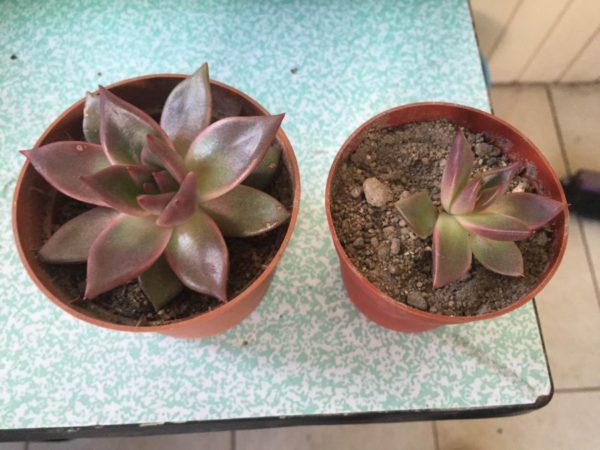
The trendy minimalist style in home interiors has given rise to the popularity of succulents, which require little care and can be used to effortlessly decorate windowsills and other areas of a room. One common type of such plant is the echeveria, whose care at home involves choosing a well-lit location, watering, and fertilizing.
Otherwise, the plant requires little care and can be incorporated into a variety of greenery arrangements, thanks to its varieties, which are well-suited to indoor growing. These easy-to-grow plants can be grown individually in pots, or you can create an entire mini-garden in a single container. Arrangements in glass globes and aquariums look particularly elegant.
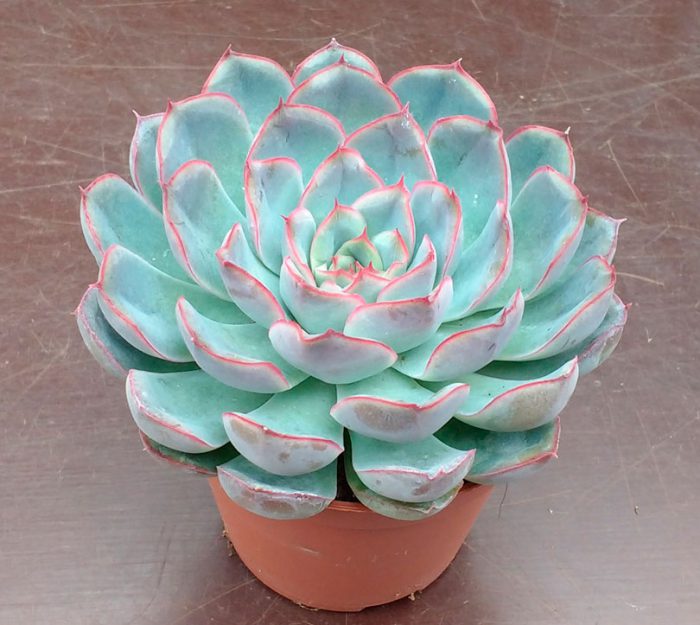
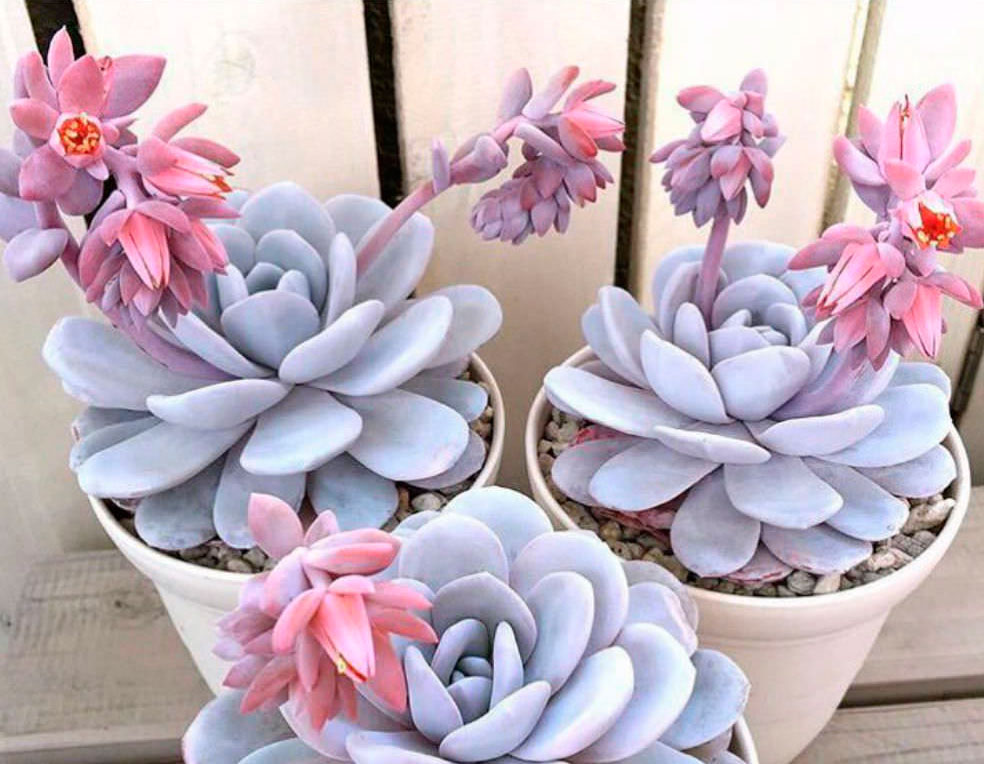
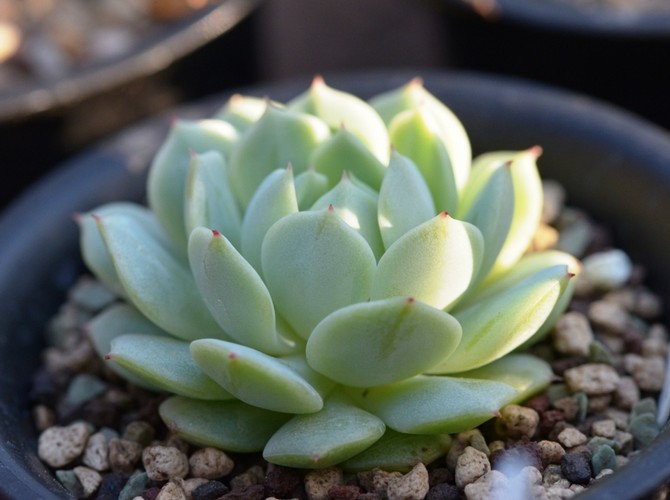
Echeveria characteristics and varieties with photos
Echeveria is native to South America and Africa, where it was first encountered by Europeans, who later introduced some species to our country. This unusual plant belongs to the genus of succulents and is also known as the "stone rose." Over 200 species of this flower exist in the wild, differing in the shape and color of their petals. This succulent thrives indoors. Characteristic features of echeveria include:
- dense leaves of various shapes, 3-30 cm long and 1-15 cm wide;
- lush rosettes formed by foliage;
- the presence of stems of different sizes depending on the variety;
- the color range of the foliage includes green, red, pink and purple shades;
- thread-like root system;
- the presence of a peduncle up to 50 cm in height;
- the shape of the flower resembles a bell;
- flowers are collected in inflorescences;
- creeping shoots in some species;
- the presence of waxy and pubescent leaves.
These features make it easy to distinguish this species from other succulents, and a more detailed description with photos will help you identify the differences between the varieties of the stone rose itself.
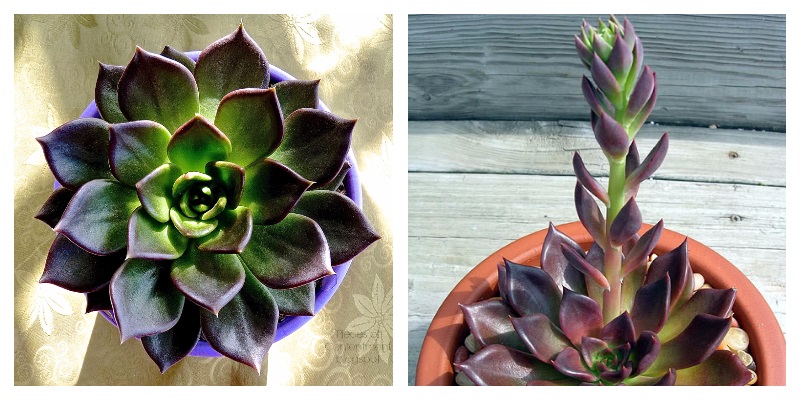
Graceful
This graceful Echeveria, a perennial plant with an unusual shade of blue and green, blooms with orange-red bell-shaped flowers on a tall stem. The leaves are shaped like rose petals and are closely packed. The succulent also has a thick, low stem.
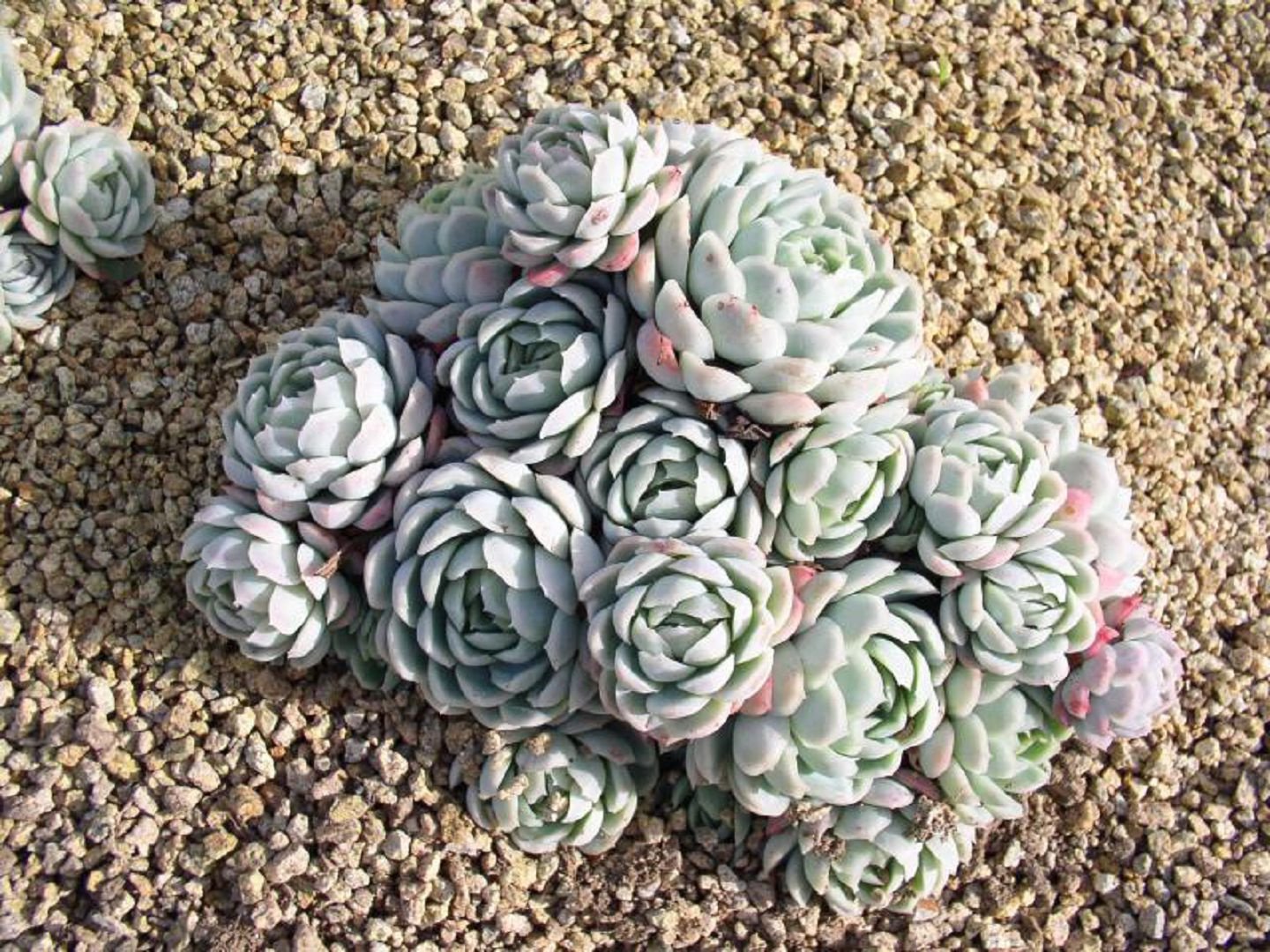

Humpbacked
Flat, diamond-shaped leaves are located on a short stem, their green color turning light pink towards the base. The flowers are light red.
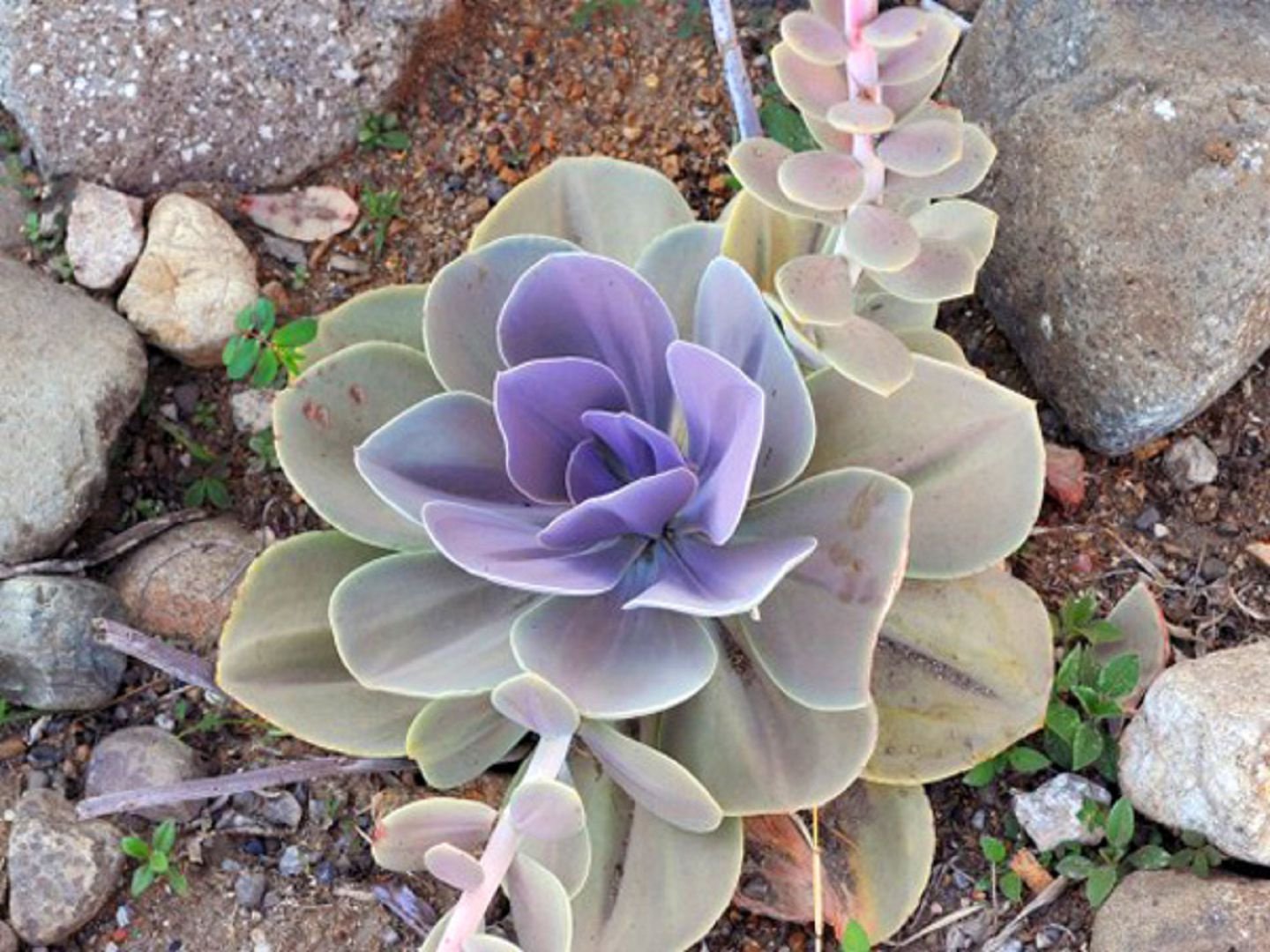

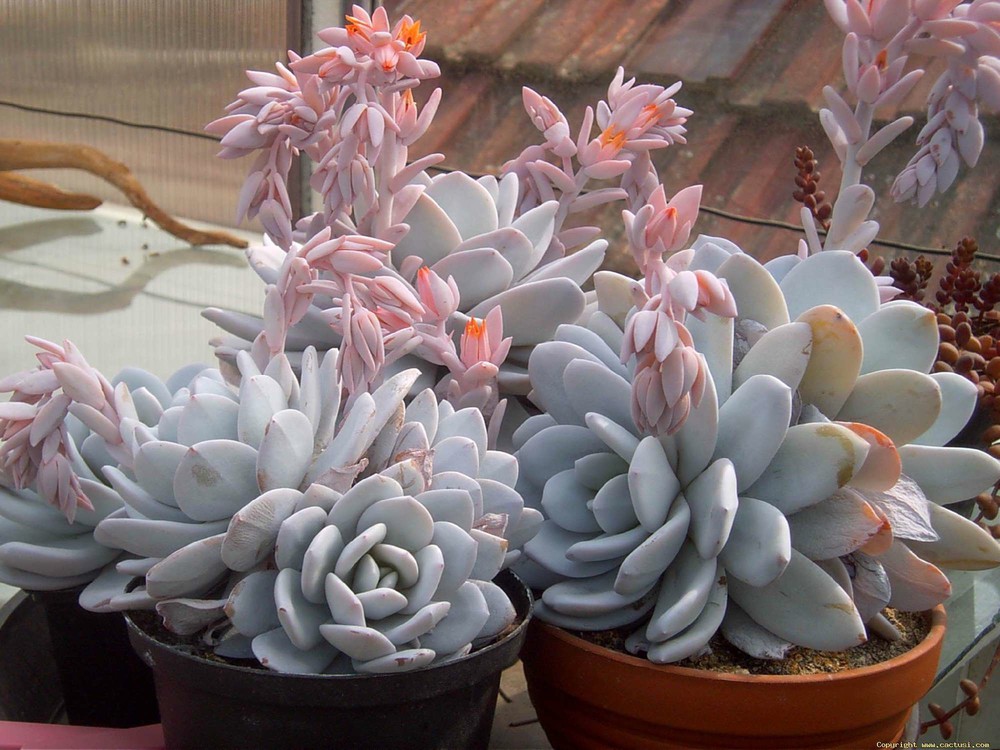
Derenberg
The leaf rosettes of this species are densely arranged, reaching 4 cm in width and pointed at the tip. The foliage is light green with a red spot at the tip, tinged with white along its entire length. In late spring, it produces orange buds.
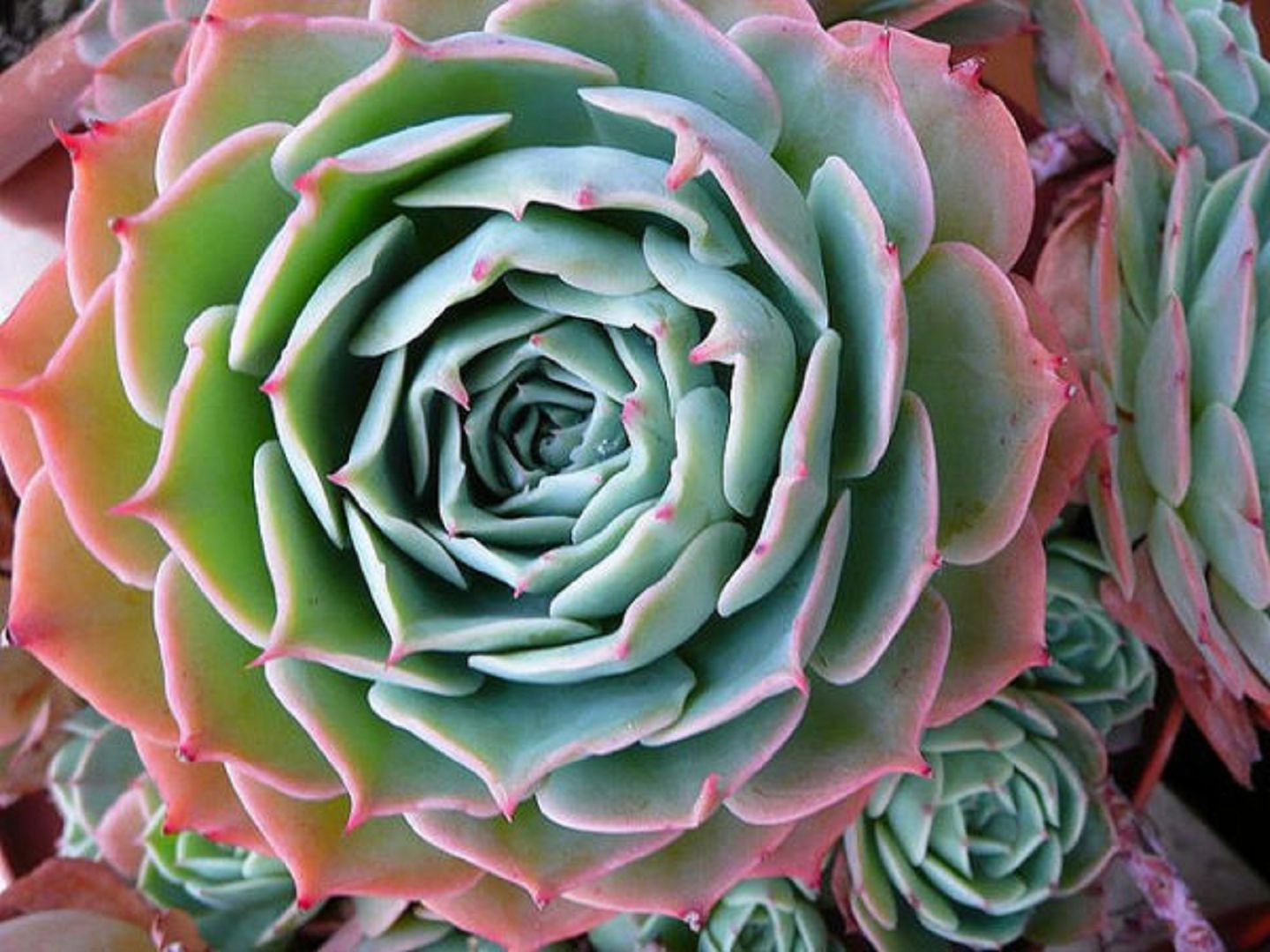

Agave
A stemless rose with pointed leaves that are symmetrically arranged to form a water lily-shaped rosette. The leaves are green with pink tips. This succulent blooms in summer with yellow-pink inflorescences.
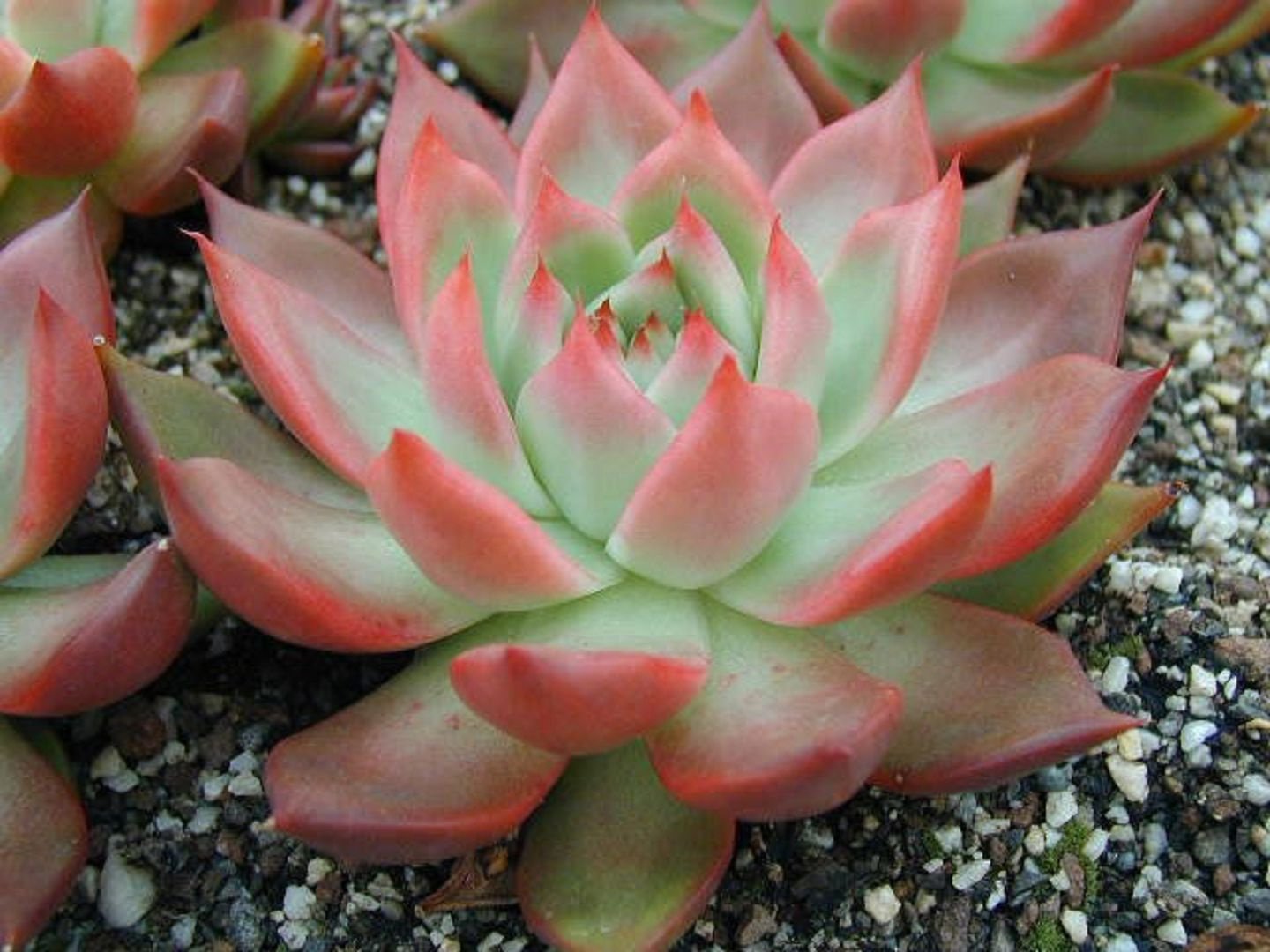

Cushion-shaped
The variety gets its name from the dense and rather wide arrangement of its foliage, creating the appearance of a green cushion. This echeveria has light green, fleshy leaves, slightly elongated and velvety. It blooms with small yellow flowers arranged in racemes.
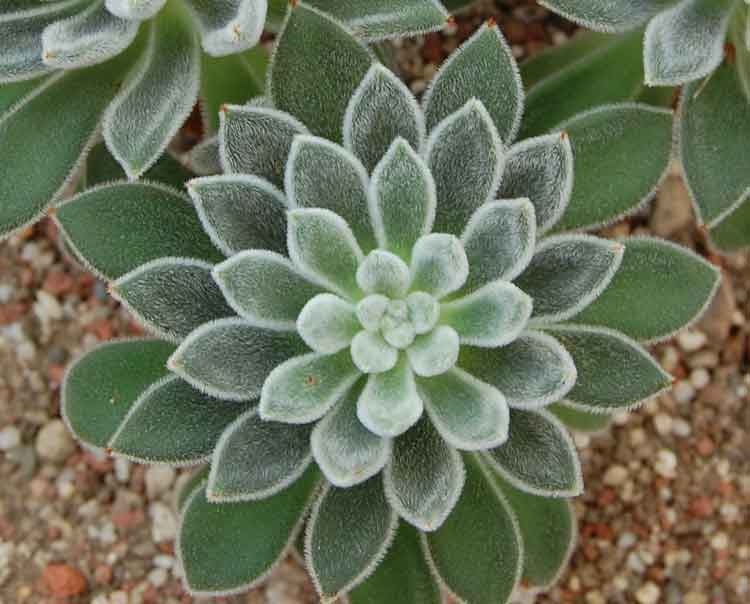

Lau
This succulent, with a rosette up to 20 cm in diameter, has a matte, waxy coating and almost white foliage with hints of blue and pink. It reaches 15 cm in height. The diamond-shaped leaves reach 6 cm in length and produce orange-hued inflorescences. A distinctive feature of this variety is the thick protective layer on the foliage and flowers.

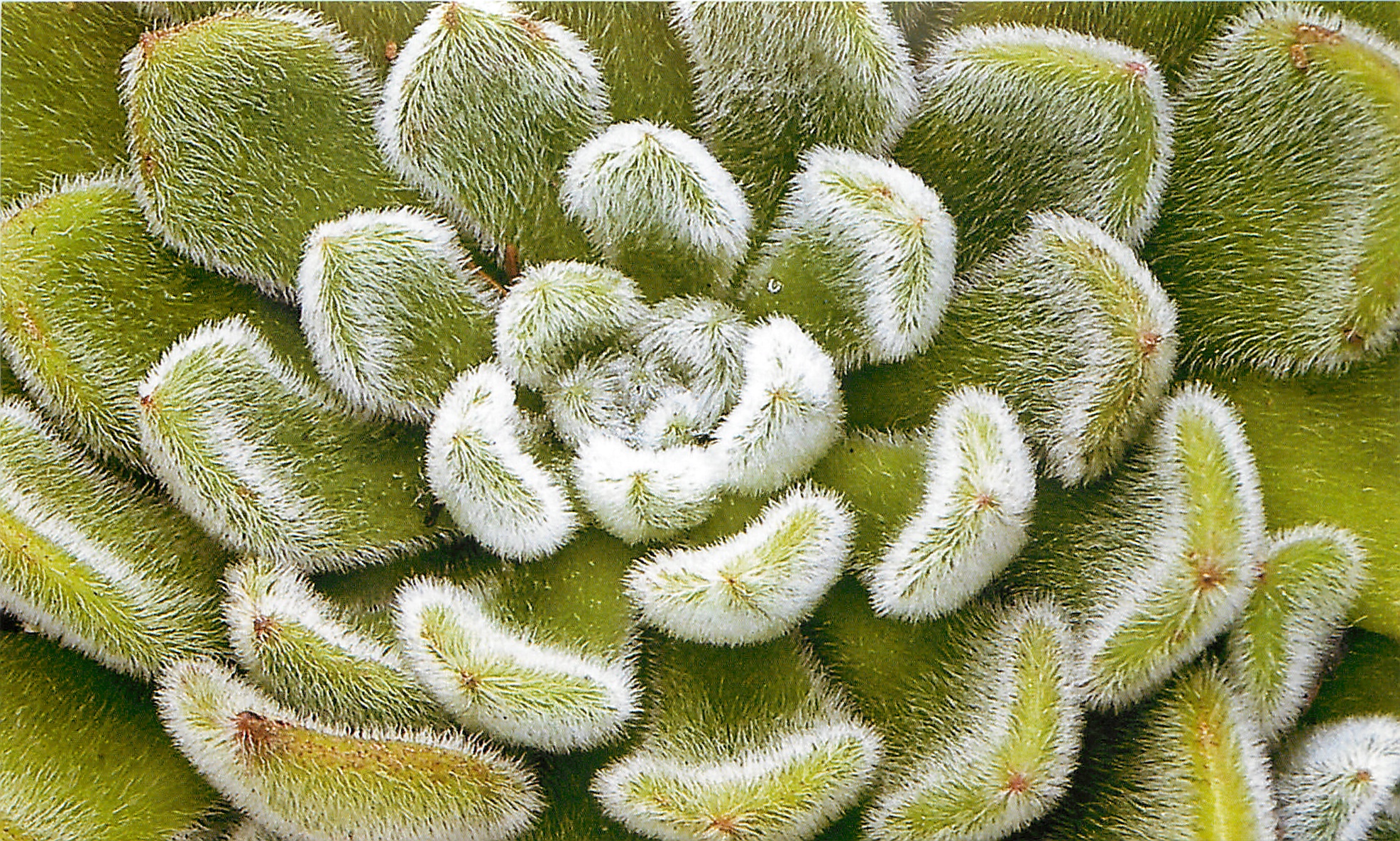
Bristly
Echeveria has a bright, uniform green coloration. It lacks a stem, and its leaves form a spherical rosette, resembling a spatula. The foliage reaches 9 cm in length and 3 cm in width, and is covered with light-colored bristles. Yellow-orange flowers bloom in summer. This variety is a bush plant.

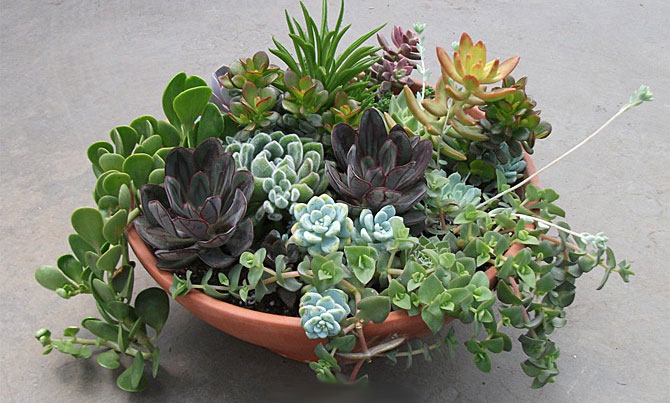
Mix
Several Echeveria varieties can be combined in a single container, each with a different color, leaf shape, and size. This mix will highlight the diversity of succulents and create an unusual combination for interior decoration. Varieties such as Romeo, Miranda, Taurus, Agave, and Graceful create an interesting effect. Be sure to leave space between plants when planting to allow them to develop, and the resulting space can be filled with various stones, bark, and other decorative elements.

Caring for Echeveria at Home
The domesticated stone rose is not very demanding in care and, if a few basic rules are followed, will grow and develop well in indoor conditions.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Selecting soil
To ensure successful growth of your succulent, use a substrate consisting of three parts: sand, crushed stone, and compost. This soil composition will ensure the stone flower thrives, and a drainage layer will allow excess moisture to drain. You can prepare the substrate yourself or purchase a special mixture for succulents and cacti at the store. Be sure to disinfect the soil if it's taken from the forest.
Watering and fertilizing
Echeveria doesn't require much moisture; it requires moderate watering with settled water. The frequency of watering should be determined based on the air temperature; it's recommended to water only when all soil layers are completely dry. The plant tolerates dry air well and doesn't require any external misting, as the leaves are sensitive to excess moisture and can rot if exposed to excess water.
Echeveria needs to be fertilized during the growing season, which runs from March to August. Once a month, along with watering, is sufficient. It is recommended to use a general-purpose mineral fertilizer suitable for cacti, which is available at flower shops. No additional feeding is necessary during the winter.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Light and temperature conditions
The plant loves plenty of light, and is best kept in a south-facing window where daylight hours are longest. Avoid direct sunlight, especially on young succulents, as it can burn the leaves.
In summer, a temperature of 25-28°C is acceptable, but in autumn and winter, it should be lowered to 10-15°C to induce dormancy. However, the temperature should not drop below 6°C, otherwise the plant will become ill or die from hypothermia.

Diseases and pests
This ornamental succulent rarely suffers from insects and pests, as its thick skin prevents them from settling and feeding on the plant's sap. However, mealybugs and root-knot nematodes can still attack. Mealybugs are easily identified by the typical white powdery coating on the plant, while nematodes are characterized by wilting leaves and the appearance of "pea-shaped" spots on the plant's roots.
If not cared for properly, a stone rose can become ill. The most common types of flower illnesses are:
- Wilting of foliage occurs due to insufficient watering. Remember that succulents are not cacti, so add liquid as the soil dries out.
- The dried layer of lower leaves is associated with the natural development of the plant and the appearance of babies and does not require any measures.
- Leaf drop may be caused by excess liquid in the pot, meaning you need to reduce the amount and frequency of watering.
- Yellowing foliage: caused by excess moisture and stagnant water in the pot. To improve the situation, reduce watering and replenish the drainage layer.

Yellowing of foliage - Curling of leaves indicates that the wrong fertilizer has been selected; the composition or type of fertilizer should be changed.
If constantly overwatered, echeveria can suffer from powdery mildew, which causes root rot. To save the plant, replace the soil, remove the affected areas, and treat the succulent with fungicides.
How to propagate and transplant a flower at home
Florists note that this variety is quite difficult to propagate at home, and it is not always possible to replant the flower, but they note several basic propagation methods that are still worth trying.
Propagation by seeds
Using seeds to propagate succulents is a labor-intensive process that is not always successful, and this should be taken into account when using this propagation method.
The brief algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Choose seeds from the store or collect them from your succulent after flowering.
- Soak the seeds for 24 hours in a weak solution of potassium permanganate to disinfect.
- Dry the seeds using a paper towel or sheet of paper.
- Prepare the soil and carefully sow the prepared seeds into it.
- Sprinkle them on top with a layer of sand, no more than 3 mm.
- Moisten the soil with settled water from a spray bottle.
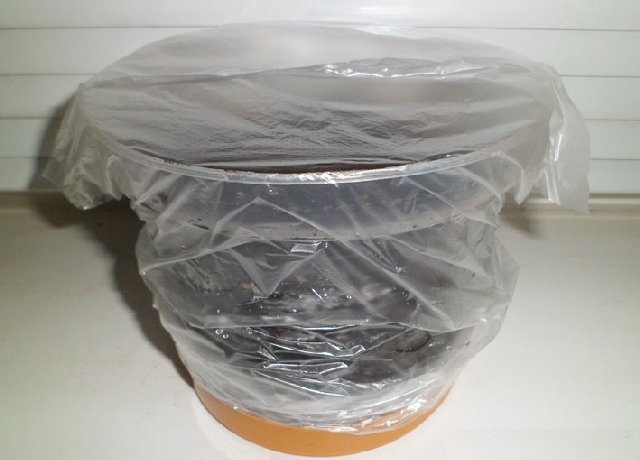
- Cover the pot with transparent film and place it in a bright and warm place, regularly ventilate and moisten.
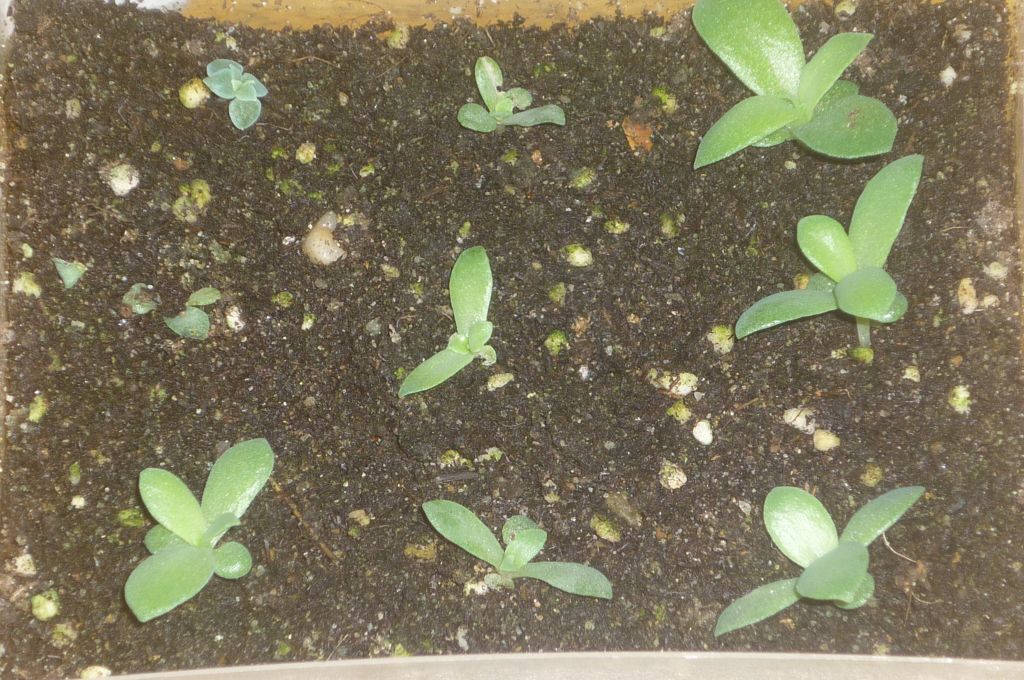
- The first sprouts will appear no earlier than in 3 weeks; when they appear, remove the film.
- Young seedlings should be replanted after a few months, when they have gained strength.
Although this method of propagating Echeveria is time-consuming and requires patience, it is cost-effective and provides the opportunity to obtain inexpensive succulents if the procedure is successful.
Vegetative method
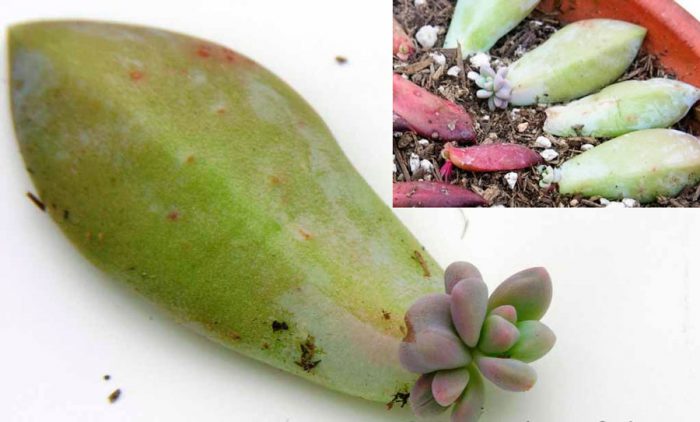
Propagating a flower is very easy, using leaves and rosettes. To propagate by leaf, use a simple algorithm:
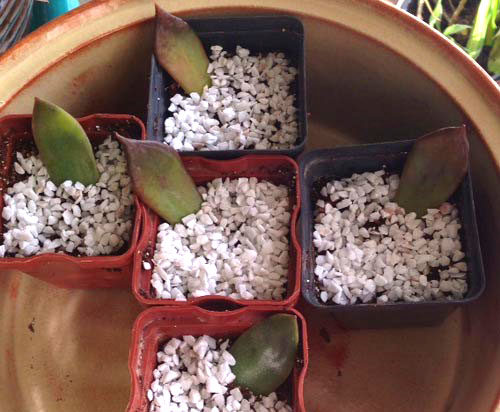
- Select and separate one large leaf from the bottom row of the succulent.
- Place it in a warm place with some sunlight.
- Wait for small roots to appear on it. This will take 3-4 weeks.
- Plant the young plant in a pre-prepared pot with substrate.
In addition to leaves, using the plant's rosettes is also suitable for propagating echeveria. This method involves the following steps:
- Cut off the rosette with a sharp knife or pruning shears.
- Remove the bottom row of leaves and dry the rosette in the shade for 3-4 hours.
- Prepare the soil and pot, moisten the soil.
- Plant the rosette shallowly in a flowerpot.
- If the temperature is maintained within 20-24°C and there is sufficient light, rooting will take about a month.
It will take several months for such a young succulent to become a full-fledged flower.
When should you replant?
Echeverias need to be repotted after purchase; store-bought potting soil is often of poor quality and doesn't allow the plant to fully develop. It's recommended to repot young succulents annually in the spring; for mature plants, changing the pot every 3-4 years is sufficient, as needed.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:How does Echeveria affect humans?
The succulent has a rich composition of useful substances and is used in folk medicine:
- for the treatment of boils and acne;
- for nervous disorders;
- for respiratory diseases;
- for the treatment of liver diseases.
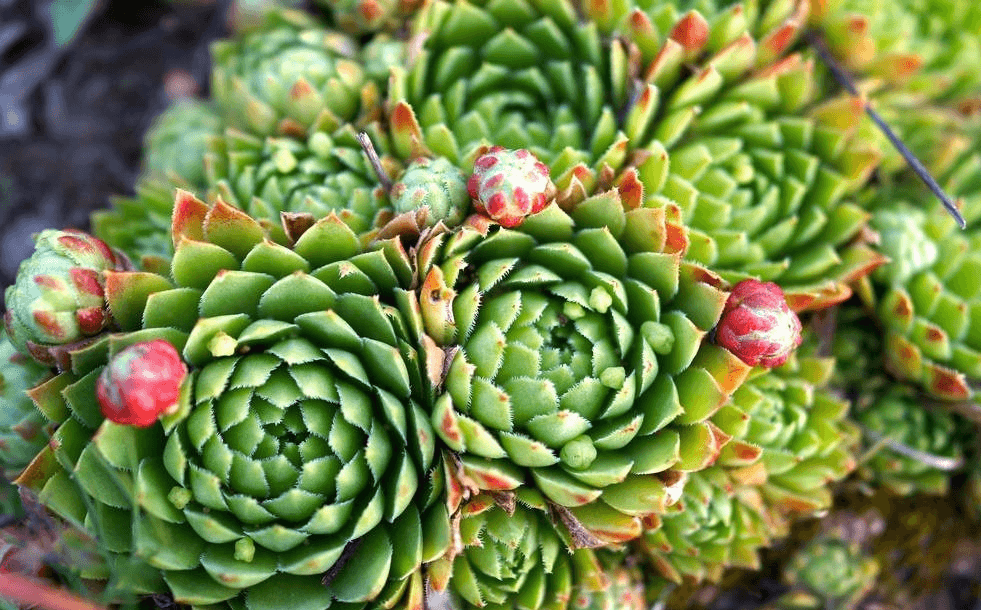
There is an opinion that the flower is also capable of influencing a person’s emotions, focusing them on positive feelings.
Frequently asked questions about growing
Echeveria is a beautiful succulent that comes in a variety of shapes and colors. It doesn't require a special microclimate to thrive, but it creates a special atmosphere in the home and has a positive effect on people. It's easy to create a unique decorative piece by simply planting several varieties in a single pot.












 The most fashionable flowers of 2025
The most fashionable flowers of 2025 Large ceramic pots and planters: what's the difference and how to choose the right one for your plants?
Large ceramic pots and planters: what's the difference and how to choose the right one for your plants? Beauty and Ease of Care: Top 10 Most Beautiful and Easy-to-Care Indoor Flowers
Beauty and Ease of Care: Top 10 Most Beautiful and Easy-to-Care Indoor Flowers Top 15 Flowers That Last Long in a Vase
Top 15 Flowers That Last Long in a Vase