
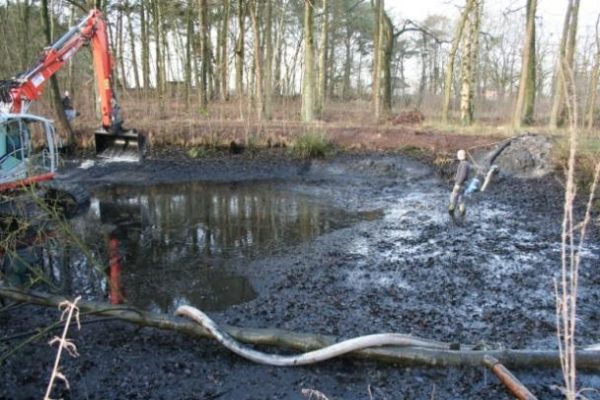
Fertilizers include chemical and organic types. Organic fertilizers include the well-known sapropel, formed from the remains of animal and plant matter. It is extracted from the bottom of freshwater bodies using specialized equipment. Much of this substance accumulates in stagnant lakes, ponds, and reservoirs. These are the primary source of sapropel. As a fertilizer, it is used in a processed form, completely free of additives, and only after drying to remove any remaining moisture.
Sapropel is a pale gray, partially black substance used as a fertilizer. It has a remarkably pure, natural composition—nature provides the soil with a fertilizer containing 96-98% organic components. When the substance, extracted from lakes and ponds, is frozen or dried, it can turn into stone. Sapropel is highly valued for its ability to nourish plants and soil with natural components and restore the soil's fertility.
Specialized centers offer a variety of fertilizers, but people always appreciate organic fertilizers, which can replace any artificial product with their natural energy. An excellent organic solution these days is Sapropel.
Sapropel Fertilizer: Description, Composition, Application, Benefits, and Reviews
Sapropel is a natural substance extracted from the bottom of freshwater bodies. It is produced by the vital processes of underwater plants and animals. Plant particles and dead organisms that fall to the bottom soil form a mineral humus, known as sapropel since ancient Greek times. The Greeks called this substance "rotten mud," which is translated from the Greek: "sapros" meaning "rotten" and "pelos" meaning "silt, mud." Essentially, it is a valuable mineral that humans have adapted to use in various aspects of life.

Description of Sapropel fertilizer
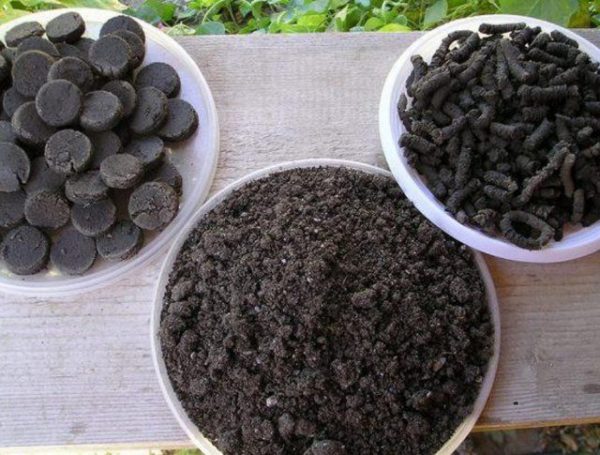
"Bottom humus" is another name for sapropel, which looks like ash—a bluish powdery substance. Granules and tablets have the same color. An important property of this fertilizer is that it retains its natural properties—minerals such as P, Fe, Mg, and many others—when processed, dried, or granulated.
The mineral's beneficial properties provide an inexhaustible source of minerals and vitamins. After processing, the fertilizer should feel moist and crumbly to the touch. The liquid form is not suitable for plant feeding; it is used to restore depleted fallow land.

It works equally well as therapeutic mud and is used in balneotherapy at sanatoriums and health resorts. This healing substance strengthens the immune system and treats skin conditions. The microelements contained in sapropel improve skin metabolism and enrich the skin with nutrients at the cellular level.
What is this?
Several varieties of sapropel are mined from lakes. They differ in their mineral composition. The most important for enriching the soil and growing crops is the organomineral fertilizer sapropel. When extracted from the lake bottom, it is distinguished by its black color. When the substance rises from the bottom in a gelatinous or liquid form, it contains ferrous compounds, which precludes the use of this natural resource as fertilizer.
Gardeners know that Sapropel should be applied to the soil in the fall, once every 3-5 years. The long-lasting action of the fertilizer's components during this period greatly improves the soil's quality. Plants can be fertilized individually, but keep in mind that each crop requires its own fertilizer ratio.
The modern fertilizer Sapropel is a soil-building agent that nourishes plants while simultaneously increasing soil fertility. There are several types of Sapropel, each with a different mineral content.
In plant growing, the two most effective types are:
- organic;
- organomineral.
They are recognizable by their almost black color. They are extracted from the bottom almost ready for processing. The extracted bottom fertilizer has a unique composition in each regional lake.
Depending on the regional location of the lakes, there are different types of sapropel:
- carbonate characteristics;
- organic;
- glandular;
- siliceous.
Plant growing finds application for each type of fertilizer.

Benefits of Sapropel
Sapropel's significant advantages over other organic fertilizers are due to its high content of micro- and macroelements, which significantly improves soil biological processes.
Advantages of sapropelic fertilizers over:
- Peat. Sapropel is rich in nitrogen. No other natural resource, neither peat nor shale, contains so much nitrogen. It also contains more organic matter than peat.
- Animal composts. Sapropel is free of weeds, pathogenic bacteria, and flora. Long-term storage in sealed bags prevents nitrogen loss.
- Chemical fertilizers. Bottom fertilizers are environmentally friendly and have no toxic effects on the environment. These fertilizers are safe for humans to handle, even without protective equipment.
Important advantages of Sapropel:
- improves the natural qualities of the soil;
- is an environmentally friendly product;
- significantly increases crop yields;
- retains moisture in the soil;
- cleanses the soil from bacteria and fungi;
- develops a strong root system of all plants;
- brings benefits to the soil for a long time, up to 5-7 years.

There's no question about using Sapropel as a fertilizer. The timing and methods for applying it to the soil are the same as other organic fertilizers. Before plowing, Sapropel is scattered throughout the garden. Even if plowing is delayed due to environmental or weather conditions, the nitrogen from the fertilizer is not lost.
Compound
Dying plants and animals in the pond settle so densely on the bottom that oxygen access to this layer is limited. This is how natural bottom material is formed, which, under natural conditions, turns into a homogeneous, dense raw material for further extraction and processing.
During the formation of bottom fertilizer, physical and chemical processes occur that last for decades in a body of water. The longer the sapropel matures, the higher its geological quality is assessed.
Hydrogeologists calculate the content of raw materials and decide on their use as:
- mud for medicinal purposes;
- raw materials for fertilizer production;
- reclamation workers - reclamation workers,
- soil formation.
The varied chemical composition of sapropels allows for the production of environmentally friendly fertilizers suitable for a variety of uses. Bottom fertilizers vary in their organic and mineral content, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur compounds. Sapropel's organic matter includes biologically active substances, humic acids, and vitamins. Fertilizer quality depends on ash content, acidity, and the percentage of silicon and iron compounds. These characteristics make it possible to combine raw materials for the production of fertilizers for various purposes, combining them with other natural components.

Sapropel fertilizers contain:
- carotenoids;
- enzymes;
- catalase;
- peroxidase;
- reductase;
- protease.
The importance of the fertilizer is given by its content:
- fulvic acids;
- macro- and microelements;
- vitamins – A, E, B2, group B;
- organic substances;
- amino acids;
- ash;
- natural stimulants;
- beneficial microflora.
Sapropel's ecological purity allows it to be used on any type of soil, for any type of plant. Using Sapropel makes the soil richer and more fertile.
Operating principle
The principle of action of Sapropel is surprisingly simple and clear.
Add Sapropel when digging up the beds, and it will “work” in the soil for at least 3-7 years:
- accelerate biological processes;
- improve seed germination and seedling establishment;
- increase yields;
- strengthen the immunity of plant crops.
Sapropel's effectiveness is evident in the regeneration of the soil layer and the restoration of its fertility. On depleted soil, such as sandy loam that doesn't retain fertilizer, or loamy soil, there's no need to remove the surface layer, as was previously practiced in crop production. A new layer of peat and black soil was then created. This labor-intensive process is no longer necessary. Soil fertility is restored with Sapropel. It is spread evenly and thickly—3 kg per square meter—over the garden or summer cottage, then the soil is dug to a depth of 10-12 cm, or half a spade's depth.

This gives:
- soil restructuring;
- nutrition of the soil with its components;
- launch of fertility restoration by fertilizer microorganisms.
The fertilizer's simple and straightforward operating principle makes it a welcome addition to gardens and summer cottages, where owners enjoy using this organic, environmentally friendly fertilizer.
Instructions for use
The instructions for use explain what Sapropel is and how to use it in the garden. They include sections on the product's description, soil-improving properties, and application instructions. A separate chapter is devoted to applying the fertilizer to potatoes and precautions. The instructions for use for Sapropel state that it is an organic, highly environmentally friendly fertilizer used both directly in the soil and as part of compost preparation.
Rules for making
The fertilizer is harmless to plants, so it is recommended to use 5 kg of Sapropel per square meter. The organic matter reduces acidity and enriches the soil with micro- and macroelements.
Potato fields can be fertilized with Sapropel at rates of up to 120 t/ha. This application significantly increases yield. For other vegetables, the recommended rate is 100 t/ha. On agricultural land, the fertilizer is enhanced by combining it with manure, cow dung, and compost.
Row crops and vegetable crops require Sapropel application at a rate of 50-100 t/ha. This fertilizer significantly increases the yield of many agricultural crops.
Application in greenhouses
Healthy seedlings grow in greenhouses when Sapropel is mixed with soil at a ratio of 1:10. When transplanting seedlings into the ground, the fertilizer should be added directly to the hole. This ensures that the plants take root easily and grow quickly.
The instructions for use will advise you on how to choose a fertilizer in the store based on its brand.

The brand indicates the purpose of using the fertilizer:
A – universal type, for use on any soil;
B – organic fertilizer intended for use on “acidic” soils;
B – for use on neutral or slightly alkaline soils.
The finished fertilizer is sold in wholesale and retail lots. Special bags or standard containers are used for this purpose. When packaging the fertilizer for retail, an important condition is ensured: complete preservation of the nutrient components.
As a rule, the following packaging is offered for retail sale:
- bulk sapropel in bags;
- granules in buckets;
- liquid product in tanks.
The instructions for using Sapropel should be carefully read to become familiar with the diverse properties of this amazing fertilizer and to use them in your garden with maximum effectiveness.
How to use for plants
The benefits of sapropel in plant cultivation have been experienced by many gardeners and homestead owners. It is used in soil mixtures.
In plants:
- the quality of the harvest improves;
- plant growth is activated;
- a healthy root system develops;
- seedlings adapt more easily to the soil;
- stimulates plant development at all stages.
Fertilizer benefits plants, as gardeners have long known. It is used for vegetable, garden, and ornamental plants.
Use when planting potatoes
Using sapropel fertilizer in potato fields increases yields by up to 35%. To achieve this, 130 tons of fertilizer are applied per hectare. In acidic soils, geotechnical experts recommend applying 80-110 tons/ha. The biogenic fertilizer is applied to the soil in the fall, when plowing the field for spring potato planting. Additionally, in the spring, when planting root crops, a powdered fertilizer is added directly to each hole. Another method is "bathing the potatoes" before planting. In summer cottages intended for potato cultivation, the fertilizer is applied at a rate of 3-6 kg per square meter. Additionally, to preserve the quality of the potatoes during storage, they are covered in piles with dry powdered fertilizer.

A mixture of Sapropel and composted manure is often used in a 2:1 ratio. Fertilizer is purchased according to its composition, as indicated on the manufacturer's packaging.
Use for soil
High-quality Sapropel fertilizer is used to improve the mechanical structure of soil, moisture levels, and aeration. Sapropel activates the natural self-cleaning processes of arable land from pathogenic fungi and organisms.
Today, scientists have scientifically confirmed the benefits of using bottom fertilizer to improve the fertile soil layer and its air supply. Sapropel reduces the accumulation of heavy metals from the environment in potato tubers and root vegetables.
The Earth receives:
- saturation with useful substances;
- reduction in the frequency of irrigation;
- reduction of nitrate content;
- activation of the earth's vital activity.
In Russia, a set of measures has been developed for the ecological restoration of land resources and increasing their fertility. Reclamation of sandy soils is particularly important, as the underlying soil and turf layers are recreated. This approach is used to save abandoned lands depleted by previous human activity, such as areas after abandoned oil and gas wells, or sandy areas near the sea and desert. Sapropel, when used for land reclamation, lasts for 7-14 years. For this purpose, the liquid fertilizer is applied evenly during shallow plowing (up to 12 cm), at a rate of 3 kg per square meter.
Types of sapropel
Sapropel fertilizers have different chemical compositions, allowing for the creation of different types of fertilizers. This depends on the geological region in which the raw material is mined.
The bottom soil contains both mineral and organic components. Based on their content, sapropels are classified as:
- siliceous;
- calcareous;
- mixed.

The content of organic components allows us to divide the fertilizer into:
- organic, ash 30%;
- organomineral, ash 30-50%;
- mineral-organic, ash 50-70%; 0
- mineralized, ash 70-85%.
Sapropel fertilizers are further categorized into liquid, paste, granular, and bulk forms. These determine the intended use of the sapropel. Fertilizers are traditionally available in bulk and granular forms. Liquid and paste forms are used for the restoration of large areas.
The types of water bodies determine the types of sapropel raw materials. Various sapropel deposits are being developed in Russia:
- lake;
- peat;
- swampy;
- marine;
- interglacial.
The main bottom soils processed into fertilizer are lake and peat. The extracted humus is processed until it becomes an excellent fertilizer called sapropel.

Reviews
Farmers who have already used Sapropel fertilizer leave positive reviews and express gratitude to its manufacturers. The creation of this unique fertilizer has facilitated soil restoration, increased crop yields, and reduced the use of chemical fertilizers.
Maria:
"In 2012, my husband and I started using sapropel tar at our garden plot—it was perfect for the soil in our region. Sapropel helped me heal my sick rose bushes. I fed them strictly according to the instructions, and the rare rose varieties, their wilted, lifeless bushes, came back to life, blooming beautifully and thriving, much to my delight."
Lyudmila:
"The tomatoes my daughters and I grew won at the school and city autumn fairs. All the neighbors were amazed, and I didn't hide my secret: I fed the seedlings with Sapropel. For the first time in my gardening life, the tomatoes grew large, round, and flawless in shape and color."
Ivan:
"I have three potato plantings. The harvest has always been just enough for a large family. An agronomist I know recommended 'bathing' the potatoes in a Sapropel solution. We got a barrel of the solution, dipped half a sack of potatoes in it, let them sit for a while, and then planted them straight away. The yield was so good that one plot provided enough potatoes for the whole family to last the entire winter, and the rest went to market."

 Ammonia for indoor plants - application and dosage
Ammonia for indoor plants - application and dosage Rabbit manure is a complex fertilizer that requires proper application.
Rabbit manure is a complex fertilizer that requires proper application. What is iontoponics and how is it used in seedling cultivation?
What is iontoponics and how is it used in seedling cultivation? How to prepare manure for application to garden beds: important rules
How to prepare manure for application to garden beds: important rules