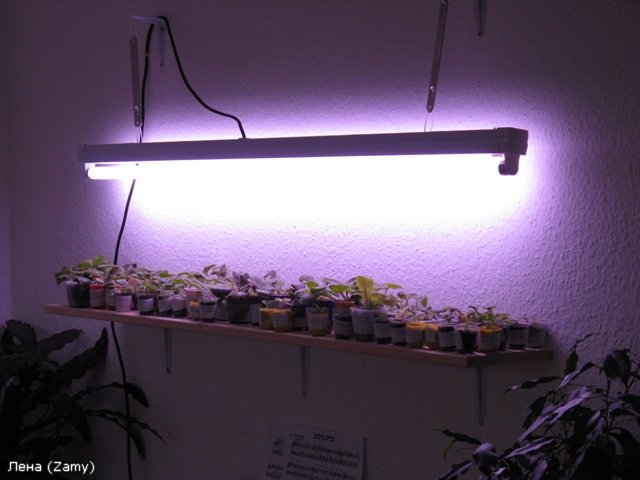
Fluorescent grow lights are considered the most suitable for illuminating houseplants, as they mimic daylight. These fixtures are much more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs. Impatiens and Saintpaulias illuminated by these lamps delight with their blooms all winter long. Another advantage of these lamps is their high radiant output with minimal heat generation, significantly reducing the risk of foliar burn.
Depending on the number of plants to be illuminated, you can choose the most suitable option:
- lamps up to 70 W are suitable for periodic illumination and are characterized by a low emission spectrum;
- Fluorescent grow lights from 35 to 50 W can be used for both full and intermittent daylight replacement. These fixtures feature an optimal emission spectrum;
- Compact devices with a power of 20 W or more are designed only for partial illumination.
The disadvantages of a fluorescent lamp include its high cost and the need to connect a ballast.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Sodium
Sodium grow lights are classified as gas-discharge lamps. They are primarily used for supplemental lighting of large numbers of pots. Their spectrum is dominated by red light, which has a positive effect on root development.
Florists recommend alternating lighting with metal halide and mercury lamps to normalize the light balance.
Metal halide
Metal halide light sources are beneficial for flowering plants, as the predominance of red light in the spectrum promotes budding. These devices offer balanced light output, good power, and a long runtime. Their main drawback is their relatively high cost.
Induction
The operating principle of an induction grow light is similar to that of a fluorescent grow light, but their design is significantly different. There are no electrodes inside the induction lamp, allowing it to operate much longer (with a lifespan of approximately 60,000 hours). By the end of its lifespan, the light intensity decreases by only 5%.
This lamp is resistant to sudden power surges and does not flicker. The bulb does not heat up significantly during operation, allowing the grow light to be placed a short distance from the flowerpot. Like fluorescent lamps, induction lamps are quite close to sunlight, so they can be used without the need for other types of grow lights.

LED
LED lights produce powerful light while consuming minimal electrical energy. Spectral composition can be easily adjusted by installing the required number of red and blue LEDs. They last for 50,000 hours.
Installation recommendations
Depending on the species, the light should be placed 25-50 cm from the plants. It should be positioned above the foliage, as side lighting will cause shoot deformation.
Number of lamps
Most flowers require approximately 8,000 lux (lx). For example, a 60-watt induction lamp produces 4,800 lm (lumens). If the lamp is installed 30 cm from the plants, the luminous flux decreases by a factor of 1.3, meaning the plants will receive the following amount of light: 4,800 / 1.3 = 3,692 lumens. Assuming a plant box area of 1 m², the required illumination is 8,000 lux x 1.0 m² = 8,000 lm.
So, a 60-watt lamp installed 30 cm from the flowers produces 3,692 lm of illumination. The required number of fixtures can be calculated as follows: 8,000/3,692 = 2.16. Round this up to the nearest whole number, which means you get two grow lights. Manufacturers often specify the illumination area in square meters, which makes choosing a fixture much easier.
Power
The lamp power is selected based on the following parameters: the distance between the plant and the fixture, the presence of a light reflector, and the plant type (partial shade, bright light, or moderate light). To provide moderate illumination for 1 m² of plants, a 400 W incandescent lamp or 5,500 lm is required. This means that a surface 1 m long and 0.5 m wide requires 2,750 lm of illumination.
Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency is a measure of how much light a lamp emits per watt of electrical energy. This indicator can be used to determine how economical a grow lamp is.

LED and fluorescent lights are considered the most suitable for flower lighting. They are the most energy-efficient, do not generate heat (which eliminates the risk of burns), and stimulate flowering and full flower growth.
Service life
Modern LED fixtures boast a long service life of up to 100,000 hours. For comparison, consider the lifespan of other fixtures:
- sodium – from 12,000 to 20,000 hours;
- metal halide – from 6,000 to 10,000 hours;
- fluorescent – from 10,000 to 15,000 hours;
- induction – up to 60,000 hours.
Making a DIY flower lamp
You can make your own grow light at home. This type of fixture is much cheaper than a store-bought one. The easiest way to build one is with an LED lamp, selecting LEDs based on wattage and color. To construct the simplest model, you'll need 3-watt bulbs in the following proportions:
- one green;
- one white;
- four blue with a light wavelength of 445 nm;
- ten red ones with a light wavelength of 660 nm.

The LEDs are attached to an aluminum heatsink plate using thermal paste. After mounting, they are soldered and wired in series, then connected to a driver with the appropriate current rating. A fan is attached to the back of the heatsink (you can use a fan from your computer's system unit).
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Frequently Asked Questions
During the cold season, some plants desperately need additional lighting, so gardeners should consider purchasing a suitable grow light. Alternatively, you can create your own supplemental lighting source for indoor plants.











 How to choose a saw for your garden: everything every gardener needs to know
How to choose a saw for your garden: everything every gardener needs to know Robotic Lawn Mowers: Should You Trust Your Grass to These Automatic Helpers?
Robotic Lawn Mowers: Should You Trust Your Grass to These Automatic Helpers? Which garden hose is best? All the aspects to consider
Which garden hose is best? All the aspects to consider Electric vs. Gasoline Trimmers: Which One to Choose for Your Yard?
Electric vs. Gasoline Trimmers: Which One to Choose for Your Yard?