The Colorado potato beetle is a dangerous pest. It can quickly destroy potato and other nightshade crops. Control should begin in early spring, when the garden is being planted. It is recommended to begin control in the fall. This will help reduce the number of adult beetles capable of reproducing.
Characteristics of the Colorado potato beetle
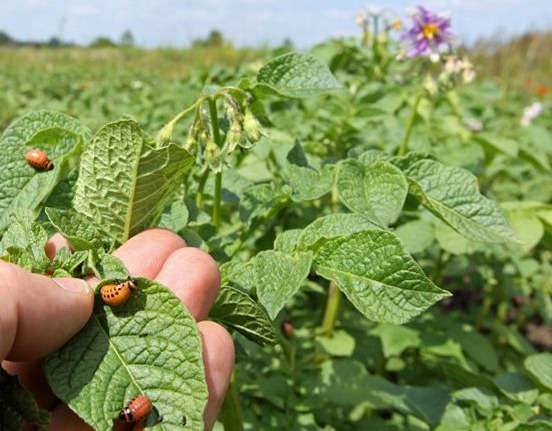

Controlling the Colorado potato beetle is difficult for many reasons.
- In autumn, adult females burrow deep into the ground, and in spring they begin to lay larvae.
- The first larvae appear on the back of the leaf, making them difficult to notice.
- He loves to eat not only potatoes, but also petunias, eggplants and other nightshades.
- A female can lay up to 80 eggs per day, and 800-1000 per season.
- The larvae and the beetles themselves have a huge appetite. A single larva can consume up to 1 gram, and a beetle up to 4.
- Adults are capable of hibernating for up to 3 years, even when hungry.
- The insect quickly becomes accustomed to insecticides, so the products should be changed regularly.
There are few natural predators for the beetle in nature. Birds and other insects are unable to control colonies of the pest, as the Colorado potato beetle reproduces rapidly.
The insect's life cycle consists of several stages. First, the female lays eggs, which are bright yellow or orange. After 10-14 days, the larvae emerge as reddish-brown adults. After another 20 days, their coloring changes, turning orange. After this, they burrow into the soil to pupate. In a single season, the insect produces four generations of Colorado potato beetles; a photo of each developmental stage will help accurately identify the presence of the pest.
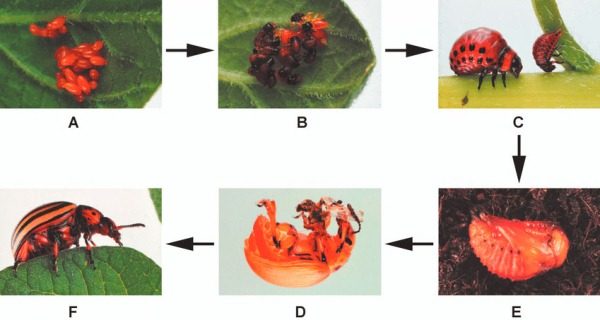
How to get rid of the Colorado potato beetle
Controlling this striped pest is a labor-intensive process that involves the use of various methods and techniques (prevention, biological and chemical treatments, and folk remedies). It's most effective to use several options simultaneously.
Preventive measures help reduce the number of pests on the site.
- During cultivation, all agricultural work is carried out correctly and in a timely manner. Plants that feed on the striped pest are planted in the same location at intervals of five years.
- Crop rotation rules are followed in the garden. Crops are planted so that garlic, beans, and legumes grow alongside potatoes and nightshades.
- Plants of the same genus (potatoes, eggplants, tomatoes) cannot be placed in one place several times in a row.
- After harvesting, the area is treated to control nightshade weeds. Once the seedlings emerge, mineral and organic fertilizers are applied, and the soil is tilled to a depth of 20 cm.
- Throughout the growing season, the beds should be kept clean. Weeds should be removed by the roots.
- During hilling, the lower leaves are covered with soil.
- Regular weeding and loosening the soil between rows reduces the number of insects.
- In the fall, before digging, you can spread onion or garlic peelings over the surface of the area.

Of course, such measures will not help to completely get rid of the pest, but it is possible to reduce its numbers.
Environmentally safe disposal methods
There are many ways to combat pests. Many prefer methods that don't contain chemicals. These don't always result in complete elimination, but they will reduce the pest's numbers.
- Using mulch. After the seedlings emerge, spread mown grass between the rows. This will prevent insects from breeding. Bark, hay, straw, and coarse sawdust are all good options for mulch.
- The perillus bug is a natural enemy of the Colorado potato beetle. If it appears on a plot along with the striped pest, the crops can be saved without the use of chemicals.
- Pest traps. Simple containers filled with the filling are placed around the perimeter of the property. The beetles are periodically destroyed and the filling is refreshed.
- Herbal infusions for spraying. Plant-based solutions (wormwood, calendula, mustard) can be used as control agents.
These methods are effective in small garden plots. However, for larger areas, chemical insecticides are essential.
Chemical means of control
Potatoes can be treated with chemicals even during the seed preparation stage. Several products are used for this purpose. They help protect potatoes from the Colorado potato beetle before germination. Another group of products is used to spray the above-ground portion of the plant during the growing season. Among all insecticides, there are proven, effective products.
https://youtu.be/Aw1PgikakAQ
Aktara
An effective Colorado potato beetle control product, the preferred choice of vegetable growers. It has an intestinal and contact effect. After treatment, the active ingredients penetrate all above-ground parts of the plant within 1-3 days. When eaten, the toxic substances enter the stomach, poisoning the body.
To ensure a homogeneous solution, first dilute 1.2 ml of Aktara in 200 ml of water. Then add the resulting mixture to 10 liters of water and shake well. Spray the solution evenly onto the leaves. 5 liters of the product is sufficient for 100 square meters.
Aktara solution is resistant to high temperatures and direct sunlight. When applied to foliage, protection lasts 2-3 weeks, and when applied to the soil, it lasts 1.5 months. It is highly compatible with other insecticides and growth stimulants. Do not use with alkaline solutions.
Golden Spark
One of the best Colorado potato beetle poisons, it has a systemic effect and demonstrates excellent pest control properties. The main active ingredient is imidacloprid. Available in 5 ml ampoules, 10 ml vials, and 40 g packs.

After treatment, the active ingredients penetrate the green parts of the plant. Protection lasts for approximately 25 days and is not washed away by rain or artificial irrigation. Larvae and beetles die within 1-2 days after spraying.
Commander
Highly effective insecticide Commander It is available as a soluble concentrate. It is effective against the Colorado potato beetle, even in cases of severe infestation. The main active ingredient is imidiacloprid.
First, dilute one ampoule (1 ml) in 1-2 liters of water, then add water to make up to 5 liters. Apply the solution using a sprayer, distributing it evenly over the foliage. Five liters of the product is sufficient for treating 100 square meters.
Colorado potato beetle control can be used on potatoes in any weather. Komandor is non-addictive and poses no danger to humans, animals, or plants. Treatments are permitted at any stage of potato planting.
Corado
Another imidiacloprid-based product with systemic action. Within 1-1.5 hours of ingestion, it prevents the insect from feeding. The pests die within a few days.
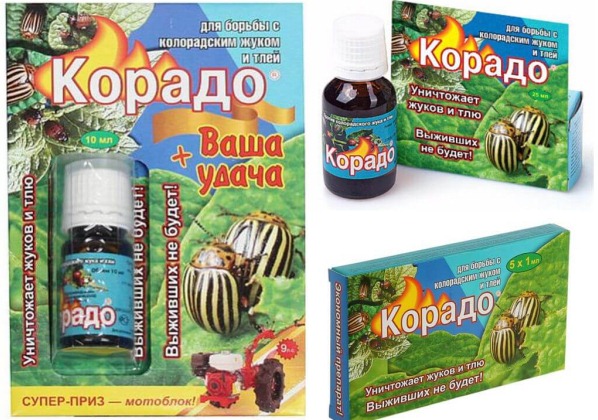

It has limited moisture tolerance, so it's recommended to apply the product in calm, dry weather. It's best to apply the product in the evening or morning. Allow at least four hours after spraying before rain begins.
Available in 10 ml bottles and 1 or 5 ml ampoules. 1 ml drug Corado Dilute in 10 liters of water. This volume is enough to spray 100 square meters. Corado remains effective for a month.
Prestige
One of the best systemic remedies for Colorado potato beetles. The main active ingredients are imidiacloprid (protects against various insects) and pencycuron (prevents fungal diseases, particularly rhizoctoria and late blight). Protection lasts for 1.5 months.
It is used for pre-planting treatment of potato tubers (1 ml per kilogram of potatoes). The solution is pink and forms a thin film after drying. The potatoes are placed on a tarp, sprayed, then turned over and treated on the other side.
Since the product penetrates the stem and leaves as the plant grows, insects consume it along with the green mass and die. They don't have time to lay eggs. It's classified as a hazard class 3 pesticide.
Additionally, treatment with Prestige stimulates crop growth and enhances stress tolerance. After its effective period, the product decomposes into components that pose no danger to the environment or humans.
Taboo
An effective systemic treatment for various garden pests, used to treat tubers before planting. The main active ingredient is imidiacloprid.
The sticky surfactants in the composition form a film on the surface of the tubers when dried.
The second way to use insecticide Taboo The method involves cultivating the soil in rows and pits with already planted potatoes. For pre-planting spraying, dilute 8 ml of the product in 1 liter of water. For spraying green foliage, dilute 4 ml of the product in 10 liters of water. The insecticide's effectiveness lasts approximately 1.5 m.
Tanrek
An excellent poison for the Colorado potato beetle. The active ingredient (imidacloprid) causes paralysis and subsequent death of the insect. After treatment, the insecticide permeates all green parts of the plant and remains there for a month.

The product poses no danger to humans, beneficial insects, or animals when used safely. It is equally effective at various temperatures.
Regent
A modern, effective remedy for Colorado potato beetles that kills them instantly. It boasts a rapid, prolonged effect. Its main active ingredient is fipronil, a phenylpyrazole. It works effectively at various temperatures, killing the pest at various stages of its development, even if it has developed immunity to other pesticides.
Regent Sold in 0.5g sachets, the contents are diluted in 20 liters of water and distributed over the foliage using a sprayer. 20 liters of product is sufficient to treat 200 square meters of plantings. Two treatments may be required per season. The protection period is 2-3 weeks after spraying.
Biological drugs
Biological insecticides, which are less safe, are widely used by gardeners. After treatment, harvesting can be done within 7-10 days, as they do not accumulate in plant tissue.

The downside of biological pesticides is that they kill larvae of various ages and adult insects, but have no effect on eggs. Therefore, treatments are carried out up to three times per season.
Among the biological insecticides that can be used to combat the Colorado potato beetle on potatoes are:
- Bitoxybacillin;
- Fitoverm;
- Nemabact;
- Akarin;
- Entonem-F.
Each product comes in a different form and has a different duration of action. The instructions for each product specify when to spray potatoes against the Colorado potato beetle and how to dilute it.
Folk remedies for fighting
Some gardeners believe that chemicals are the only way to control the pest. Others fight the Colorado potato beetle the old-fashioned way, using folk remedies that remain effective.
Controlling the Colorado potato beetle is a long process. The pest easily adapts to new conditions. Various control methods are recommended. Despite the abundance of chemicals on the shelves, many people use folk remedies to control Colorado potato beetles on potatoes.
Hand-picking Colorado potato beetles
If the plot is small and you have plenty of time, you can use the old method of hand harvesting. Many people avoid this method because they consider it ineffective and too time-consuming.
There are several tricks and secrets that will help speed up the process and rid your plants of the pest for a few days.
- To prevent insects from flying away, take a bucket filled with soap or salt solution.
- Do not crush beetles and larvae on the ground between rows, as they may survive and return to the bushes.
- In hot weather, insects are especially active at the tops of plants, but don't forget to inspect the lower rows of plants.
- The egg clutches are removed along with pieces of leaves.
Kerosene can be poured into the collection bucket, but prolonged inhalation of the odor can cause symptoms of poisoning. It's better to use salt or soap.

Herbal infusions and decoctions
You can prepare decoctions and infusions for treatment against Colorado potato beetles using plants and household ingredients.
- Wormwood tincture. Chop the leaves and stems and fill a bucket one-third full. Pour boiling water over the mixture and let it steep for several days. The resulting mixture can then be sprayed on plants.
- Birch tar solution. Dissolve 100 grams of tar in 10 liters of water. Spray in the evening.
- Garlic and onions can also repel them. Add 200 grams of onion skins and crushed garlic cloves to 10 liters of water and simmer over low heat. You can add 200 grams of shag tobacco. Strain the mixture and bring it to 10 liters. To ensure the mixture adheres and stays on the foliage, add 40 grams of finely ground soap.
- Juniper infusion. Several shoots are steeped in 10 liters of water for 3-4 hours. The strained solution is then sprayed on the plants.
- Celandine. It can be used as mulch or as a decoction. Fill a bucket with the plant stems, add water, and boil for 15 minutes. Strain the resulting decoction. For spraying, use 0.5 liters of the prepared decoction per bucket of water.
Chemical-free measures to control the Colorado potato beetle help get rid of the Colorado potato beetle on potatoes without the use of chemicals.
Colorado potato beetle bait
An effective control method is setting traps. They will attract the pests, saving time on manual harvesting. Place several slices of chopped potato in a liter jar. Coat the rim of the jar with potato juice. Bury the traps between rows, keeping the rims above the soil surface.
After a while, the traps will fill with pests. They are removed and the beetles destroyed. One such trap is sufficient for 5 square meters. Instead of jars, you can use a simpler option: spread cut potatoes around the area, then remove the pests.
Plants against the Colorado potato beetle
For effective control, consider crop rotation principles. It's impossible to completely eliminate the pest, but you can reduce its numbers on your property.
This insect dislikes the scent of some flowering plants, so they can be placed near the planting. This will brighten the area, and the striped enemy will be discouraged from moving into the nightshade beds.

The Colorado potato beetle is afraid of the aroma of the following plants:
- nasturtium;
- hemp;
- marigold;
- calendula;
- coriander;
- night violet.
Nearby beds of garlic, beans and other legumes repel beetles.
Is it possible to destroy the Colorado potato beetle forever?
Humans have long been developing new methods to combat this resilient pest. But the Colorado potato beetle adapts to any conditions, adapting and surviving even in extreme situations. Every season, gardeners use various methods and compounds, but eradicating the beetle forever is impossible. Many factors play a role.
- High fertility. A female can lay over 1,000 eggs in a single season.
- The insect has no real enemies except humans.
- In winter, the beetle hides very deep underground, which protects it from the pesticides that gardeners use to treat their plots.
- These are very resilient insects. They can make long flights.
- Widespread. This pest infests vast territories. It's impossible to eradicate it everywhere at once. Therefore, it migrates from garden to garden, changing settlements.

Careful and thoughtful pest control will only help reduce the pest population in your garden and help preserve the harvest.
Recommendations and tips for spraying
Simple tips and recommendations from experienced gardeners will make the fight more effective.
- Potatoes should be treated against Colorado potato beetles in dry, windless weather. The plant leaves should be dry.
- It is best to kill pests in the evening.
- To make the solution stick to the leaves (for a longer lasting effect), add a little laundry or liquid soap to the working mixture.
- Once prepared, the solution should be used within a few hours. Over time, it loses its effectiveness.
- After each treatment, be sure to wash your hands and clothes.
Safety precautions when working with drugs
Insecticides used to control Colorado potato beetles can be harmful to humans if used carelessly. Before treating potatoes for Colorado potato beetles, it's important to follow safety precautions. These precautions will protect you and others.

The following must be completed:
- Wear thick clothing that covers all parts of the body.
- Use a mask and glasses.
- The drugs are diluted according to the instructions, after checking the expiration date of the drug.
- The tops are treated by spraying.
- You cannot mix different preparations in one treatment.
- To prevent the solution from settling, stir the container with the solution periodically.
- After finishing work on plants, wash your hands and face thoroughly, and wash your clothes.
Naturally, when using chemical or biological products, do not eat, drink, or smoke. No other work should be performed on the area for several days after spraying.
Reviews
Tatyana, Smolensk
I can't use strong chemicals because small children are always around the garden beds. At first, I tried picking them, but it was simply impossible to kill them all, so I started using biological insecticides to combat the Colorado potato beetle on my potatoes.
Vladimir, Volgograd
I don't spend much time thinking about how to treat my potatoes against Colorado potato beetles. I immediately start using chemicals. I never treat the tops with the same product twice. I change them regularly. This is the first time I'm treating the seeds.
Svetlana, Minsk
I fight the disease every year. My plot is small, so I start by collecting the pests by hand. I don't buy chemicals; I use homemade Colorado potato beetle poison. I alternate between folk remedies, alternating between wormwood and birch tar infusions.
Protecting potato and other nightshade crops from pests should be done year-round. If you need to protect a small area, simple methods can be used, such as manually collecting and removing leaves containing Colorado potato beetle larvae. For larger areas, insecticides are best. Choosing the most effective pest control product is difficult, as the pest can become resistant to these products, requiring the constant development of new control methods.

 Ammonia for indoor plants - application and dosage
Ammonia for indoor plants - application and dosage Rabbit manure is a complex fertilizer that requires proper application.
Rabbit manure is a complex fertilizer that requires proper application. What is iontoponics and how is it used in seedling cultivation?
What is iontoponics and how is it used in seedling cultivation? How to prepare manure for application to garden beds: important rules
How to prepare manure for application to garden beds: important rules
Anatoly Prusakov
CAUTION! DANGER!
I've been using Prestige for two years (wetting the tubers). I noticed an aversion to potatoes, which I've always been partial to. Beetles eat the leaves and immediately fall off (that's what alerted me).
This is how I realized the reason for my disgust.
But potatoes boiled in soup are still delicious. Now I collect the beetles and crush the larvae. I also use other means.
Beetles don't approach potato pieces laid on the soil. But they immediately attack new potatoes.