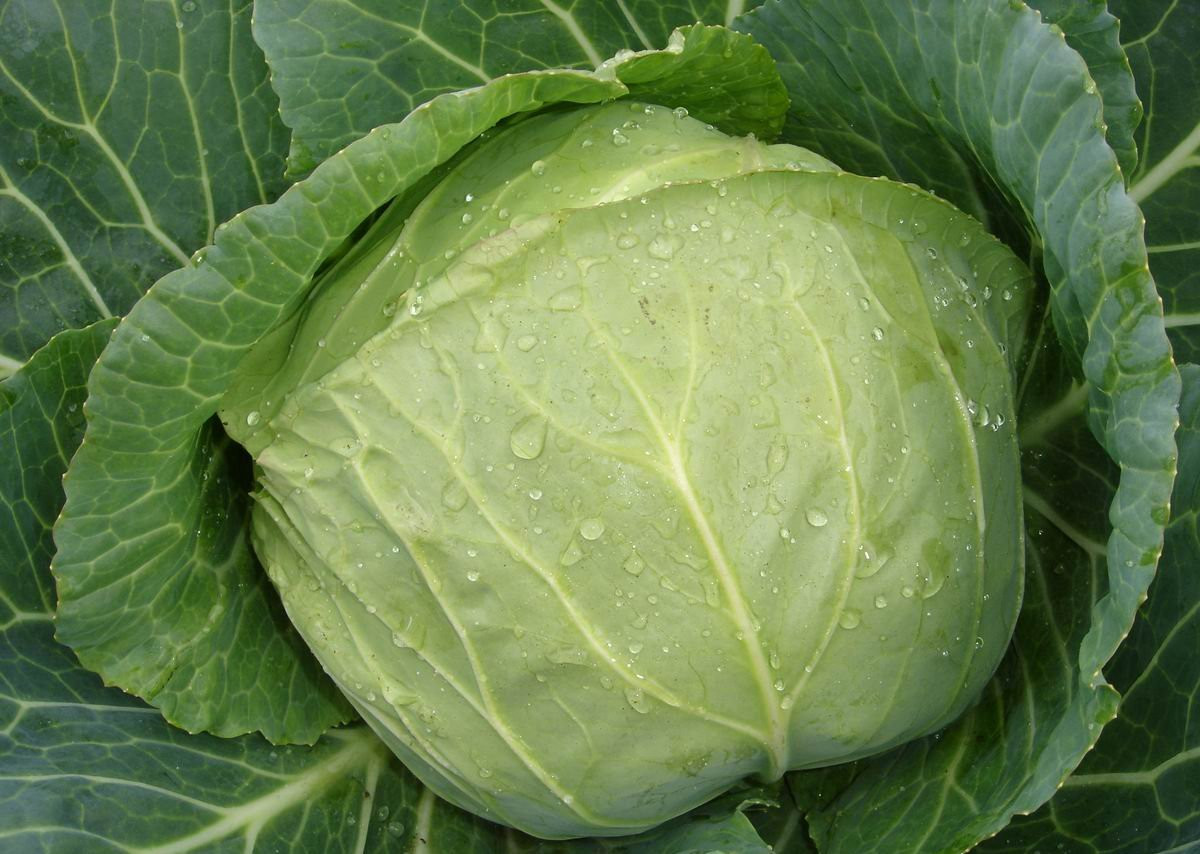
 Cabbage is an easy-to-grow vegetable that produces seeds in its second year. To avoid buying seed, simply save a couple of heads of your favorite variety. Get high-quality seeds It's also possible to grow pods at home, provided you follow proper agricultural practices and know how to store the mother plant during the winter. Following all the recommendations of experienced gardeners will allow you to get a good harvest of pods.
Cabbage is an easy-to-grow vegetable that produces seeds in its second year. To avoid buying seed, simply save a couple of heads of your favorite variety. Get high-quality seeds It's also possible to grow pods at home, provided you follow proper agricultural practices and know how to store the mother plant during the winter. Following all the recommendations of experienced gardeners will allow you to get a good harvest of pods.
Features of culture

Cabbage is a crop in the cruciferous family. It is grown outdoors as an annual plant. In the first year, the plant produces food organs, and in the following year, seeds. The edible part of the plant is the head, which can be round, conical, or flat. The "heads" are formed by the growth of leaves from the apical bud.
Cabbage stems are erect and short. The leaves are entire, large, sessile or petiolate. They can be light or dark green, and some varieties have a purple tint. The upper leaves have a waxy coating. Flower stalks reach 1.5 m in length. Yellow or white buds are collected in clusters. After 14 to 30 days, they develop into fruits—two-celled pods containing round, dark-brown seeds.
Cabbage is very moisture-loving and cold-resistant. Its seeds germinate Even at temperatures of +2…+3°C, but the optimal range is considered to be +17…+20°C. Seedlings and young plants can withstand frosts down to -2°C, and mature specimens – down to -5°C. For normal development, cabbage requires temperatures of no lower than +12°C and no higher than +30°C. In hot weather, moisture evaporates more rapidly, and without timely watering, the leaves become tough. During the period of head formation, water requirements increase. However, excess moisture is also harmful to the plant, causing root death.
Choose a sunny location, as cabbage grows poorly in the shade. Long daylight hours promote vigorous growth, while short days stunt growth, resulting in small flower stalks and heads. The best predecessors are early potatoes, zucchini, onions, cucumbers, green manure, carrots, and peas. It is recommended to plant vegetables Plant in medium loamy soil containing at least 3-4% organic matter. The pH should be between 6.5 and 7, as cabbage is often susceptible to clubroot in acidic soil. This disease is caused by a parasitic fungus that damages plant roots.
How to get cabbage seeds
 At the end of the season, mature heads of cabbage are selected as mother plants. The following rules are observed when growing them:
At the end of the season, mature heads of cabbage are selected as mother plants. The following rules are observed when growing them:
- Early varieties of cabbage sown for seedlings Slightly later than usual: mid-May or early summer. Late and mid-early varieties should be sown earlier to allow the heads to ripen before the autumn frosts.
- Avoid overfeeding cabbage grown for seed with nitrogen-containing fertilizers. Otherwise, the mother plants will rot during winter storage. Fertilize the soil with a mineral mixture: 30 g of ammonium nitrate, 50 g each of potassium salt and superphosphate per 1 m3.2.
Selection of queen cells
 To obtain good cabbage seeds, you need to select the right mother plants:
To obtain good cabbage seeds, you need to select the right mother plants:
- Firm, healthy, undamaged heads of cabbage are suitable. Their characteristics and ripening time should correspond to the characteristics of the variety.
- Late and mid-season cabbage varieties store better than early ones.
- Good mother plants have a large head, a relatively small mass of outer leaves, and a shortened and thin stalk.
- The heads of cabbage should be dug up before the fall frosts. If the cabbage isn't harvested in time, it should be allowed to "recover" for 7-10 days before being stored.
- The mother plants are carefully removed from the soil along with the roots, being careful not to damage the stalk. There is no need to shake off the soil.
Features of storing mother plants
 To ensure that the mother plants develop normally and produce high-quality seeds next season, they need to be stored in the correct conditions:
To ensure that the mother plants develop normally and produce high-quality seeds next season, they need to be stored in the correct conditions:
- Before storing in the cellar, most of the top leaves are cut off from the cabbage, leaving only 2-3, tightly adjacent to the head of cabbage.
- For warning fungal diseases The dug up plants are sprinkled with crushed chalk or sifted wood ash.
- Mother plants store well in a dark room at a temperature of +1°…+2°C. Heads of cabbage left in a warm place over winter develop dense leafy masses instead of good flower stalks. If cabbage is stored at temperatures below 0°C, it will become over-chilled and, after planting, will grow poorly and become diseased.
- The optimal humidity level in storage is 80-85%. If this level is exceeded, plants will be susceptible to gray mold.
- Mother plants are placed on slatted shelves with their stalks facing upwards or hung upside down. They should not touch each other.
- To during storage heads of cabbage to prevent drying out, the roots are dipped in a clay slurry.
- A month before planting, cut the stems of the mother plants into a cone shape, creating a diameter of 15-20 cm at the base. Remove any rotted leaves and small roots. Place the prepared plants in a bright location where the temperature does not drop below 7°C. Stack them in a pile. Sprinkle the roots with damp peat or rotted manure, then cover with plastic wrap.
- In areas with long winters, dug-up cabbage heads should be immediately trimmed into cones and planted in containers filled with soil, placed in the basement. Rooted cabbage overwinters well in a dark, cool storage area until warmer weather arrives. Transplant it into the garden beds with a lump of soil, after generously watering with warm water.
Planting mother plants
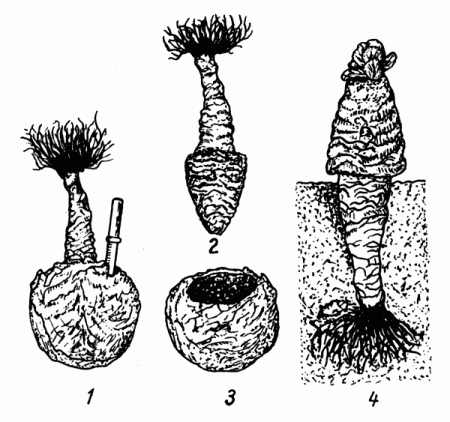 Cabbage produces seeds in the second year of growth. If the seedlings are planted correctly, they actively develop, turning into seedpods. The plants produce flower stalks, which produce pods in late summer. When planting seedlings, follow these guidelines:
Cabbage produces seeds in the second year of growth. If the seedlings are planted correctly, they actively develop, turning into seedpods. The plants produce flower stalks, which produce pods in late summer. When planting seedlings, follow these guidelines:
- Overwintered plants need to be planted earlierso that they have time to form ovaries before the summer heat sets in. At temperatures above 25°C, pollen does not germinate, resulting in the formation of a large number of barren flowers. The optimal temperature for fruit set is 15–20°C. You can begin planting mother plants as early as April. The timing depends on climate conditions. The plants tolerate light spring frosts well.
- The site is prepared in the fall: the soil is dug up, manure or compost is added. Per 1 m2 4-6 kg of organic matter is enough. In spring, per 1 m2 20 g of phosphorus and 10 g of potassium fertilizers are added.
- Before planting, the roots of the mother plants are dipped in a paste-like mixture of mullein and clay, prepared in a 1:1 ratio. Fitosporin-M can be added to this mixture. It will protect the plants from fungal and bacterial diseases.
- When planting, the cabbage stalk should be positioned at an angle, deepening it into the soil to the base of the head. The mother plants are planted in a 70x50 cm pattern. The soil around the plants is watered generously and lightly compacted.
- Cabbage is a cross-pollinating plant, so avoid planting seeds of other varieties nearby. The optimal distance is at least 500 m.
Testicular care
 Care for planted mother plants includes the following activities:
Care for planted mother plants includes the following activities:
- At first, the cabbage is shaded from bright sunlight. In cold weather, the plants are covered with straw, which is removed after 7-10 days.
- The first time the mother plants are fed after two weeks is with a 1:10 solution of mullein, pouring 3 liters under each plant. The second time they are fertilized before flowering, using nitrogen-containing mixtures at a rate of 15-20 g per 1 m.2.
- The plants are hilled up when flower stalks appear.
- The flower stalks are tied to high supports to prevent them from breaking. A trellis can be created by installing stakes every three seed stalks, with rope stretched to them on both sides of the row. This design prevents the flower stalks from lodging.
- During the growing season, which lasts 90-130 days, old or diseased leaves are regularly removed.
- To obtain viable seeds, remove excess flower stalks. They only weaken the plants. High-quality seeds come from the central stems, so it's best to remove the side stems.
- Flowering lasts about 30 days. Then, over the course of 1-1.5 months, the seeds ripen. The emerging shoots are removed immediately to prevent the cabbage from blooming a second time.
- The seed beds are regularly weeded, removing weeds. The plants are watered moderately.
Pest control
 As soon as the queen cells begin to grow, they begin to be attacked by pests:
As soon as the queen cells begin to grow, they begin to be attacked by pests:
- turnip white butterfly;
- cruciferous flea beetles;
- cabbage butterfly;
- weevil;
- mole cricket;
- May beetle larvae;
- cabbage moth.
Soil pests chew through the roots, causing plant death. To protect the mother plants, each hole is sprayed with a Vofatox solution during planting. The solution is prepared at a ratio of 10 ml per 3 liters of water. Insects that infest the cabbage suck the sap from the leaves. The presence of pests can be detected by wilted and yellowed foliage. Such plants are treated with insecticides such as Actellic, Decis, Aktara, or Enzhio. The plants are sprayed twice, 14-20 days apart.
Collecting cabbage seeds
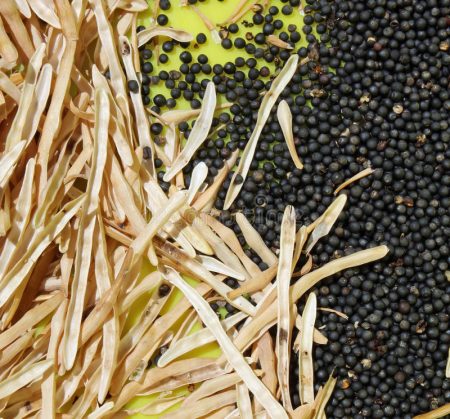 Cabbage seeds ripen unevenly. The pods are harvested selectively when they turn brown. If you miss this moment, the first and strongest seeds will spill onto the ground. The flower stalks are cut in dry weather, tied into bundles, and dried for 10-15 days. They are hung in a warm, ventilated area. Avoid overexposing the pods, as they may open.
Cabbage seeds ripen unevenly. The pods are harvested selectively when they turn brown. If you miss this moment, the first and strongest seeds will spill onto the ground. The flower stalks are cut in dry weather, tied into bundles, and dried for 10-15 days. They are hung in a warm, ventilated area. Avoid overexposing the pods, as they may open.
One plant yields an average of 50 grams of cabbage seeds. Ripe seeds are light brown. To extract them, the dried pods are threshed. The seeds, winnowed from their husks, are placed in paper bags or cloth sacks. Store them in a cool, dry place. The seeds can be used for 3-5 years.
Cabbage seeds are easy to collect yourself. Simply plant a few mother plants in your garden to obtain a large number of pods. If you follow proper agricultural practices, you can grow high-quality seeds. However, planting F1 hybrids for seed is pointless, as they do not retain varietal characteristics.
 We calculate favorable days for sowing broccoli seedlings in 2021 according to the moon
We calculate favorable days for sowing broccoli seedlings in 2021 according to the moon Favorable days for planting cauliflower in 2021: a table by day and month
Favorable days for planting cauliflower in 2021: a table by day and month Favorable days for harvesting cabbage for storage in 2020 and storage tips
Favorable days for harvesting cabbage for storage in 2020 and storage tips Why cabbage roots and stalks should be left in the garden beds over the winter
Why cabbage roots and stalks should be left in the garden beds over the winter