Molds and fungi have existed on planet Earth long before the advent of humanity. They are extremely resilient organisms, essential for the normal functioning of natural ecosystems. Molds are dangerous to humans, as they can be fatal. However, they also bring enormous benefits to humanity. Some species are used in medicine to produce antibiotics, saving people from illness.
Types of mold fungi and their descriptions with photos
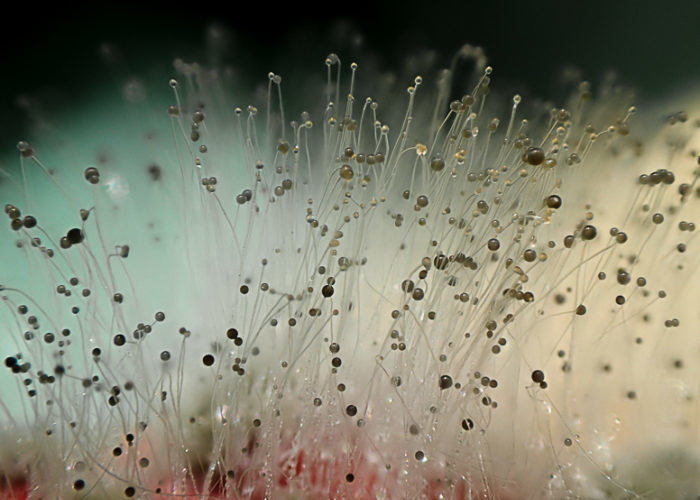
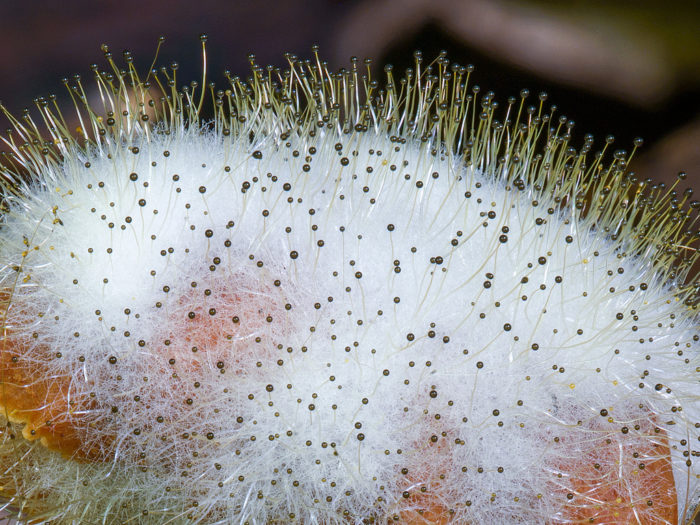
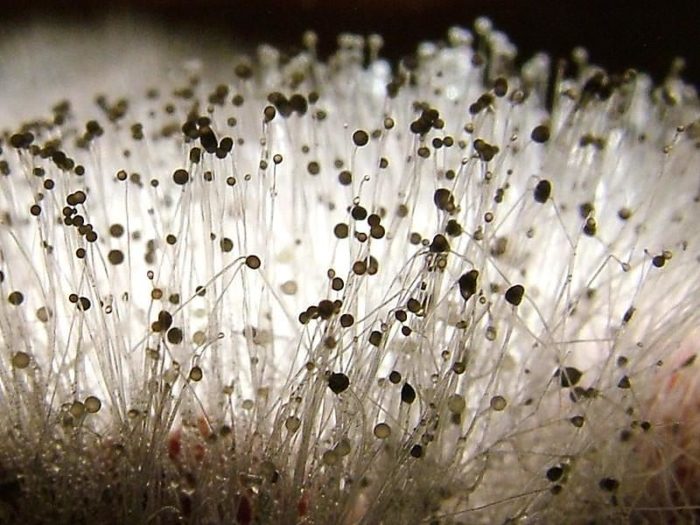
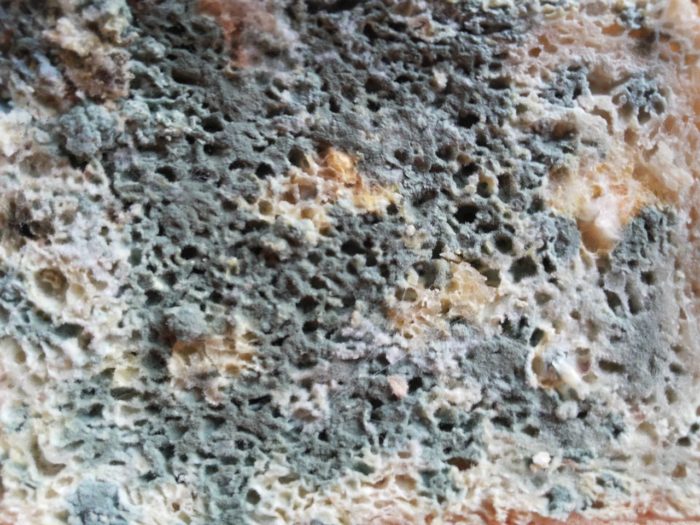
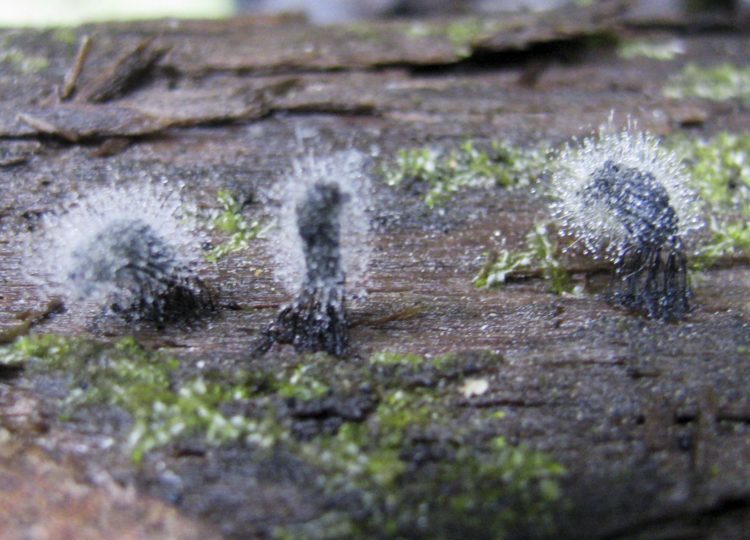
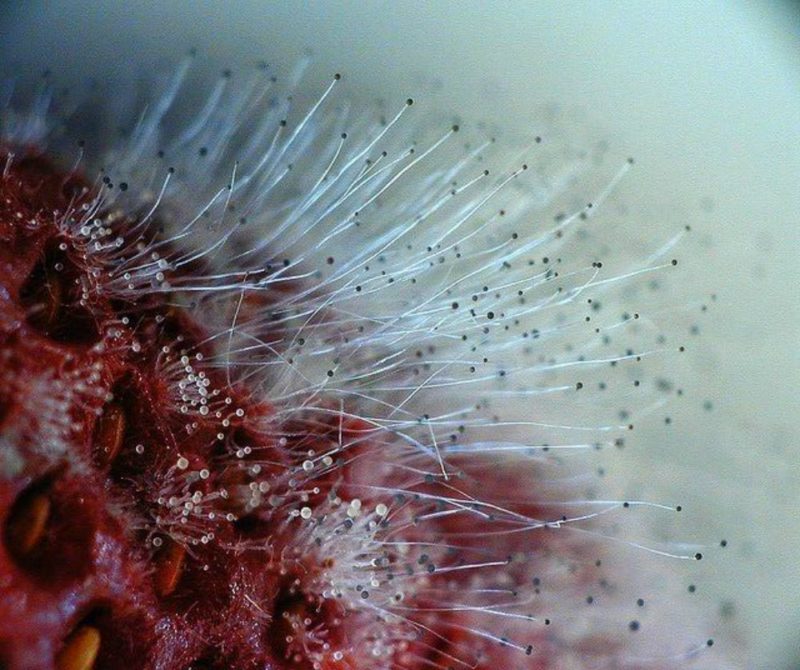
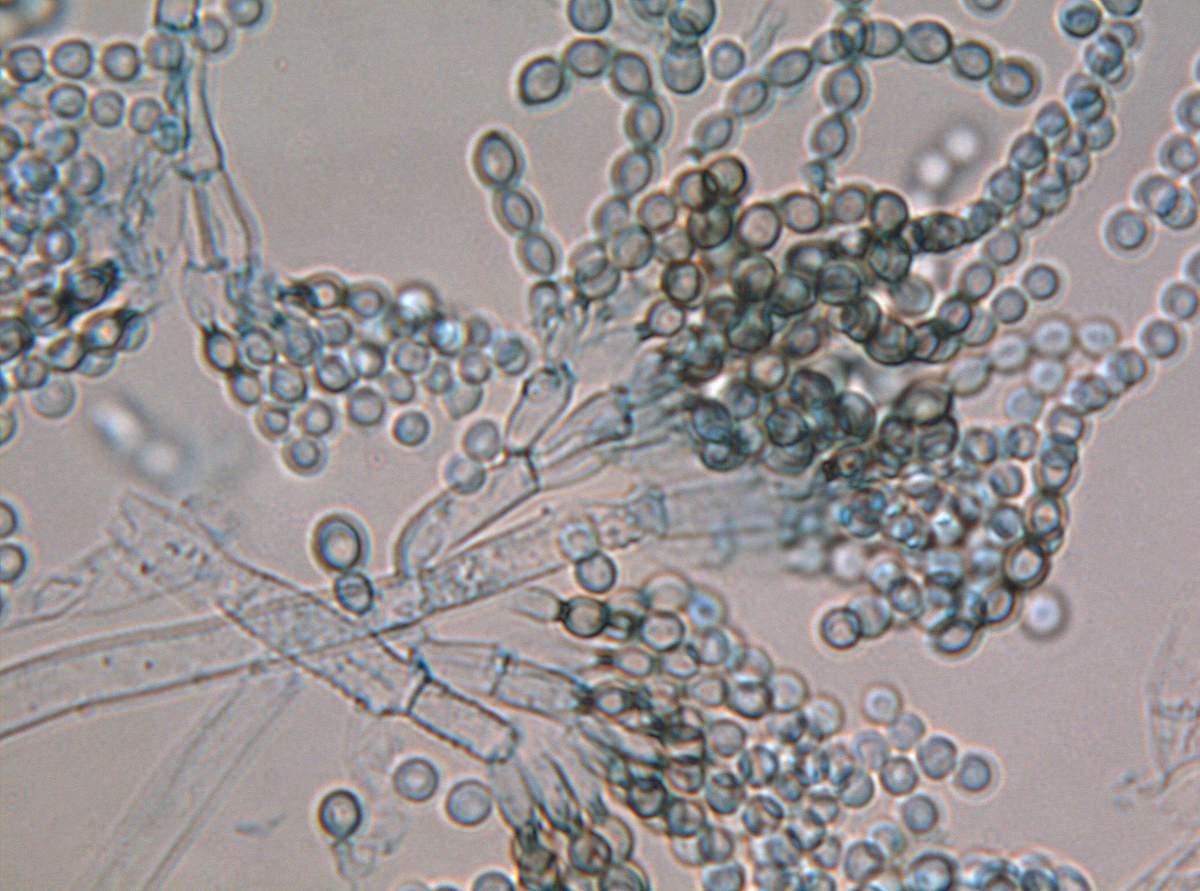
Mold fungi are called micromycetes. They have a microscopic structure, consisting of a very thin, multi-rowed body called mycelium. This body is branched, rarely septated, and forms the base of a multinucleate mycelium. Details of the structure can be seen in the photo.
The characteristic features of the Mold are the following:
- The mycelium is the basis of the vegetative body – thread-like branched hyphae.
- Large size of mycelium.
- Mycelium, unlike yeast, is divided into cells.
- There are three possible ways of reproduction: vegetative, asexual, sexual.
There are several classifications of mold. The most commonly used are classification by color (mushrooms can be white, yellow, black, green, brown, or red) and classification by cell count.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Based on cell count, molds are divided into two types: zygomycetes and ascomycetes. Zygomycetes are a small group of single-celled fungi. Ascomycetes are multicellular fungi.
Mycologists distinguish 4 genera of molds:
- Aspergillus.
- Botrytis.
- Penicillium.
- Hypomyces.
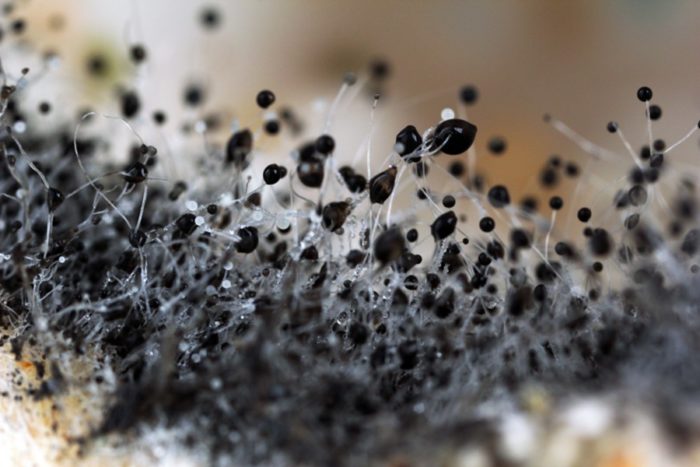
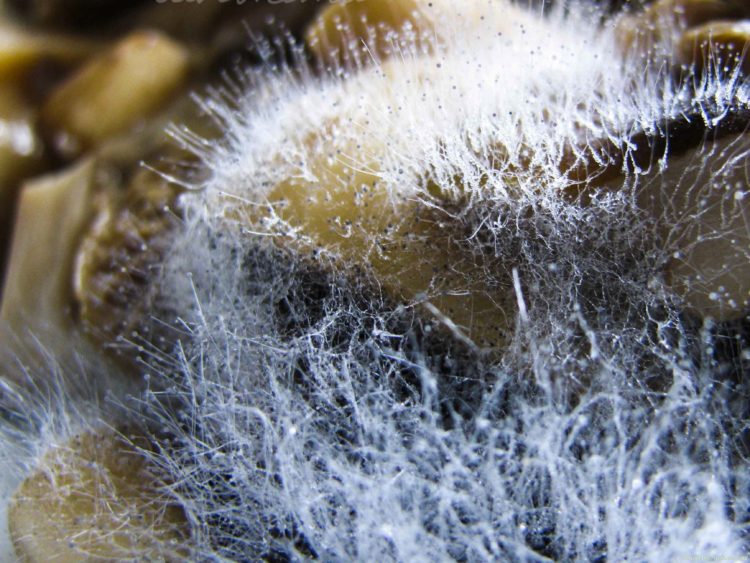
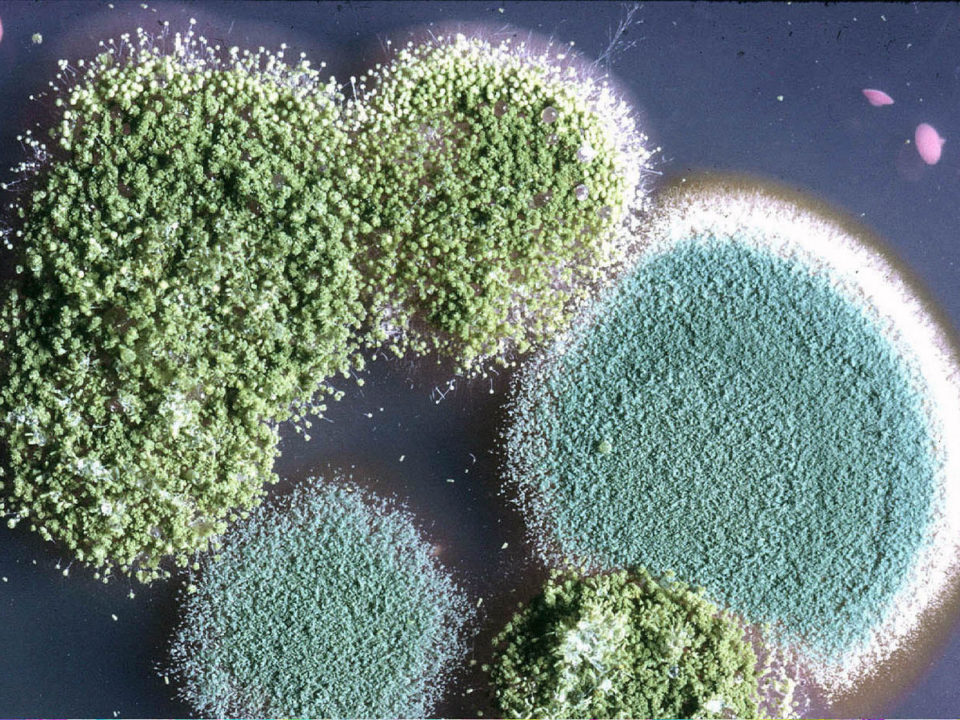
The genus Aspergillus comprises several hundred species. Its mycelium has septa, characteristic of higher fungi. Initially, the mold is white, but as it matures, it acquires a wide variety of shades. Aspergillus species reproduce asexually, but some higher species are capable of sexual reproduction.
Many species of Aspergillus are hazardous to human health. They can cause serious illnesses in humans. Various species are actively used in the food industry and medicine.
 You may be interested in:
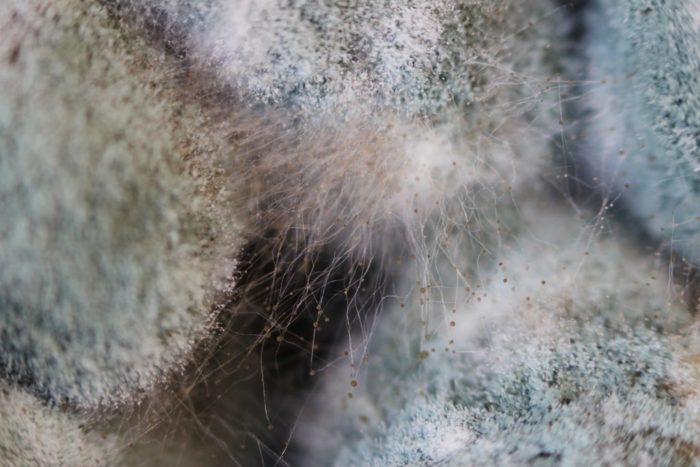
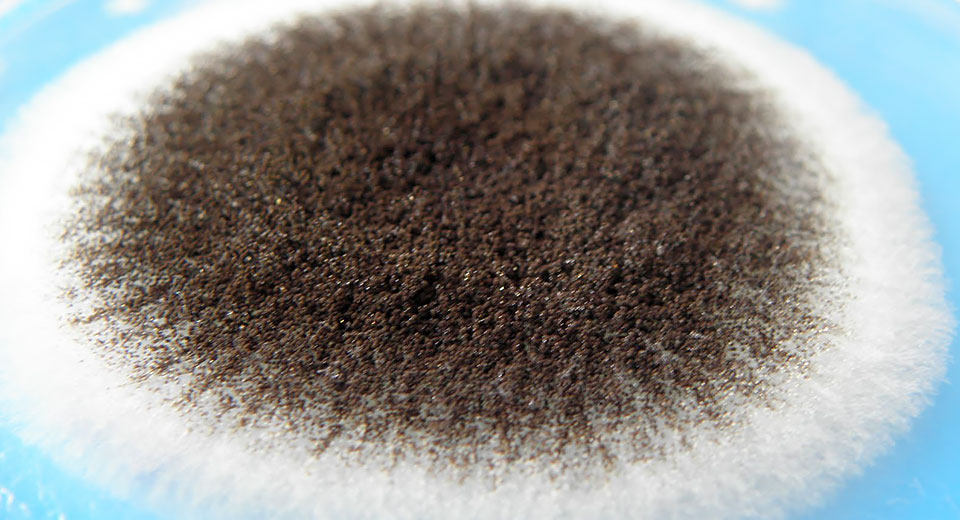
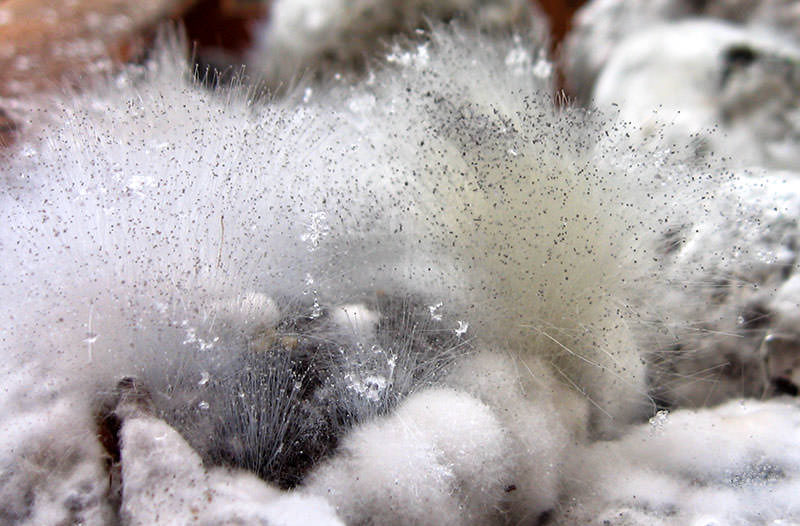
You may be interested in:Botrytis is commonly known as gray mold. The mycelium forms dense, colorless colonies, which, due to their density, take on a smoky gray hue. Botrytis species are single-celled fungi that colonize soil and plant debris.
Hyphae are visible to the naked eye. Species of this genus are highly variable, and can assume a wide variety of forms. Botrytis species are indispensable in winemaking and pose no particular danger to humans. Botrytis species can be affected by hyperparasitic fungi.
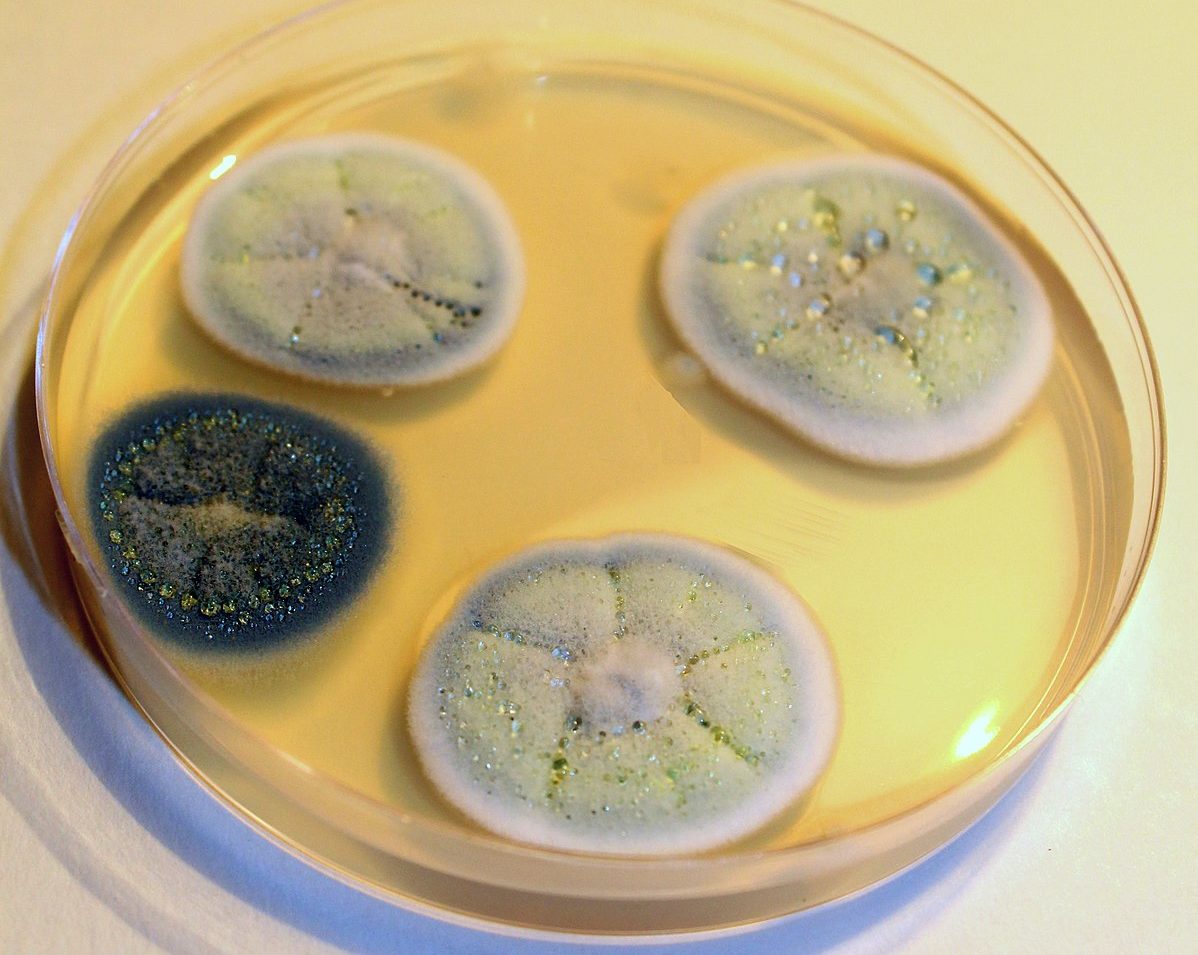
Penicillium is considered a noble mold. It is widely used in traditional medicine, as well as in cheese and sausage production. There are four species groups within the genus Penicillium:
- velvety;
- felt;
- tufted;
- species with coremia.
Species of the genus Penicillium inhabit soil, water, and air. Many prefer plants and food. The mold's color varies depending on the species. It is most commonly white, yellow, orange, or brown. Red and black specimens are less common.
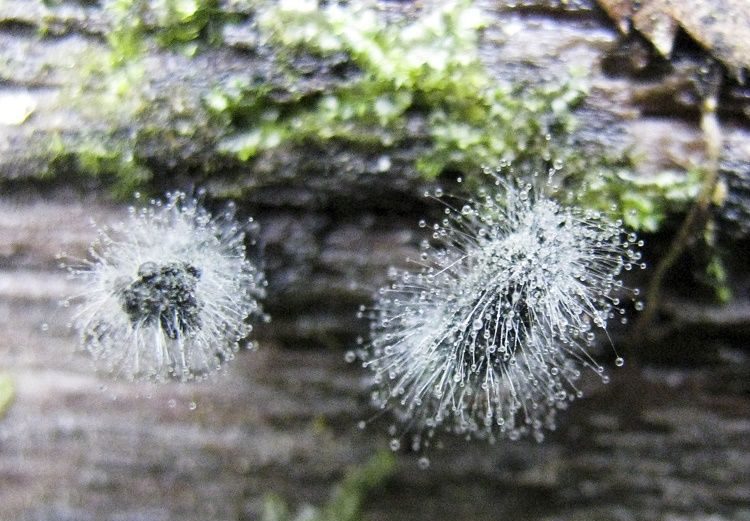
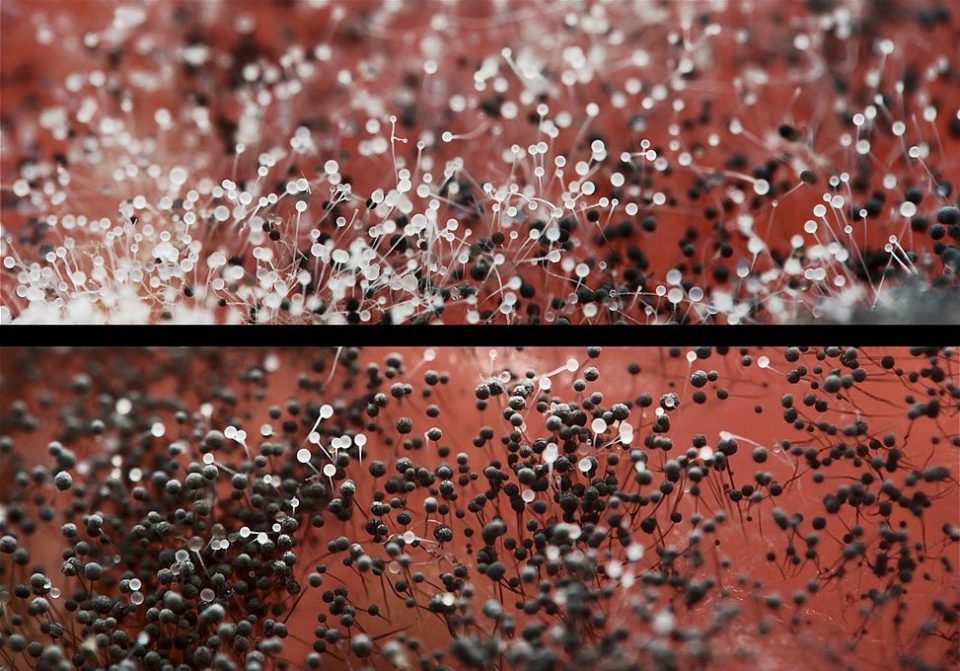
Hypomyces lactiferous is a type of edible mold. This genus of mold grows on edible mushrooms, such as russula and lactarius.
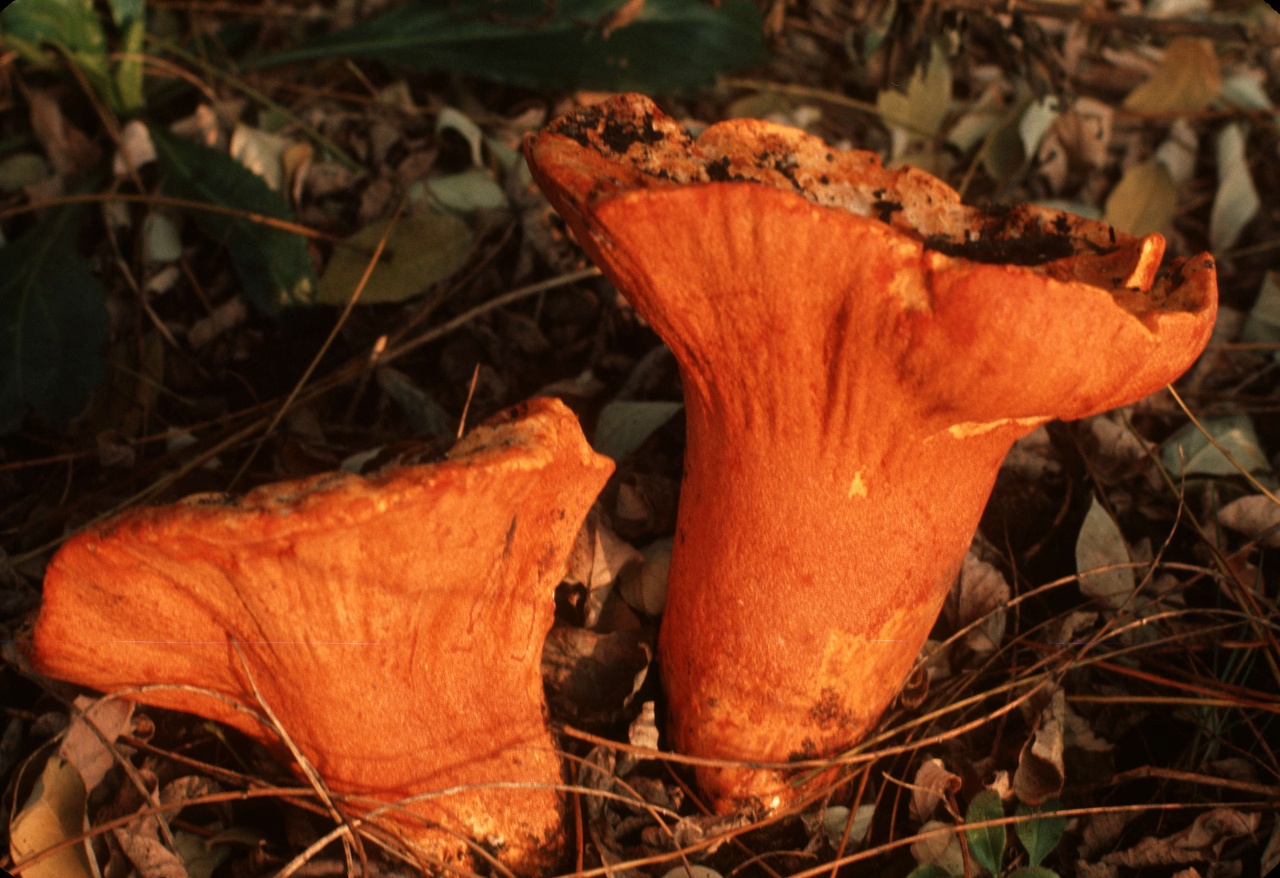

Initially, mold appears as a thin, bright red or bright orange coating. This coating then develops into perithecia—flask-shaped bodies visible with a magnifying glass.
Hypomyces lactiflora is considered a delicacy. Mushroom pickers call it "mushroom lobster" for its color, reminiscent of boiled lobster, and its smell and taste, comparable to seafood. Mushroom lobster isn't just eaten—it's hunted. This species poses absolutely no threat to human life or health.
Use of molds by humans
Mold fungi are widely used by humans in various industries, from food production to pharmaceutical manufacturing. The most common types of mold used include:
- Strains of Aspergillus niger are used to produce citric acid.
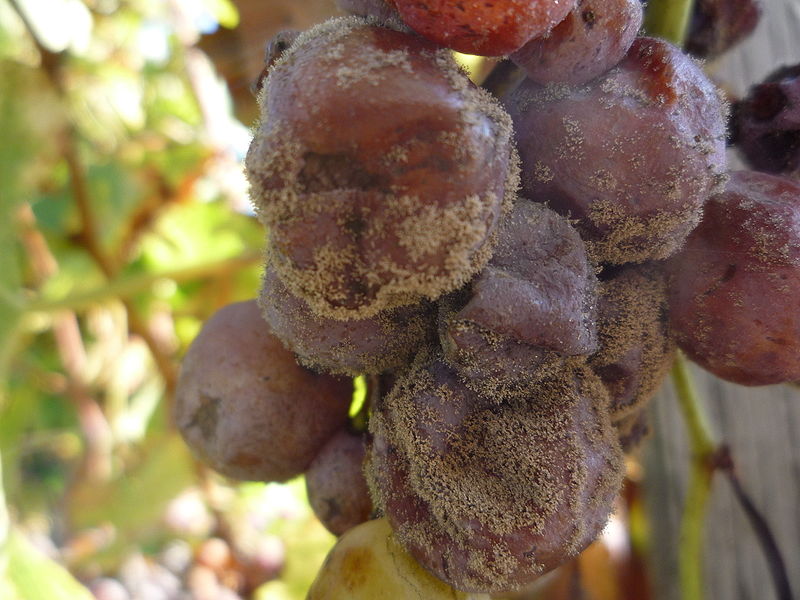
- Strains of the genus Botrytis are actively used in winemaking and the preparation of other alcoholic beverages.

Botrytis cinerea on grape berries - Some noble types of mold are used to make special types of cheese (Roquefort, Camembert) and dry-cured sausage.
- Members of the Penicillium genus are the main components of penicillin-class medications. These drugs have antibiotic and bactericidal effects. Penicillin-class medications are widely used in traditional medicine.
The harm of mold
Despite their benefits, molds can cause significant harm. Members of the genus Aspergillus are considered the most dangerous. They can infect humans and animals. The most common symptoms include skin lesions, outer ear infections, and allergic reactions. A serious condition called mycetoma is also caused by molds of this genus.
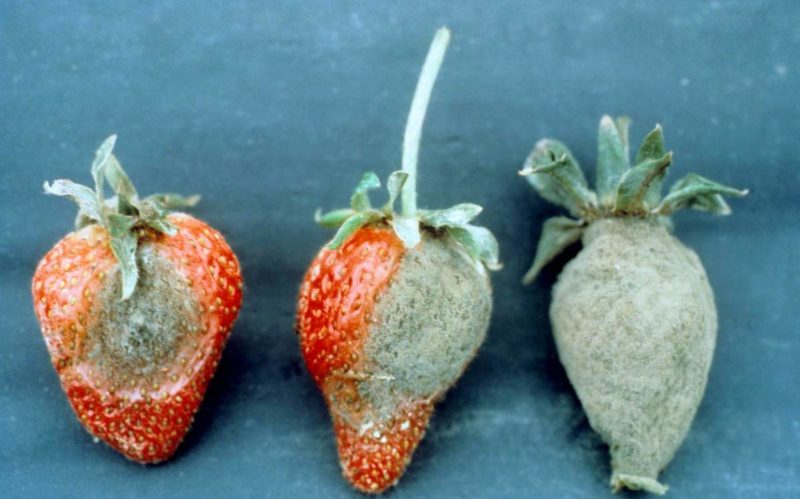
The genus Botrytis can safely be called a garden pest.
Representatives of this genus cause a large number of fungal diseases in the following plants:
- strawberries;
- grape;
- onion;
- some root vegetables;
- citrus;
- nightshade;
- beans;
- flax;
- salad;
- peas.
In humans, botrytis causes allergies. Sometimes, fungal spores cause lung diseases in people predisposed to respiratory diseases.
Conditions for cultivation
Molds are very common. They grow practically everywhere on Earth, forming huge colonies. Molds can live in air, soil, and water. They colonize food and plants.
The colony's goal is to absorb all nutrients. Once the colony's food source is depleted, active sporulation begins. Mature spores spread to new, nutrient-rich locations, while old mycelium remains on the dead source.

Molds are completely unpretentious in their environment and thrive regardless of conditions. However, the most favorable conditions for fungi to thrive and develop are considered to be:
- Abundance of carbohydrates.
- High temperature.
- Increased air humidity.
Molds thrive on starch-rich substrates. Some scientists claim that molds don't thrive in bright sunlight. This isn't entirely true. They thrive in high humidity, and direct sunlight dries it out. Therefore, fungi don't thrive under it. However, bright light or partial shade, both of which accompany moisture, make no difference.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Answers to frequently asked questions
This familiar mold is currently the subject of scientific debate. People are persistently searching for new uses and abilities of mold, blaming it for many illnesses and attributing miraculous medicinal properties to it. Below are answers to the most frequently asked questions about mold:
Mold species are extremely diverse. The benefits of these fungi to humanity are invaluable. However, some species pose a serious danger to humans.
















 What are the benefits and harms of oyster mushrooms for humans (+27 photos)?
What are the benefits and harms of oyster mushrooms for humans (+27 photos)? What to do if salted mushrooms become moldy (+11 photos)?
What to do if salted mushrooms become moldy (+11 photos)? What mushrooms are considered tubular and their description (+39 photos)
What mushrooms are considered tubular and their description (+39 photos) When and where can you start picking honey mushrooms in the Moscow region in 2021?
When and where can you start picking honey mushrooms in the Moscow region in 2021?