Gardeners interested in growing fresh vegetables year-round use greenhouse heating in winter. Infrared heaters, heating cables, ovens, or heat guns are used to heat the space. Other heating methods are also available, and their equipment is quick and easy to install. These include heat lamps, underground gas heating with pipes, or helium collectors. The cost of installation can be reduced by two to three times if the installation is done independently.
Construction material
Permanent greenhouses on a foundation are built for owners with a large family or who intend to grow vegetables for sale. These pavilions are constructed from a sturdy metal frame, with glass walls and roof panels. Construction is not cheap, but the investment pays for itself within 3-4 years.
Less expensive but equally effective are polycarbonate structures. Pre-fabricated greenhouses are available at specialty stores. They vary in type and assembly method. Heating both polycarbonate and polycarbonate greenhouses will be more expensive than heating smaller greenhouses built from scrap materials.
These structures are built on a wooden or soil foundation. Old window frames, pieces of polycarbonate, or composite coverings are used as construction materials. Small greenhouses require minimal heating costs.

How to keep warm
The reasons for the greenhouse's low air temperature should be addressed before the heating season begins. In the fall, the entire structure should be carefully inspected. Any structural defects should be identified and corrected.
| Reasons | How to fix |
| Damage to the frame or coating |
Remove worn or rotten wooden beams and posts and replace them with new elements. Remove polycarbonate sheets and glass with cracks, repair minor scratches with special means. The joints between the frames and the glass should be carefully treated with sealants.
|
| Deterioration of the wooden foundation | The wooden foundation, which has become unusable, must be dismantled and a more reliable foundation made of brick or concrete must be built. |
| Exposure to cold wind or a drop in air temperature |
Install winter greenhouse closer to the walls of the main house or another building (barn, garage). Build a hedge that is tall enough to not block the light that plants need during the day. Apply additional insulation from thick film or polycarbonate sheets no more than 8 mm thick |
Types and design of heating systems
There are various ways to heat greenhouse pavilions. Some are more complex, while others are simpler and don't require any special skills. Small spaces can be heated by installing several low-power heating units. Larger greenhouses require more efficient heating systems.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Heating with IR devices
Greenhouse heating with infrared heaters is accomplished using electric, gas, or diesel units that emit infrared rays. Heating elements come in a variety of shapes: ceramic, carbon, or heating elements. They also vary in shape. These include lamps, strips, and panels that heat the soil surface.
Manufacturers produce portable or stationary IR lamps. Portable units are easy to install and can be moved to a convenient location. Their position can be changed in just a few minutes. Thermostats can be used to increase or decrease the heat output to plants. Stationary lamps are mounted on ceilings, walls, baseboards, or suspended from special brackets.

The power of the devices is determined by two factors: the heating temperature (from 600 to 1000°C and above) and the wavelength of the infrared waves (long, medium, short). The lamps are installed according to several rules:
- The heater should be located at a height of at least 1 m from the plant. As the seedlings grow, the lamps are gradually raised or the power of the lamps is reduced;
- Place the fixtures at least 50 cm apart from each other. In larger greenhouses, the fixtures can be placed in a checkerboard pattern;
- Light gas IR devices are more effective for heating large winter pavilions, while dark emitters are used in small greenhouses.
| Advantages of the system | Flaws |
| Uniform heating of a specific area | Increased price of IR equipment |
| Reduced area heating time | The risk of purchasing counterfeit products |
| Energy savings of up to 70% | Difficulty in accurately calculating the number of devices required to heat a specific room |
| Silent operation of devices | — |
| Oxygen is not burned, dust does not rise upwards, normal air humidity is maintained | — |
| The risk of spreading fungal diseases and pest proliferation is reduced | — |
| Possibility of using flat or spherical devices | — |
| Small size, high level of fire safety | — |
| Easy to install if you do it yourself | — |
Electric heating systems
This group of devices includes electric heaters, convectors, boilers, and cables. The availability of electricity and ease of installation allow gardeners to set up electric heating in both large and small spaces themselves.
Installing cable heating in a greenhouse is inexpensive, and any gardener can afford it:
- The site is leveled and the soil is removed to a depth of 20-30 cm (a shovel blade).
- A 5 cm layer of sand is poured into the hole, leveled and compacted.
- A protective metal mesh is laid.
- A heating cable is placed on top (in a zigzag pattern).
- Cover with a second mesh and a layer of sand.
- The last layer is a fertile substrate up to 30 cm high.
The bed is slightly raised above the ground. A low fence is built around the perimeter of the bed using scrap materials: boards, small beams, or bricks.
Convectors and other heating devices are installed near walls, but not closer than 0.5 m, so that the polycarbonate coating does not melt.

Electric boilers can be used if the greenhouse has a hydronic circuit. This is a convenient heating system, but additional piping will be required if it hasn't already been installed.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Low cost of equipment | High cost of electricity |
| Easy to install and operate | Lack of conditions for connecting devices of the required power (remoteness of power lines) |
| Universal availability of electricity | — |
| Fast and stable heating of air and soil | — |
| High, modern automation system | — |
Economical heating methods
Not all gardeners have the budget for expensive heating systems. There are affordable yet highly effective options available. These can be installed yourself. These include:
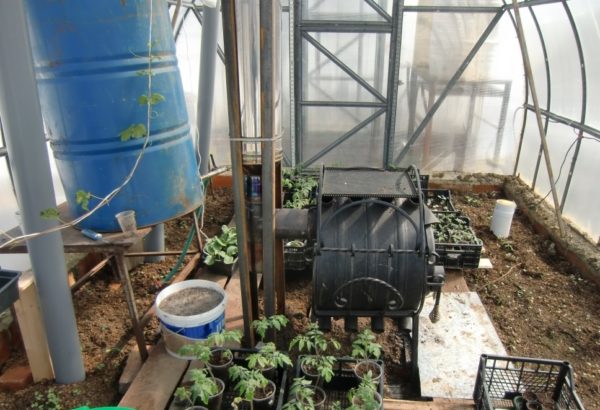
- potbelly stoves, which quickly heat the air in a room, they are lightweight, can be moved and installed in a specific place;
- Regular stationary brick stoves, connected to pipes that supply warm air to the greenhouse. This option can be achieved by using a nearby fire and a pipe directed into the room;
- Air heating of a greenhouse can be organized by installing 2-3 small generators or fans that supply a directed flow of heated air to the plants;
- Heat guns or pumps are not as economical due to the high cost of equipment, but they heat large greenhouse pavilions;
- An infrared film heater is used to warm the soil in garden beds. The film is laid at a depth of 30-40 cm, insulated with mesh, and covered with fertile soil. The method is simple but effective over a long period of time.
Installation of gas underground heating
Natural gas is cheaper than electricity, so it's more cost-effective to use equipment powered by this fuel for heating greenhouses. Many country houses and summer cottages have gas boilers and gas heating systems.

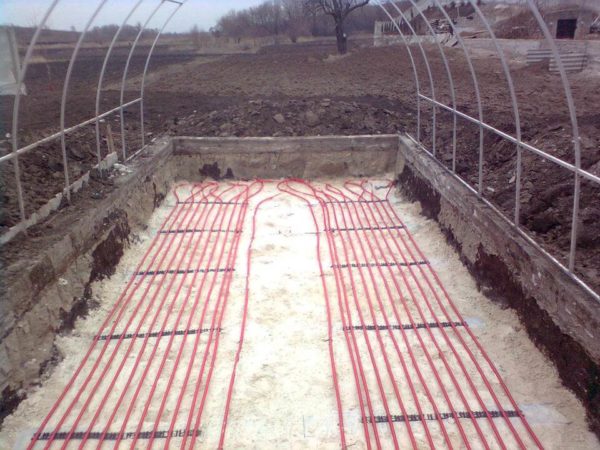
Owners can install the pipeline themselves and connect it to the centralized system. Specialists are only needed to inspect the pipeline and make the connection. Owners can perform the main gas pipe installation work themselves:
- A trench is dug to the size of the heated area and to a depth of about 50 cm.
- The pipes are laid in a “snake” shape and connected with corner elements.
- The diameter of the pipeline for direct supply must be larger than that for the return water outlet.
- Under the supervision of a specialist, connect the pipeline to the boiler and check the entire system for leaks and heating levels. The required heating temperature is set using the regulator.
- The trench is filled with removed soil, and a 30-40 cm layer of fertile soil is placed on top.
You can use either metal or polyethylene pipes. Experienced gardeners recommend using PVC pipes under greenhouses. They are corrosion-resistant and don't require additional insulation like metal pipes. Both types will last a long time without repair if installed correctly (see video).
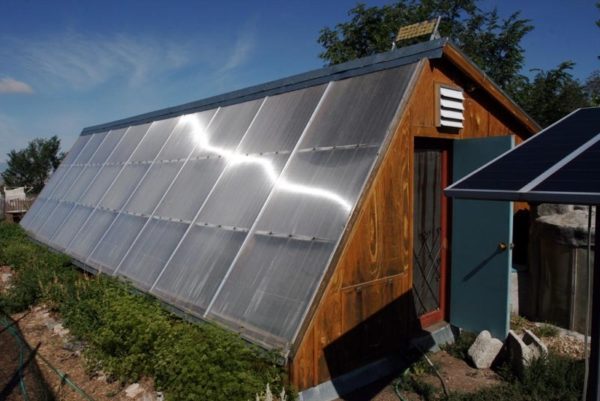
Solar heating
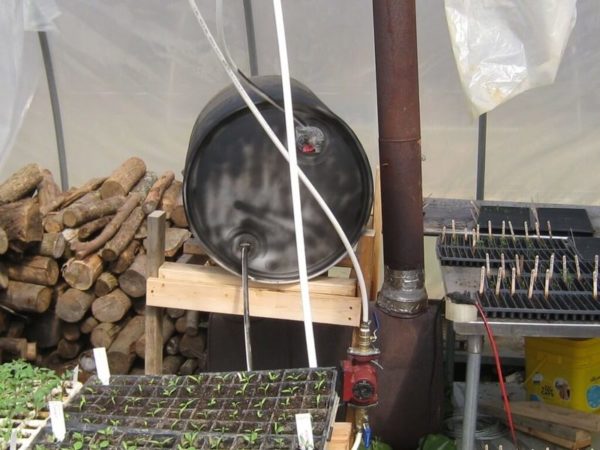
Electricity consumption for heating greenhouses can be reduced by using solar-powered collectors. The main types of such devices include vacuum flasks, heat-absorbing panels, and air collectors. These devices differ in design and operating principle.
| Type | Design | Operating principle |
| Tubular water heater made of vacuum flasks |
Glass vacuum tubes. The heat exchanger is a hollow copper rod. Heat distributor. Solar reflector |
Provides the room with warmth in winter at temperatures down to -50°C by 15-20% |
| Heat-absorbing panels |
The metal plate is painted with a special paint that absorbs solar heat. An aluminum or copper heat exchanger is located at the bottom |
Thermal energy is transferred to storage tanks and heats the water to 40° |
| Air collectors | The bottom of the device is covered with a special paint that absorbs the thermal energy of the sun's rays. | When the paint is exposed to sunlight, heat energy is released. The heated air is forced into the room using fans. |
Such equipment is most effective in southern regions with mild winters and longer daylight hours. Solar-powered systems are less effective in areas where winter temperatures drop below -25°C. At such temperatures, they freeze and cease to function properly.

| Advantages | Flaws |
| Savings on other types of greenhouse heating costs. Up to 50% of all heat comes from free solar energy. | Initial investment required |
| Additional heating of water for watering plants | Dependence of the operation of devices on the duration of daylight hours |
| The use of air collectors allows you to normalize the air humidity in the room | In winter, heat production decreases by 20-30%. |
| Quick payback within 2-3 years |
— |
Greenhouse owners are willing to invest in heating systems. They see real benefits. In winter, families have access to fresh vegetables, and some of the produce can be sold at the market for profit. Doing simple DIY projects can cut costs in half.
