Preparing seedlings for your own environmentally friendly and abundant harvest requires space and favorable conditions. This smart composting planter solves the problem of limited space on windowsills and loggias. This design not only allows for strong, hardened seedlings but also solves the problem of organic waste disposal on the property.
What is a compost bin?
The device is a mini-greenhouse installed on a compost bin. The organic matter decomposing in the bin naturally generates heat. A layer of fertile soil is added on top of the decomposing compost, which is heated from below. Nutrient-rich soil, comfortable air and soil temperatures, and sunlight create optimal conditions for plant growth.
The structure can be made by hand from any available materials. The top of the nursery is assembled from a frame covered with polyethylene or honeycomb carbonate. The bottom part—the box—can be constructed from:
- boards;
- sheet iron;
- slate;
- plywood or chipboard;
- polymer plastic.
The lower segment serves as a storage area for organic matter and is a frame that is lined with the materials listed above. It's important to create a stable and reliable structure for the compost bin, as it will have to withstand the pressure of the organic matter on its walls and the weight of the greenhouse/nursery.
Requirements for materials
 When constructing the lower part of the compost bin, the main requirements for materials and components are their strength and corrosion resistance. The top section of the seed bin must be:
When constructing the lower part of the compost bin, the main requirements for materials and components are their strength and corrosion resistance. The top section of the seed bin must be:
- hermetically sealed;
- easy;
- with good light transmittance;
- easy to maintain.
For the convenience of growing seedlings with your own hands, automatic ones are installed on the compost-nursery irrigation systems and ventilation.
Dimensions of the structure
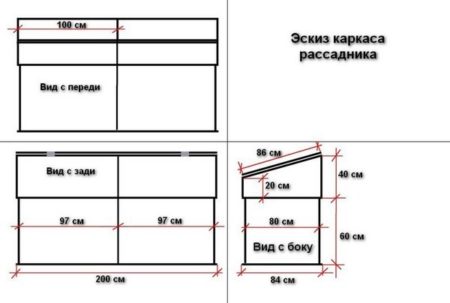 To build a compost bin/nursery, you can build a structure of any size. Consider the following factors:
To build a compost bin/nursery, you can build a structure of any size. Consider the following factors:
- You should not build a compost bin higher than 70-100 cm. High placement of planted plants creates inconvenience for maintenance;
- the compost bin should not be lower than 50 cm. The higher the seedlings are from the ground surface, the more favorable the conditions;
- It's not recommended to build a large nursery. A large nursery is difficult to maintain. It's better to build two or three smaller structures.
The top of the compost bin/nursery can be divided into compartments that can be opened separately from each other. This allows you to plant different varieties of crops and create optimal conditions for each. For example, you can densely plant one compartment with beets and cabbage, another with tomatoes, which require space and sunlight, and a third with cucumbers, which prefer high humidity.
Advantages and disadvantages of the design
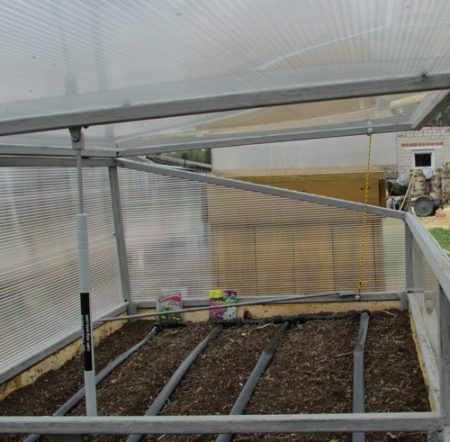 A compost bin with a seedbed is a convenient structure that can be installed in a garden plot. Its advantages include:
A compost bin with a seedbed is a convenient structure that can be installed in a garden plot. Its advantages include:
- Early planting of seedlings is possible. In the southern regions and central Russia, you can begin sowing as early as early March. In the European North, the Far East, Siberia, and the Urals, this can begin in early April.
- Compactness. A single nursery bed is no larger than a regular garden bed. You can grow seedlings for an entire garden in a single structure.
- Efficiency. The greenhouse effect and sufficient sunlight create favorable conditions for rapid plant growth. In a single nursery, you'll grow seedlings much faster than on your windowsills at home;
- Organic recycling. You'll not only clear your garden of tops, old leaves, grass clippings, peelings, and table scraps, but you'll also receive a valuable, comprehensive, environmentally friendly fertilizer for your garden beds;
- Ease of plant care. You can create optimal growing conditions for each crop by creating a nursery with compartments;
- Accessibility. You can assemble the structure from any available materials or buy them inexpensively at the store;
- Easy to assemble. You don't need any special carpentry skills to build this structure. Simply construct a sturdy frame for the top and bottom and cover it with suitable materials.
- Custom sizes. You decide the size of the nursery to suit your needs;
- Installing automated systems. Simple watering and ventilation devices will save you time caring for seedlings and allow you to leave the structure unattended.
 If you don't want or can't grow seedlings at home and then find a way to transport them to your garden, build a smart composting planter. This will ensure your plants receive the maximum amount of nutrients and sufficient light. You can plant your crops as soon as the first warmth of spring arrives.
If you don't want or can't grow seedlings at home and then find a way to transport them to your garden, build a smart composting planter. This will ensure your plants receive the maximum amount of nutrients and sufficient light. You can plant your crops as soon as the first warmth of spring arrives.
The only drawback of a composting bin is the time required to construct it. If you build a sturdy structure, you won't have to worry about where to plant your garden or flowerbed seedlings for the next 10 seasons. With proper care, the device will last a long time.
Tools and materials
 One of the most reliable frame materials is metal tubular profile. It is highly durable, resistant to moisture and temperature fluctuations, and can withstand heavy loads. You can also build a frame out of wood. Keep in mind that decaying organic matter will attack metal or wood. Therefore, it is necessary to provide effective materials protection.
One of the most reliable frame materials is metal tubular profile. It is highly durable, resistant to moisture and temperature fluctuations, and can withstand heavy loads. You can also build a frame out of wood. Keep in mind that decaying organic matter will attack metal or wood. Therefore, it is necessary to provide effective materials protection.
A convenient design for a composting bin is one with a single- or double-pitched roof. For the frame, prepare a square or rectangular pipe or a wooden block.
For example, to assemble a single-pitched structure with several compartments, it is necessary:
- 28 m of tubular profile or wooden block from which the pieces should be made.
|
Number of elements, pcs. |
Length of each segment, m |
|
8 |
2 |
|
2 |
0.8 |
|
6 |
0.64 |
|
3 |
0.4 |
|
3 |
0.2 |
|
5 |
0.82 |
- To cover the compost bin box, you'll need boards at least 1 cm thick. To assemble the box, you'll need eight 2-meter boards and eight 0.8-meter boards for the side walls.
- To cover the top of the nursery, prepare cellular polycarbonate with a total area of at least 4 square meters. Cut the pieces using a hacksaw or scissors.
|
Number of elements, pcs. |
Piece dimensions, m |
|
1 pc. for the longitudinal rear wall |
2.1 x 1.0 |
|
1 pc for the lid |
2.0 x 0.45 |
|
1 pc. for the longitudinal front wall |
2.1 x 0.25 |
|
2 pcs. for sewing up the ends in the form of a trapezoid |
0.85 x 0.45 x 0.25 |
If you're planning to build a smart nursery with internal compartments, make internal partitions out of polycarbonate, plywood, or another material slightly smaller than the end walls. You can cut the lid to fit the number and size of the compartments.
- Door hinges for fastening the lid - at least 2 pcs. for each compartment.
- Fasteners – nails, self-tapping screws, screws with washers and rubber gaskets.
To build a mobile structure, prepare four or more wheels, which should be secured to the bottom of the box. For construction, you'll need a hacksaw, a hammer or screwdriver, an angle grinder, and a tape measure.
Assembling a compost bin
Before construction, select a site where you will collect organic waste and grow seedlings. It's best to choose an area protected from drafts and with adequate lighting. Avoid building the nursery next to a residential building, under trees, or near outbuildings. Ensure that a watering source is located close to the structure.
The compost bin-nursery is assembled in the following order:
- Assembling the frame for the compost bin and mini-greenhouse with a pitched roof. Pipe sections or wooden beams are secured with angle brackets, screws, or welding.
- Covering the box with boards or other material.
- Cover the nursery with polycarbonate or polyethylene. The sides can also be completely covered with boards, plywood, or metal.
- Installing a polycarbonate cover on hinges.
Build the structure well in advance. You can build a compost bin in the fall or late summer, fill it with organic waste, and leave it to rot until spring. Then, when the weather warms up, build the upper part—a greenhouse.
For a gable-roof design, you'll need to construct pentagon-shaped side walls, with a long crossbar installed at the tops to support lids that open on both sides. For this type of structure, you can make the compost bin/nursery wider.
Compost and fertile soil
 Any organic material from your garden, vegetable patch, or home can be used as compost. This includes tops, leaves, newspaper, food scraps, spoiled vegetables, scraps, peat, and manure. All rotting waste can be composted, which you can then spread on your garden beds after growing seedlings. Compost is a complete organic fertilizer rich in potassium, phosphorus, and nitrogen. Avoid composting pet feces, glossy paper, and foods containing preservatives or dyes.
Any organic material from your garden, vegetable patch, or home can be used as compost. This includes tops, leaves, newspaper, food scraps, spoiled vegetables, scraps, peat, and manure. All rotting waste can be composted, which you can then spread on your garden beds after growing seedlings. Compost is a complete organic fertilizer rich in potassium, phosphorus, and nitrogen. Avoid composting pet feces, glossy paper, and foods containing preservatives or dyes.
In the spring, after the snow melts, it is necessary to organize fertile soil on top of the rotting compost. soil for seedlingsIn a large container, mix together the following ingredients:
- 60% of garden land;
- 5% wood ash;
- 10% peat;
- 25% rotted cow dung, horse manure or bird droppings.
All ingredients must be thoroughly mixed and poured into a layer at least 10-15 cm thick. This is enough for the seedlings to develop a strong root system and receive sufficient nutrients. SoilThe area in which you will be sowing will be heated by the rotting compost in the lower compartment.
How to care for and maintain a compost bin
Seedlings should be planted once the weather becomes consistently warm. Before sowing, it is recommended to treat the seeds and soak them in a fungicide solution. This will protect the plants from fungal diseases afterward. planting seedlings in open ground or greenhouses.
Seedlings require regular watering and ventilation. If you can't constantly monitor the seedlings, install automatic systems. To ensure the compost bin and greenhouse lids open automatically for ventilation, install a motorized temperature sensor inside the structure. As soon as the temperature inside the structure rises, the lid opening mechanism will activate.
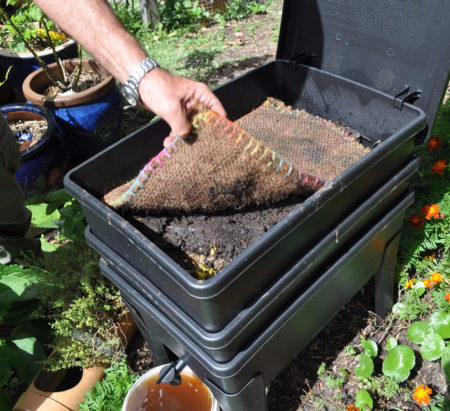

More and more people are taking care of the environment, recycling organic waste themselves with the help of earthworms and,…
For automatic watering, set up a system using standard medical drippers. Run a hose from a water tank placed near the seedling bed on a raised bed and attach the drippers. Turn on a low water flow. The drip water will evenly moisten the soil and create favorable conditions for seedling growth.
In the composting box, you can grow strong and healthy seedlings of any variety and species. After planting, the device can be used to quickly and environmentally friendly harvest parsley, onions, lettuce, and sorrel. Over the summer, you can plant at least three greens in the structure for your table. In the fall, the composted soil can be transferred to the garden beds, and a new batch of compost can be added to the box.
